| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plants, like all other living organisms, consist of basic elements, or cells.
The structure of cells can be examined through a microscope. To be able to do this, it is necessary to learn how a microscope is operated. This will also unlock further possibilities in your studies.
Your educator will introduce you to the parts of a microscope to show you how it is constructed and how it is used, and to give you the rules for when you use such an expensive piece of apparatus.
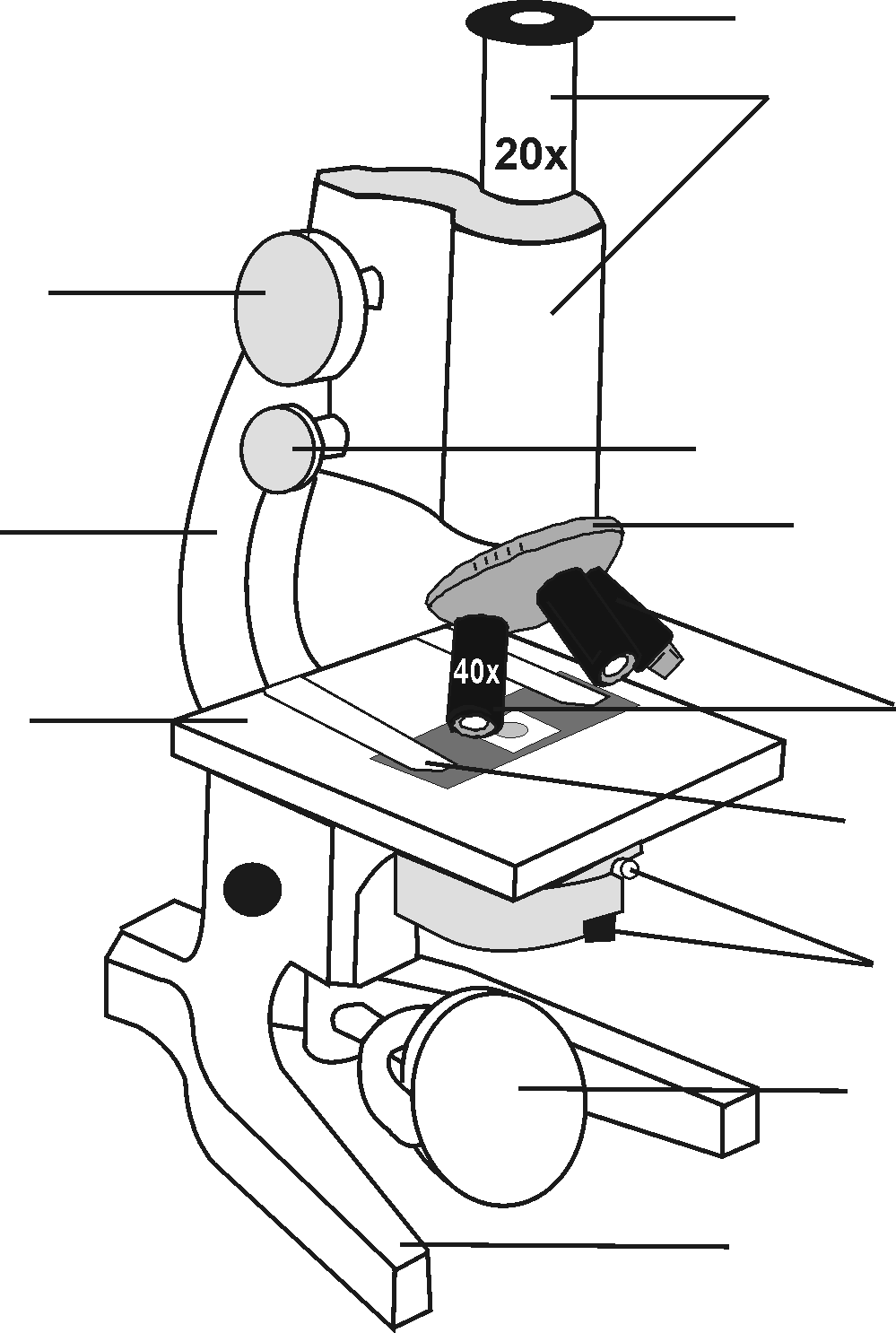
Assignment 1:
| Part of Microscope | |
| 1. | Eyepiece / ocular |
| 2. | Barrel |
| 3. | Arm |
| 4. | Coarse adjustment screw |
| 5. | Fine adjustment screw |
| 6. | Rotating nose-piece / objective turret |
| 7. | Objectives / lenses |
| 8. | Clamps |
| 9. | Stage |
| 10. | Diaphragm |
| 11. | Condenser |
| 12. | Light bulb or mirror |
3. Write down some of the important rules for handling a microscope:
4. Explain how to determine magnification:
5. What is the magnification to which the microscope that you are using has been set? Show your calculation.
Assessment: The functions of the microscope
Were you able to identify the names and functions of the basic parts?
[LO 1.2; LO 1.3]
Assignment 1 Work together in groups to do the following:
Write notes on what you observe.
Assignment 2:
Prepare a wet specimen from a piece of the epidermis of an onion leaf. Your educator will demonstrate the technique for doing this. First use a low magnification for studying the specimen and then increase the magnification.
Draw the specimen as seen with the naked eye, and then as seen through the microscope.
The brick-like structures are cells . The whole body of any plant or animal (including people) is built up of cells .
Assignment 3:
You are now experienced in handling a microscope. Write down any suggestions that you would like to mention about handling the microscope and adjusting it for finding the correct image.
Why might you want to use a colorant to stain the specimen?
Ask your educator about a suitable colourant.
Assessment: The practical use of the microscope
Were you able to handle the items and complete the sketches?
[LO 1.2; LO 1.3]
LO 1: Scientific investigations:
The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
This is evident when the learner:
LO 2: Constructing Science Knowledge:
The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
This is evident when the learner:
2.4 applies knowledge.
MINIMUM CONTENT
Activity 1
Assignment 1:
HOW A MICROSCOPE IS CONSTRUCTED
| FUNCTION |
| Lens at the upper end of the barrel facilitates enlargement |
| Beams of light travel through this barrel, which separates the ocular and the objectives |
| Handle for holding |
| Moves the stage towards the object lens; Initial focussing |
| For finer, closer focussing |
| For moving objectives into position |
| These lenses make it possible to achieve different magnifications |
| Holds the microscope slide in position |
| For the positioning of the microscope slide |
| Controls the amount of light that passes from the object to the eye |
| Concentrates light on the object |
| Light source |
How to handle a microscope
1. Carry it carefully – using both hands.
2. Take care not to mark it with fingerprints.
3. Never remove the lenses.
4. Handle the highest objective with great care.
5. Protect the microscope from dust and damp.
Magnification
Activity 2:
Assignment 1:
Assignment 2:
1. Select a microscope slide / object glass and wipe it clean.
2. Use a dropper to place a single drop of water in the centre of the slide.
Water dropMicroscope slide
3. Using a tweezer or dissecting needle, select the object (specimen) and place it in the drop of water. Open it up and flatten it.
4. Stand a dissecting needle vertically in the centre of the object.
5. Position a cover-glass at an angle against the needle.
6. Quickly remove the needle to allow the cover-glass to fall into place over the specimen.
7. Tap the cover-glass lightly, using the back of the needle, to release bubbles that might be trapped.
8. Use an iodine solution to stain the specimen for greater cell definition. Starch grains will also be stained.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?