| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The names of the various intervals, and the way they are written on the staff, are mostly the result of a long history of evolving musical notation and theory. But the actual intervals - the way the notes sound - are not arbitrary accidents of history. Like octaves, the other intervals are also produced by the harmonic series. Recall that the frequencies of any two pitches that are one octave apart have a 2:1 ratio. (See Harmonic Series I to review this.) Every other interval that musicians talk about can also be described as having a particular frequency ratio. To find those ratios, look at a harmonic series written in common notation .
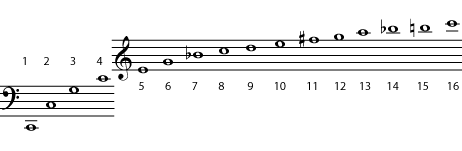
Look at the third harmonic in [link] . Its frequency is three times the frequency of the first harmonic (ratio 3:1). Remember, the frequency of the second harmonic is two times that of the first harmonic (ratio 2:1). In other words, there are two waves of the higher C for every one wave of the lower C, and three waves of the third-harmonic G for every one wave of the fundamental. So the ratio of the frequencies of the second to the third harmonics is 2:3. (In other words, two waves of the C for every three of the G.) From the harmonic series shown above, you can see that the interval between these two notes is a perfect fifth . The ratio of the frequencies of all perfect fifths is 2:3.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Understanding basic music theory' conversation and receive update notifications?