| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| 1.1 19 + 21 + 17 = ............ | 1.11 ............ ÷ 5 = 8 |
| 1.2 125 + 175 = ............ | 1.12 45 ÷ ............ = 5 |
| 1.3 1 004 – 9 = ............ | 1.13 ............ ÷ 9 = 8 |
| 1.4 Halveer 196 : ............ | Skryf as ’n desimale breuk: |
| 1.5 Verdubbel 225 : ............ | 1.14 13 : ............ |
| 1.6 7 × 4 = ............ | 1.15 124 : ............ |
| 1.7 3 × 8 = ............ | 1.16 1 : ............ |
| 1.8 ............ × 5 = 45 | 1.17 2 : ............ |
| 1.9 ............ × 6 = 42 | Skryf as ’n desimale breuk: |
| 1.10 24 ÷ 4 = ............ | 1.18 4,9 : ............ |
| 1.19 12,8 : ............ | |
| 1.20 109,2 : ............ | |
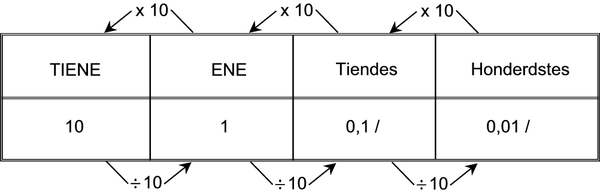
Kyk goed na die volgende:
100 c = R1,00
1c = van ’n rand
1c = R R0,01
1. Jy het seker al ontdek dat wanneer ons met rand en sent werk, ons eintlik met honderdstes werk. Kyk goed na die voorbeeld hierbo en skryf dan die volgende in rand:
1.1 4 c .........................
1.2 38 c .........................
1.3 2 c .........................
1.4 303 c .........................
1.5 460 c .........................
Het jy geweet?
word so as ’n desimale breuk geskryf: 0,01. Ons lees dit as nul komma nul een. As ons minder as het, moet ons ’n 0 (nul) as plekhouer skryf na die desimale komma in die plek van die tiendes.
Kom ons kyk weer na ons getallestelsel:
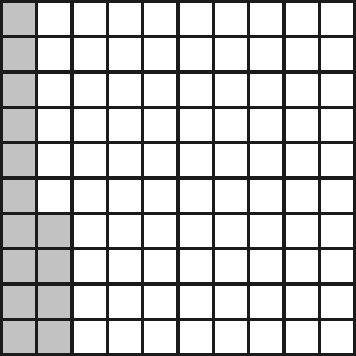
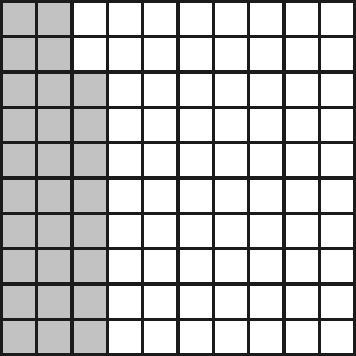
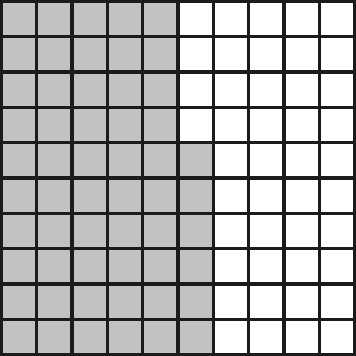
2. Watter breuk van die volgende is NIE ingekleur nie? Skryf dit ook as ’n desimale breuk.
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
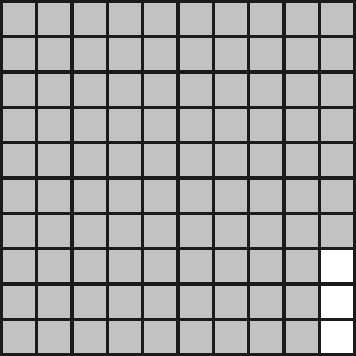
2.5
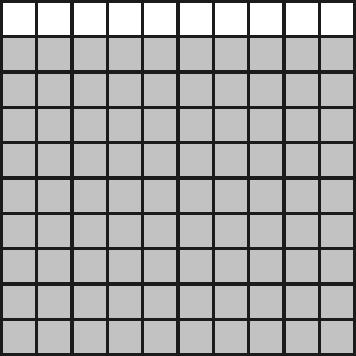
2.6
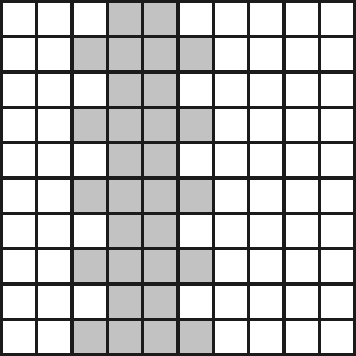
| Leeruitkomstes(LUs) |
| LU 1 |
| Getalle, Verwerkings en VerwantskappeDie leerder is in staat om getalle en die verwantskappe daarvan te herken, te beskryf en voor te stel, en om tydens probleemoplossing bevoeg en met selfvertroue te tel, te skat, te bereken en te kontroleer. |
| Assesseringstandaarde(ASe) |
| Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder: |
| 1.3 die volgende getalle herken en voorstel, sodat dit beskryf en vergelyk kan word: |
| 1.3.3 desimale breuke in terme van 0,5; 1,5; 2,5, ensovoorts, in konteks van meting; |
| 1.5 ekwivalente vorms van die bogenoemde getalle herken en gebruik, insluitend: |
|
1.6 probleme in kontekste oplos, insluitend kontekste wat gebruik kan word om ‘n bewustheid van ander leerareas, asook van menseregte-, sosiale, ekonomiese en omgewingskwessies, te bevorder, soos:
|
1.8 deur geskikte bewerkings skat en bereken vir die oplossing van probleme in verband met die volgende te kies en gebruik:
|
| 1.9 hoofberekenings uitvoer wat die volgende behels:1.9.1 optelling en aftrekking;1.9.2 vermenigvuldiging van heelgetalle tot minstens 10 x 10; |
| 1.10 ‘n verskeidenheid tegnieke gebruik om sowel skriftelike as hoofberekeninge met heelgetalle te doen, insluitend:1.10.2 opbou en afbreek van getalle;1.10.5 gebruik van ‘n sakrekenaar; |
| 1.11 ‘n verskeidenheid strategieë gebruik om oplossings te kontroleer en die redelikheid van oplossings te beoordeel. |
AKTIWITEIT 1
1. 1.1
2. 2.1 0,03
2.3 0,4
3. ; ; ; ; ; ; ;
0,3; 0,7; 0,9; 1,2; 1,3
4. 4.1 0,8; 1; 1,2; 1,4; 1,6
4.2 4,1; 3,9; 3,7; 3,5; 3,3
4.3 2,5; 3,5; 4,5; 5,5; 6,5
4.4 2,8; 2,4; 2; 1,6; 1,2
4.5 9; 8,9; 8,8; 8,7; 8,6
AKTIWITEIT 2
1.1 4,3; 4,9; 5,5; 6,1; 6,7; 7,3; 7,9; 8,5; 9,1; 9,7
1.2 8,9; 8,5; 8,1; 7,7; 7,3; 6,9; 6,5; 6,1; 5,7; 5,3
AKTIWITEIT 3
1. 1.1 /
2. 2.1 0,8
3. Verander noemer na 10 of 100 (ekwivalente breuke)
4. Teller + noemer =
AKTIWITEIT 4
12. 1.1 57 1.11 40
AKTIWITEIT 5
1. 1.1 R0,04
2. 2.1 = 0,86
2.2 = 0,72
2.3 = 0,44
2.4 = 0,03
2.5 = 0,10
2.6 = 0,70

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wiskunde graad 5' conversation and receive update notifications?