| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
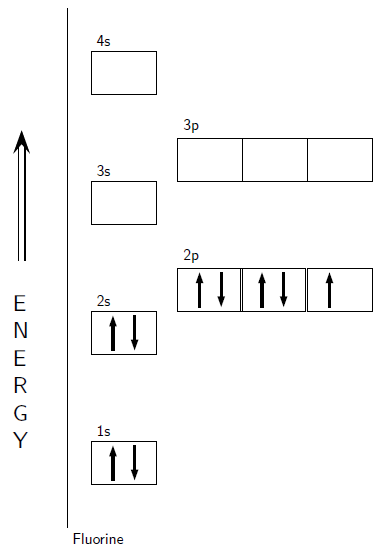
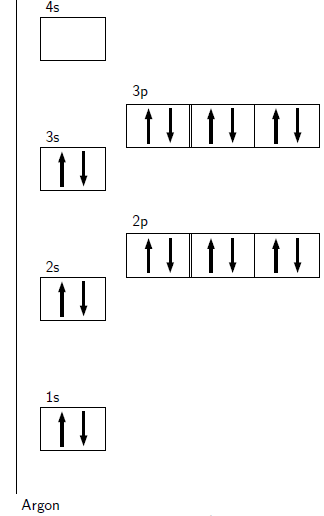
Give the electron configuration for sodium ( ) and draw an aufbau diagram.
Electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom are called valence electrons . The electrons that are in the energy shells closer to the nucleus are called core electrons . Core electrons are all the electrons in an atom, excluding the valence electrons. An element that has its valence energy level full is more stable and less likely to react than other elements with a valence energy level that is not full.
The electrons in the outer energy level of an atom
All the electrons in an atom, excluding the valence electrons
By this stage, you may well be wondering why it is important for you to understand how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom. Remember that during chemical reactions, when atoms come into contact with one another, it is the electrons of these atoms that will interact first. More specifically, it is the valence electrons of the atoms that will determine how they react with one another.
To take this a step further, an atom is at its most stable (and therefore unreactive ) when all its orbitals are full. On the other hand, an atom is least stable (and therefore most reactive ) when its valence electron orbitals are not full. This will make more sense when we go on to look at chemical bonding in a later chapter. To put it simply, the valence electrons are largely responsible for an element's chemical behaviour and elements that have the same number of valence electrons often have similar chemical properties.
One final point to note about electron configurations is stability. Which configurations are stable and which are not? Very simply, the most stable configurations are the ones that have full energy levels. These configurations occur in the noble gases. The noble gases are very stable elements that do not react easily (if at all) with any other elements. This is due to the full energy levels. All elements would like to reach the most stable electron configurations, i.e. all elements want to be noble gases. This principle of stability is sometimes referred to as the octet rule. An octet is a set of 8, and the number of electrons in a full energy level is 8.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry grade 10 [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?