| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
These smaller intervals all work out well in mean-tone tuning, but the result is a fifth that is noticeably smaller than a pure fifth. And a series of pure thirds will also eventually not line up with pure octaves, so an instrument tuned this way will also have a problem with wolf intervals.
As mentioned above, Pythagorean tuning made sense in medieval times, when music was dominated by fifths. Once the concept of harmony in thirds took hold, thirds became the most important interval ; simple perfect fifths were now heard as "austere" and, well, medieval-sounding. So mean-tone tuning was very popular in Europe in the 16th through 18th centuries.
But fifths can't be avoided entirely. A basic major or minor chord, for example, is built of two thirds, but it also has a perfect fifth between its outer two notes (see Triads ). So even while mean-tone tuning was enjoying great popularity, some composers and musicians were searching for other solutions.
In just intonation, the fifth and the third are both based on the pure, harmonic series interval. Because chords are constructed of thirds and fifths (see Triads ), this tuning makes typical Western harmonies particularly resonant and pleasing to the ear; so this tuning is often used (sometimes unconsciously) by musicians who can make small tuning adjustments quickly. This includes vocalists, most wind instruments, and many string instruments.
As explained above , using pure fifths and thirds will require some sort of adjustment somewhere. Just intonation makes two accommodations to allow its pure intervals. One is to allow inequality in the other intervals. Look again at the harmonic series .
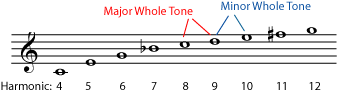
As the series goes on, the ratios get smaller and the notes closer together. Common notation writes all of these "close together" intervals as whole steps (whole tones) or half steps (semitones), but they are of course all slightly different from each other. For example, the notes with frequency ratios of 9:8 and 10:9 and 11:10 are all written as whole steps. To compare how close (or far) they actually are, turn the ratios into decimals.
These are fairly small differences, but they can still be heard easily by the human ear. Just intonation uses both the 9:8 whole tone, which is called a major whole tone and the 10:9 whole tone, which is called a minor whole tone , in order to construct both pure thirds and pure fifths.
The other accommodation with reality that just intonation must make is the fact that a single just-intonation tuning cannot be used to play in multiple keys. In constructing a just-intonation tuning, it matters which steps of the scale are major whole tones and which are minor whole tones, so an instrument tuned exactly to play with just intonation in the key of C major will have to retune to play in C sharp major or D major. For instruments that can tune almost instantly, like voices, violins, and trombones, this is not a problem; but it is unworkable for pianos, harps, and other other instruments that cannot make small tuning adjustments quickly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Frequency and music' conversation and receive update notifications?