| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nutrients in soil and water are generally beneficial when they exist at naturally occurring levels. Nitrogen fertilizers have been applied to farm fields for decades in order to maximize production of agricultural lands. However, an unintended consequence is that the same nutrients can be detrimental to aquatic ecosystems when introduced excessively for agricultural or other purposes. Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) are introduced by fertilizers that are used intensively in agriculture, as well as golf courses and some lawns and gardens. Farm animal waste and sewage also provide large amounts of reactive N and P. Phosphorus was formerly used heavily as an additive in laundry and dishwater detergents, but since the 1970's it has been phased out in both through a combination of state and federal regulations. Overall, our modern society has altered the global N and P cycles such that there is an overabundance in many settings.
Although atmospheric nitrogen gas is abundant, the gas is neither reactive nor utilized by most plants. Reactive nitrogen, in nitrate and ammonia fertilizers, is utilized by plants at some rate. However, excessive nutrients (not utilized) are often washed into drainage ways, streams, and rivers during rainfall and storm events. High N and P levels in surface water runoff have the effect of dramatically increasing algae growth downstream due to eutrophic conditions. The algal blooms have the unwanted effect of strong decreases in dissolved oxygen, which is needed for survival of fish and other aquatic life. Enhanced algae growth can thus disrupt normal functioning of the ecosystem and cause what are known as "dead zones" (see Figure Aquatic Dead Zones ). The waters may locally become cloudy and colored a shade of green, brown, or red. Eutrophication can occur naturally, but it has been greatly enhanced due to the use of fertilizers. As a result of eutrophication, many coastal waters contain increasingly problematic dead zones where major rivers discharge nutrient-rich agricultural runoff or poorly treated sewage and wastewater (e.g. Gulf of Mexico, Chesapeake Bay, Baltic Sea, East China Sea) (see Figure Aquatic Dead Zones ). This issue is of great importance because the dead zones are near inhabited coastlines with commercially and ecologically vital aquatic life.
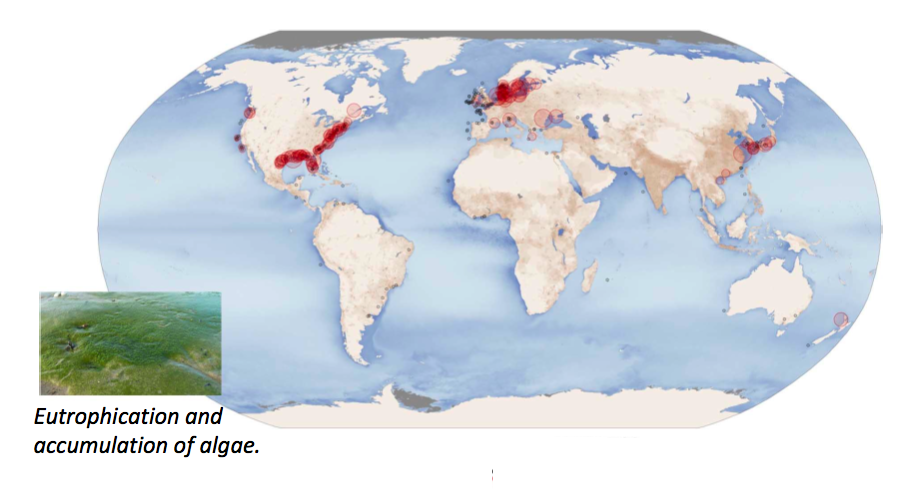
One of the most notorious dead zones (second to the Baltic Sea) is an 8,500 square mile region in the Gulf of Mexico (see Figure Aquatic Dead Zones ). The Mississippi River dumps high-nutrient runoff from its drainage basin that includes vast agricultural lands in the American Midwest. Increased algal growth produced by these nutrients has affected important shrimp fishing grounds in the Gulf. The primary source of the nutrients is the heavily tile-drained areas of farmland in the Midwest corn and soybean belt (SW Minnesota, N Iowa, NE Illinois, N Indiana and NW Ohio). Improved soil drainage systems over the past century or more have allowed for effective transport of nitrate compounds as stormwater runoff into drainage basins (Ohio River, Wabash River, Illinois River, Missouri River, etc.) that feed into the Mississippi River. In other words, the same drainage tiles that allow for the agricultural benefit of having rich bottomland/wetland soils in production, have the disadvantage of increased and more rapid movements of nitrate solutes to the Gulf of Mexico. Such large-scale problems, across state governmental boundaries, can only be fully addressed in the future with a national system of incentives, regulations, or laws.
In addition to fertilizers, Nitrogen inputs to watersheds can also include atmospheric deposition, livestock waste, and sewage, but nitrogen fertilizers comprise a significant majority of the input to monitored streams, particularly in springtime when much fertilizer is applied. Possible solutions to this problem include encouraging farmers to apply a more limited quantity of fertilizer in the spring (only as much as necessary), rather than in the fall, to allow for considerably less time for stormwater or meltwater runoff. Other solutions include maintaining cover crops, or restoring wetlands in key locations to contain nitrate losses. An overall strategy that limits the excess capacity of nutrients can simultaneously benefit farmers (by limiting cost), the ecology of stream watersheds and coastal ecosystems (also locally stressed by oil spills and other pollution). Over the long term, more efforts will need to be made in the Mississippi River Basin, and globally in similarly stressed agricultural or urban watersheds (see Figure Aquatic Dead Zones ), to improve the health and sustainability of our soil, land, and aquatic ecosystems.
What is the importance of soil to our society today?
How has human activity changed the physical, chemical, or biological character of native soil?
What practices can be used to improve the long-term sustainability of soil health?
Hassett, J.J.&Banwart, W.L. (1992). Soils and Their Environment . New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Birkeland, P.W. (1999). Soils and Geomorphology . London: Oxford University Press.
A wealth of information may be obtained from your local county soil report (USDA) or online , including detailed interactive soil maps, along with useful data concerning soil types and their physical and chemical properties (useful for home owners, in construction, land-use planning, agriculture, etc.).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?