| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The learners must be able to:
1. identify and solve problems and make decisions using critical and creative thinking;
2. work effectively with others as members of a team, group, organisation and community;
3. organise and manage themselves and their activities responsibly and effectively;
4. collect, analyse, organise and critically evaluate information;
5. communicate effectively using visual, symbolic and/or language skills in various modes;
6. use science and technology effectively and critically, showing responsibility towards the environment and the health of others;
6. demonstrate an understanding of the world as a set of related systems by recognising that problem-solving contexts do not exist in isolation;
7. reflect on and explore a variety of strategies to learn more effectively;
8. participate as responsible citizens in the life of local, national, and global communities;
9. be culturally and aesthetically sensitive across a range of social contexts;
10. explore education and career opportunities; and
develop entrepreneurial opportunities.
MODULE 1
| Critical and developmental outcomes: | Pages: |
| CO 1 | E-4, 10, 11, 14, 18, 19, 20, 21, 24 |
| CO 2 | E-1, E-5, 15, 25 |
| CO 3 | 3, 4, E-2, 16, 17 |
| CO 4 | 5 |
| CO 5 | 1, 7, 8, 9, 12,13, 22 |
| CO 6 | 28 |
| CO 7 | 5, 6, 27, 28, 29 |
| CO 8 | 26, E-9 |
Look at the shapes around you.
How many sides?
How many corners?
| LO 3.1 | LO 3.2 |
| LO 1.9 |
On the board.
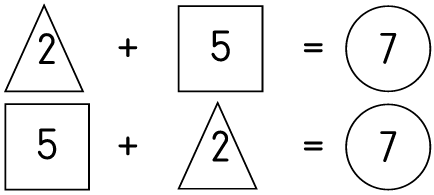
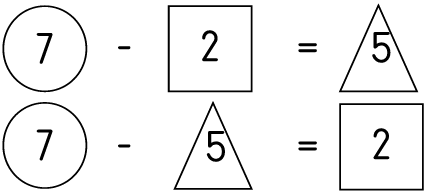
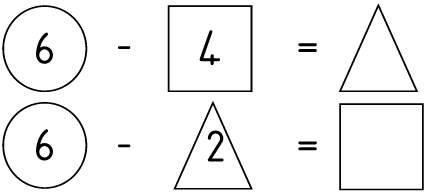
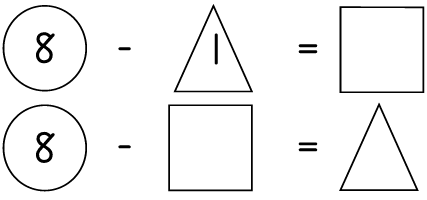
| LO 1.9 |
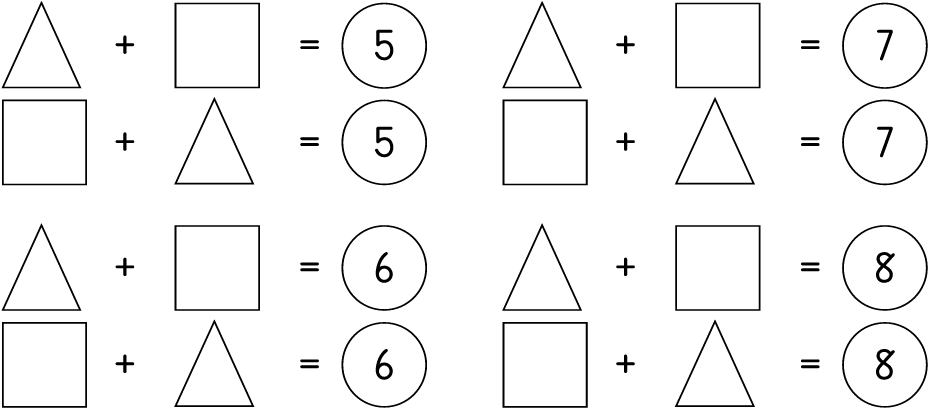
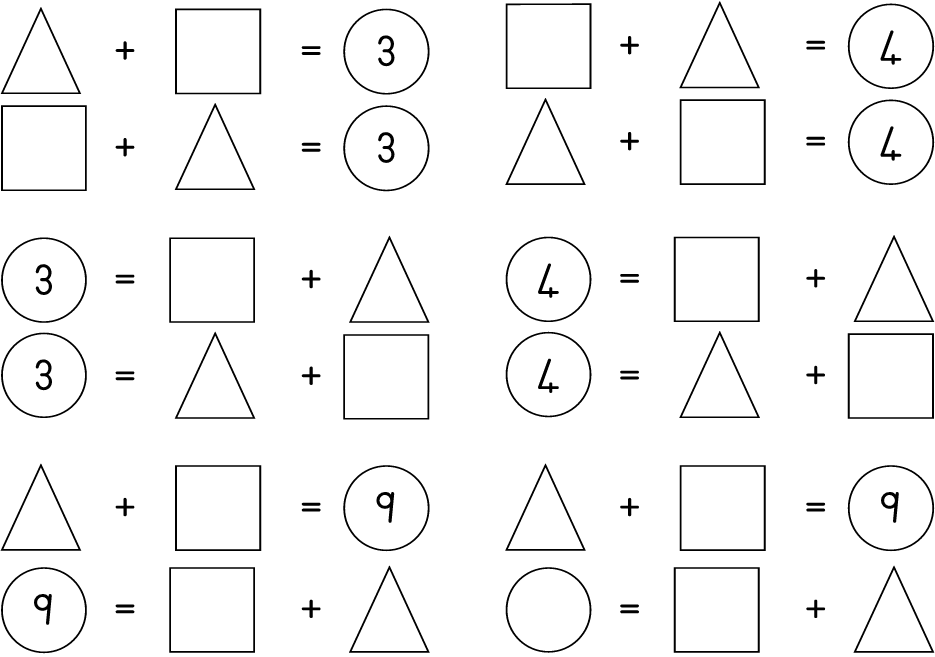
More number puzzles
| LO 1.9 | LO 1.11 |
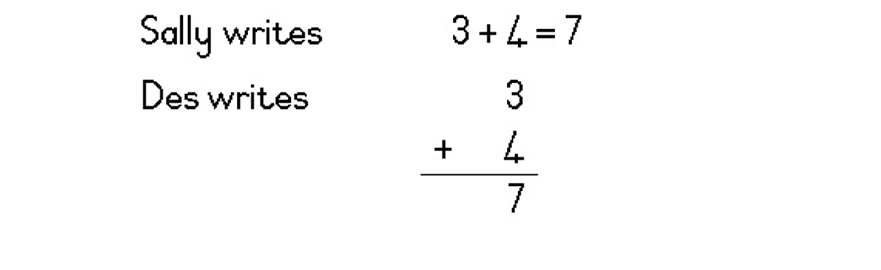
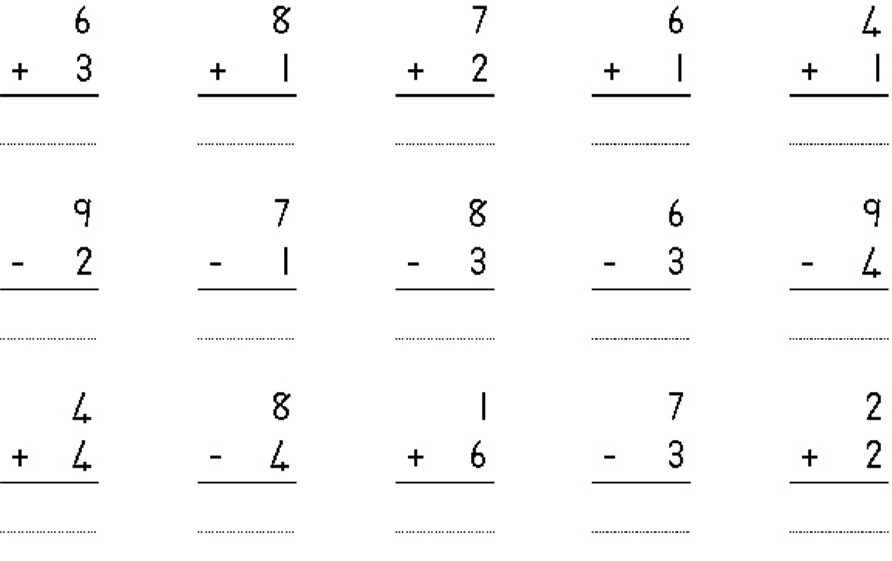

| LO 1.9 |
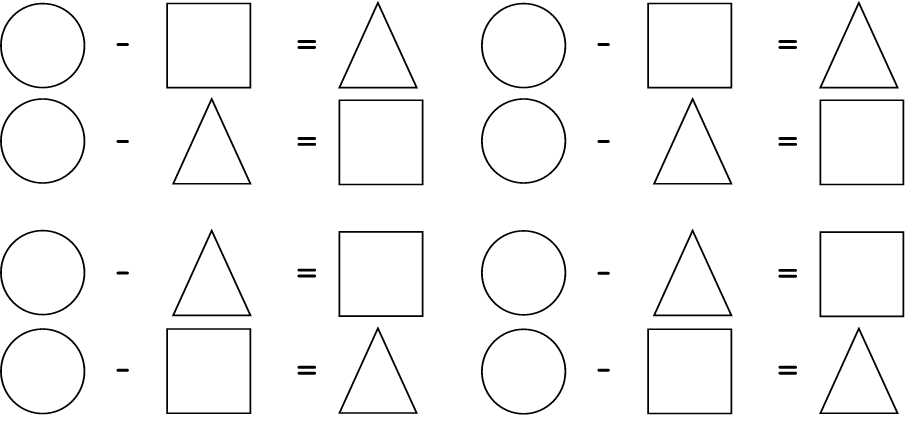
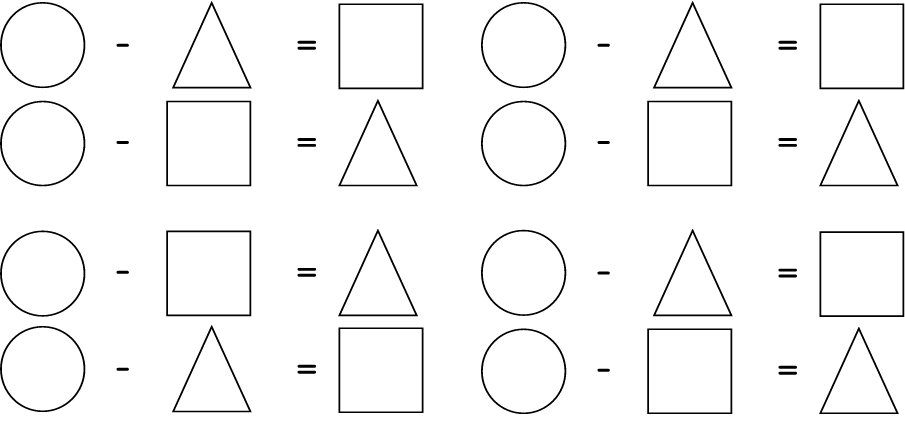
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.9: We know this when the learner performs mental calculations involving:
1.9.1 addition and subtraction for numbers to at least 20;
1.9.2 multiplication of whole numbers with solutions to at least 20;
Assessment Standard 1.11: We know this when the learner explains own solutions to problems.
Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner recognises, identifies and names two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in the school environment and in pictures, including:
3.1.1 boxes (prisms), balls (spheres) and cylinders;
3.1.2 triangles, squares and rectangles;
Assessment Standard 3.2: We know this when the learner describes, sorts and compares two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in pictures and the environment according to:
3.2.1 size;
3.2.2 objects that roll or slide.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 2' conversation and receive update notifications?