| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One measure of business confidence is published by the OECD: the "business tendency surveys". Business opinion survey data are collected for 21 countries on future selling prices and employment, among other elements of the business climate. After sharply declining during the Great Recession, the measure has risen above zero again and is back to long-term averages (the indicator dips below zero when business outlook is weaker than usual). Of course, either of these survey measures is not very precise. They can however, suggest when confidence is rising or falling, as well as when it is relatively high or low compared to the past.
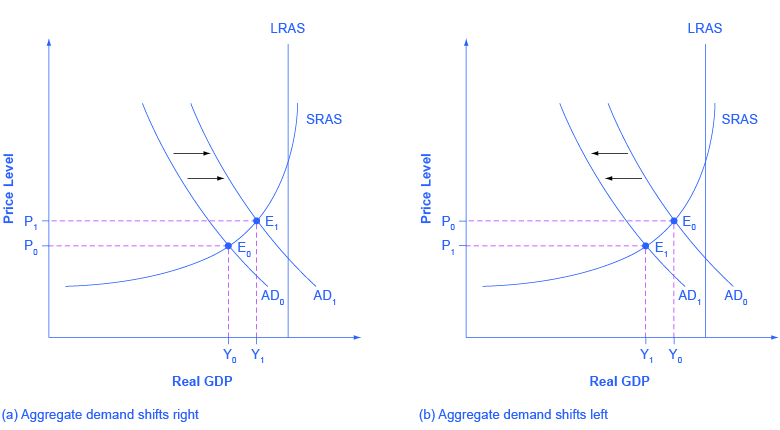
Because a rise in confidence is associated with higher consumption and investment demand, it will lead to an outward shift in the AD curve, and a move of the equilibrium, from E 0 to E 1 , to a higher quantity of output and a higher price level, as shown in [link] (a).
Consumer and business confidence often reflect macroeconomic realities; for example, confidence is usually high when the economy is growing briskly and low during a recession. However, economic confidence can sometimes rise or fall for reasons that do not have a close connection to the immediate economy, like a risk of war, election results, foreign policy events, or a pessimistic prediction about the future by a prominent public figure. U.S. presidents, for example, must be careful in their public pronouncements about the economy. If they offer economic pessimism, they risk provoking a decline in confidence that reduces consumption and investment and shifts AD to the left, and in a self-fulfilling prophecy, contributes to causing the recession that the president warned against in the first place. A shift of AD to the left, and the corresponding movement of the equilibrium, from E 0 to E 1 , to a lower quantity of output and a lower price level, is shown in [link] (b).
Government spending is one component of AD. Thus, higher government spending will cause AD to shift to the right, as in [link] (a), while lower government spending will cause AD to shift to the left, as in [link] (b). For example, in the United States, government spending declined by 3.2% of GDP during the 1990s, from 21% of GDP in 1991, and to 17.8% of GDP in 1998. However, from 2005 to 2009, the peak of the Great Recession, government spending increased from 19% of GDP to 21.4% of GDP. If changes of a few percentage points of GDP seem small to you, remember that since GDP was about $14.4 trillion in 2009, a seemingly small change of 2% of GDP is equal to close to $300 billion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of economics' conversation and receive update notifications?