| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. organismes
omgewing
nie-lewende
2. produsente (voedselproduseerders)
verbruikers
herbivore
karnivore
omnivore
3. Ligging, klimaat, grond, water, atmosferiese gasse (meer spesifieke faktore kan ook genoem word, bv helling en suid-/oos-/wes-/noordwysend ipv ligging, of temperatuur, reën en wind ipv klimaat).
Diagram:
1. Alle materiale word in die natuur gehersirkuleer en daarom raak die bronne nie uitgeput nie. Wat uit die grond of lug geneem word, keer uiteindelik weer terug.
2. Water: uit grond na plante en diere (en in lug in), weer terug na grond (urine en ontlasting) of lug (sweet, verdamping).
Koolstofdioksied: uit lug na plant, vasgelê in voedsel, na dier, vrygestel aan lug.
Bestanddele in grond, na plant, vorm voedsel, na dier wat plant vreet, met urine of ontlasting of as dier of plant vrek, terug na grond
3. Om te voorkom dat die natuurlike bronne uitgeput raak/die stowwe opgebruik word.
Toets jou kennis
Jy het in graad 6 reeds met die begrip “ekosisteem” kennis gemaak. Kom ons kyk wat jy nog kan onthou:
Voltooi: ‘n Ekosisteem is al die lewende ______________________ wat in ‘n
bepaalde _______________ lewe, asook al die ___________ faktore wat die
aard van die omgewing bepaal.
In ‘n ekosisteem is die plante die ___________________, terwyl die diere die
____________________ is. Diere kan op grond van hul voedingswyse in drie
groepe verdeel word, naamlik _________________, ____________________
en ___________________________________________________________ .
Die nie-lewende faktore wat die toestande in die ekosisteem bepaal, is _______________________________, _____________________________,
_______________________________ en ___________________________ .
‘n Ekosisteem kan diagrammaties soos volg voorgestel word:
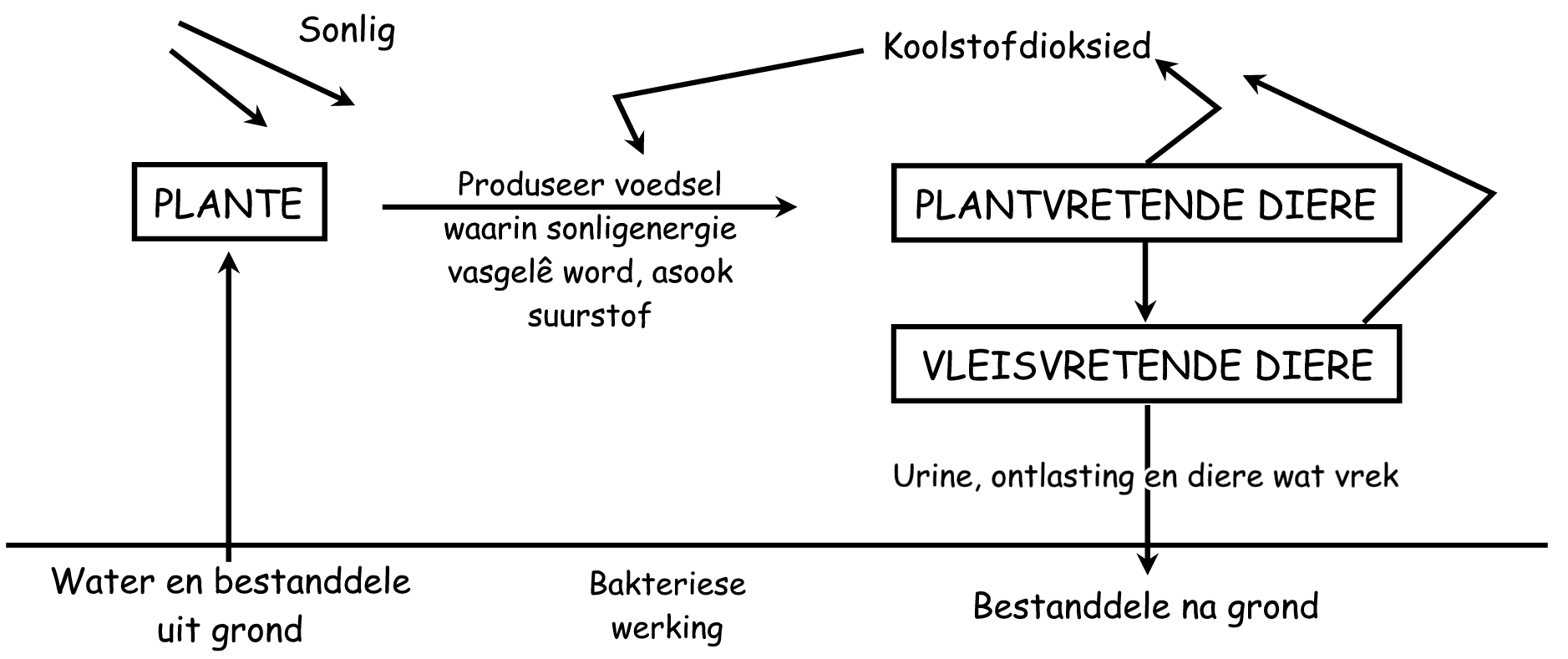
Probeer om die volgende vrae wat oor die diagram handel te beantwoord:
1. Hoekom word die ekosisteem in die vorm van ‘n siklus voorgestel?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
2. Noem drie stowwe/verbindings wat volgens die diagram in ‘n ekosisteem gesirkuleer word en beskryf elke siklus kortliks:
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
3. Hoekom is dit belangrik dat die stowwe gesirkuleer word?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Leeruitkomste 2: Die leerder ken, interpreteer en pas wetenskaplike, tegnologiese en omgewingskennis toe.
Assesseringstandaard 2.1: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder betekenisvolle inligting onthou: onthou, ten minste, definisies en komplekse feite;
2.3 inligting interpreteer: interpreteer inligting deur kernidees in die teks te identifiseer, patrone in aangetekende data te vind en gevolgtrekkings te maak uit inligting in verskeie vorme (bv. prente, diagramme en geskrewe teks);

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natuurwetenskappe graad 7' conversation and receive update notifications?