| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An algorithm should be (at least)
–complete (i.e. cover all the parts)
–unambiguous (no doubt about what it does)
–finite (it should finish)
This step consists of translating the algorithm into a computer program using a programming language.
This step requires testing of the completed computer program to ensure that it does, in fact, provide a solution to the problem. Any errors that are found during the tests must be corrected.
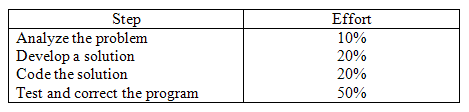
Figure below lists the relative amount of effort that is typically expended on each of these four development and design steps in large commercial programming projects.
Documentation requires collecting critical documents during the analysis, design, coding, and testing.
There are five documents for every program solution:
This phase is concerned with the ongoing correction of problems, revisions to meet changing needs and the addition of new features. Maintenance is often the major effort, and the longest lasting of the three phases. While development may take days or months, maintenance may continue for years or decades.
An algorithm is defined as a step-by-step sequence of instructions that describes how the data are to be processed to produce the desired outputs. In essence, an algorithm answers the question: “What method will you use to solve the problem?”
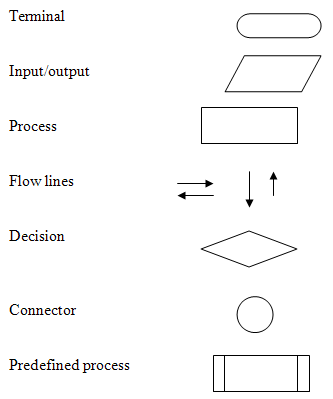
You can describe an algorithm by using flowchart symbols. By that way, you obtain a flowchart which is an outline of the basic structure or logic of the program.
To draw flowchart, we employ the symbols shown in the Figure below.
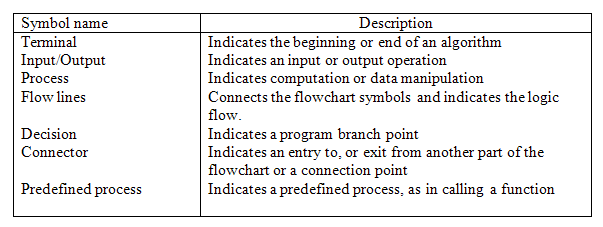
The meaning of each flowchart symbol is given as follows.
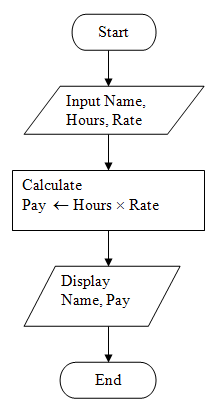
To illustrate an algorithm, we consider the simple program that computes the pay of a person. The flowchart for this program is given in the Figure below.
Note: Name, Hours and Pay are variables in the program.
You also can use English-like phases to describe an algorithm. In this case, the description is called pseudocode. Pseudocode is an artificial and informal language that helps programmers develop algorithms. Pseudocode has some ways to represent sequence, decision and repetition in algorithms. A carefully prepared pseudocode can be converted easily to a corresponding C++ program.
Example: The following set of instructions forms a detailed algorithm in pseudocode for calculating the payment of person.
Input the three values into the variables Name, Hours, Rate.
Calculate Pay = Hours
Rate.
Display Name and Pay.
Many problems require repetition capability, in which the same calculation or sequence of instructions is repeated, over and over, using different sets of data.
Example 1.1. Write a program to do the task: Print a list of the numbers from 4 to 9, next to each number, print the square of the number.
The flowchart for the algorithm that solves this problem is given in Figure below. You will see in this figure the flowchart symbol for decision and the flowline that can connect backward to represent a loop.
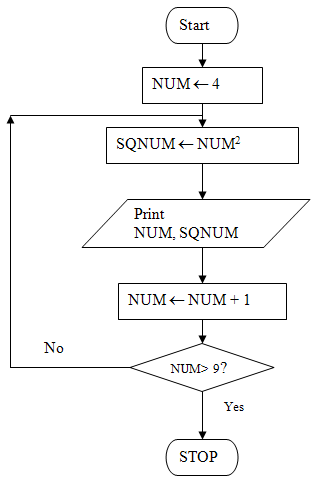
Note:
NUM = NUM + 1
means “old value of NUM + 1 becomes new value of NUM ”.
The above algorithm can be described in pseudocode as follows:
NUM = 4
do
SQNUM = NUM*NUM
Print NUM, SQNUM
NUM = NUM + 1
while (NUM<= 9)
You can compare the pseudo-code and the flowchart in Figure above to understand the meaning of the do… while construct used in the pseudo-code.
Since flowcharts are inconvenient to revise, they have fallen out of favor by programmers. Nowadays, the use of pseudocode has gained increasing acceptance.
Only after an algorithm has been selected and the programmer understands the steps required can the algorithm be written using computer-language statements. The writing of an algorithm using computer-language statements is called coding the algorithm, which is the third step in our program development process.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Programming fundamentals in c++' conversation and receive update notifications?