| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
free(pa);
free(pb);
a. Phép gán con trỏ: Hai con trỏ cùng kiểu có thể gán cho nhau.
Ví dụ:
int a, *p, *a ; float *f;
a = 5 ; p =&a ; q = p ; /* đúng */
f = p ; /* sai do khác kiểu */
Ta cũng có thể ép kiểu con trỏ theo cú pháp:
(<Kiểu kết quả>*)<Tên con trỏ>
Chẳng hạn, ví dụ trên được viết lại:
int a, *p, *a ; float *f;
a = 5 ; p =&a ; q = p ; /* đúng */
f = (float*)p; /* Đúng nhờ ép kiểu*/
b. Cộng, trừ con trỏ với một số nguyên
Ta có thể cộng (+), trừ (-) 1 con trỏ với 1 số nguyên N nào đó; kết quả trả về là 1 con trỏ. Con trỏ này chỉ đến vùng nhớ cách vùng nhớ của con trỏ hiện tại N phần tử.
Ví dụ: Cho đoạn chương trình sau:
int *pa;
pa = (int*) malloc(20); /* Cấp phát vùng nhớ 20 byte=10 số nguyên*/
int *pb, *pc;
pb = pa + 7;
pc = pb - 3;
Lúc này hình ảnh của pa, pb, pc như sau:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||||||
| pa | pc | pb |
c. Con trỏ NULL: là con trỏ không chứa địa chỉ nào cả. Ta có thể gán giá trị NULL cho 1 con trỏ có kiểu bất kỳ.
d. Lưu ý:
- Ta không thể cộng 2 con trỏ với nhau.
- Phép trừ 2 con trỏ cùng kiểu sẽ trả về 1 giá trị nguyên (int). Đây chính là khoảng cách (số phần tử) giữa 2 con trỏ đó. Chẳng hạn, trong ví dụ trên pc-pa=4.
Giữa mảng và con trỏ có một sự liên hệ rất chặt chẽ. Những phần tử của mảng có thể được xác định bằng chỉ số trong mảng, bên cạnh đó chúng cũng có thể được xác lập qua biến con trỏ.
Ta có các quy tắc sau:
&<Tên mảng>[0] tương đương với<Tên mảng>
&<Tên mảng>[<Vị trí>] tương đương với<Tên mảng>+<Vị trí>
<Tên mảng>[<Vị trí>] tương đương với *(<Tên mảng>+<Vị trí>)
Ví dụ: Cho 1 mảng 1 chiều các số nguyên a có 5 phần tử, truy cập các phần tử theo kiểu mảng và theo kiểu con trỏ.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
/* Nhập mảng bình thường*/
void NhapMang(int a[], int N){
int i;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
printf("Phan tu thu %d: ",i);scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
}
/* Nhập mảng theo dạng con trỏ*/
void NhapContro(int a[], int N)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
printf("Phan tu thu %d: ",i);scanf("%d",a+i);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[20],N,i;
clrscr();
printf("So phan tu N= ");scanf("%d",&N);
NhapMang(a,N); /* NhapContro(a,N)*/
printf("Truy cap theo kieu mang: ");
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\nTruy cap theo kieu con tro: ");
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("%d ",*(a+i));
getch();
return 0;
}
Kết quả thực thi của chương trình:
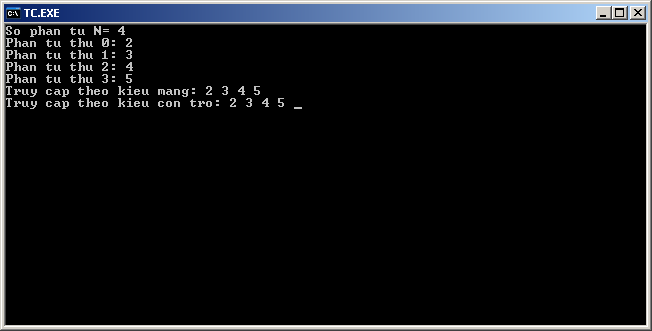
<Tên biến>[<Vị trí>] tương đương với *(<Tên biến>+<Vị trí>)
&<Tên biến>[<Vị trí>] tương đương với (<Tên biến>+<Vị trí>)
Trong đó<Tên biến>là biến con trỏ,<Vị trí>là 1 biểu thức số nguyên.
Ví dụ: Giả sử có khai báo:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<alloc.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main(){
int *a;
int i;
clrscr();
a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*10);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
a[i] = 2*i;
printf("Truy cap theo kieu mang: ");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\nTruy cap theo kieu con tro: ");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
printf("%d ",*(a+i));
getch();
return 0;
}
Kết quả chương trình:
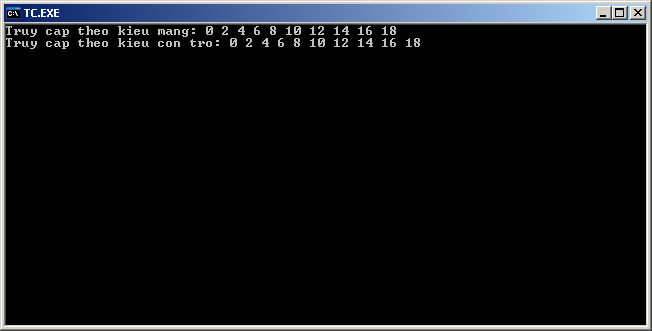
Với khai báo ở trên, hình ảnh của con trỏ a trong bộ nhớ:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||||||||||
| 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | ||||||||||
| a | 2 byte |
Giả sử con trỏ ptr chỉ đến phần tử a[i] nào đó của mảng a thì:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cấu trúc dữ liệu' conversation and receive update notifications?