Convolve (n = 4)
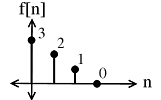
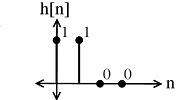
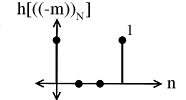
Multiply and to yield:
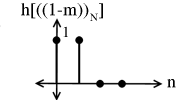
Multiply and to yield:
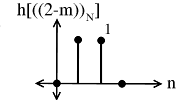
Multiply and to yield:
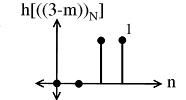
Multiply and to yield:
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This module relates circular convolution of periodic signals in one domain to multiplication in the other domain.
You should be familiar with Discrete-Time Convolution , which tells us that given two discrete-time signals , the system's input, and , the system's response, we define the output of the system as
Given a signal
with Fourier coefficients
and a signal
with Fourier coefficients
,
we can define a new signal,
,
where
We find that the
Fourier
Series representation of
,
,
is such that
.
is the
circular convolution of two periodic signals and is equivalent to the convolution
over one interval,
What happens when we multiply two DFT's together, where is the DFT of ?
Using the DFT synthesis formula for
And then applying the analysis formula
Seems like a roundabout way of doing things, but it turns out that there are extremely fast ways to calculate the DFT of a sequence.
To circularily convolve -point sequences: For each : multiples, additions
points implies multiplications, additions implies complexity.
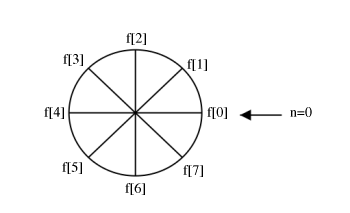
We can picture periodic sequences as having discrete points on a circle as the domain
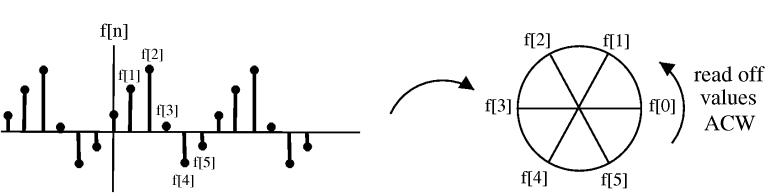
Shifting by , , corresponds to rotating the cylinder notches ACW (counter clockwise). For , we get a shift equal to that in the following illustration:
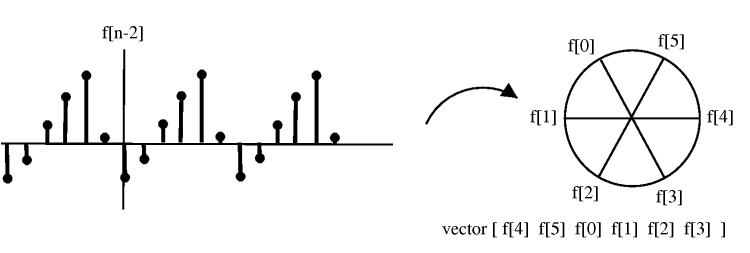
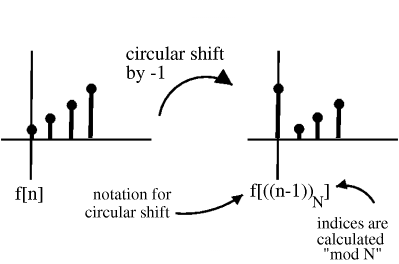
To cyclic shift we follow these steps:
1) Write on a cylinder, ACW
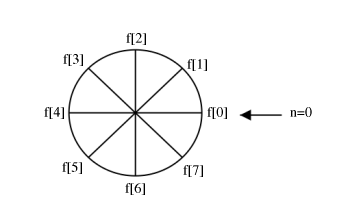
2) To cyclic shift by , spin cylinder m spots ACW
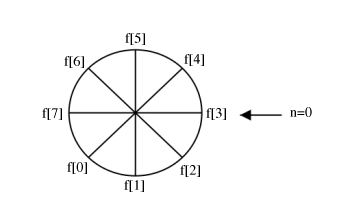
Spinning spots is the same as spinning all the way around, or not spinning at all.
Shifting ACW is equivalent to shifting CW
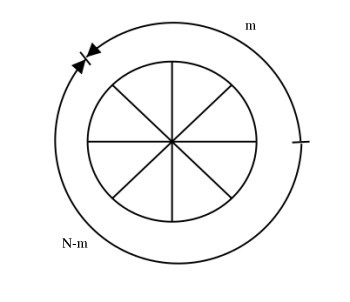
The above expression, simply writes the values of clockwise.
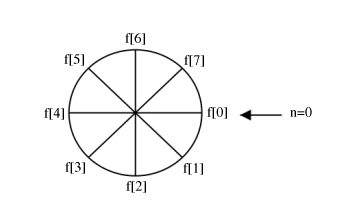



Multiply and to yield:

Multiply and to yield:

Multiply and to yield:

Multiply and to yield:
Take a look at a square pulse with a period of T.
For this signal
Take a look at a triangle pulse train with a period of T.
This signal is created by circularly convolving the square pulse with itself. The Fourier coefficients for this signal are
Find the Fourier coefficients of the signal that is created when the square pulse and the triangle pulse are convolved.
If
then
(
Circular convolution in the time domain is equivalent to multiplication of the Fourier coefficients in the frequency domain.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Signals and systems' conversation and receive update notifications?