| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To appreciate the chemistry of chlorine in comparison to that of fluorine it is necessary to appreciate the differences and trends between the elements. As may be seen in [link] , chloride is significantly larger than fluorine. In addition while chlorine is an electronegative element its electronegativity is significantly less than that of fluorine, resulting in less polar bonding.
| Element | Ionic radius (Å) | Covalent radius (Å) | van der Waal radius (Å) | Electronegativity |
| Fluorine | 1.33 | 0.64 | 1.47 | -4.1 |
| Chlorine | 1.81 | 0.99 | 1.75 | -2.9 |
The X-Cl bond is an electron pair covalent bond with a highly polar nature. In this regard, chlorine is similar to fluorine. However, there are two key features with regard to chlorine’s bonding that differentiates it from fluorine.
The chloride ion (Cl - ) forms salts with ionic lattices (e.g., NaCl) but also forms a wide range of complexes, e.g., [Fe(H 2 O) 5 Cl] 2+ and [RhCl 6 ] 3- . Chloride also acts as a bridging ligand in which one, two or three chlorides can bridge two metal centers ( [link] ).
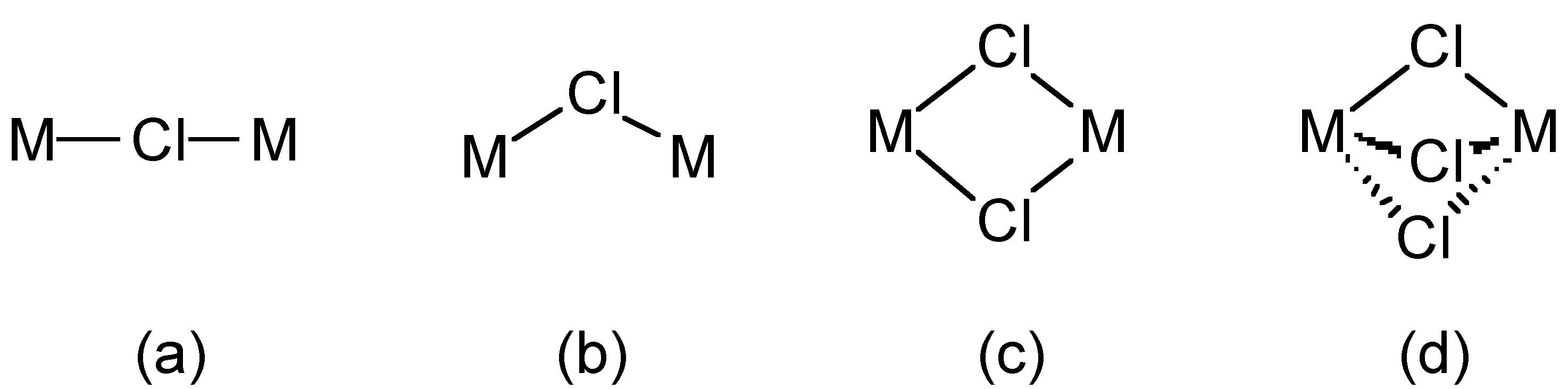
Chloride (and bromide) bridges are usually bent, whereas fluoride bridges can be either linear or bent. As an example, BeF 2 and BeCl 2 are isostructural, consisting of infinite chains with bent bridges ( [link] ). In contrast, transition metal pentahalides show different structures depending on the identity of the halide. This, TaCl 5 dimerizes with bent bridges ( [link] a), while TaF 5 forms a cyclic tetramer with linear fluoride bridges ( [link] b).
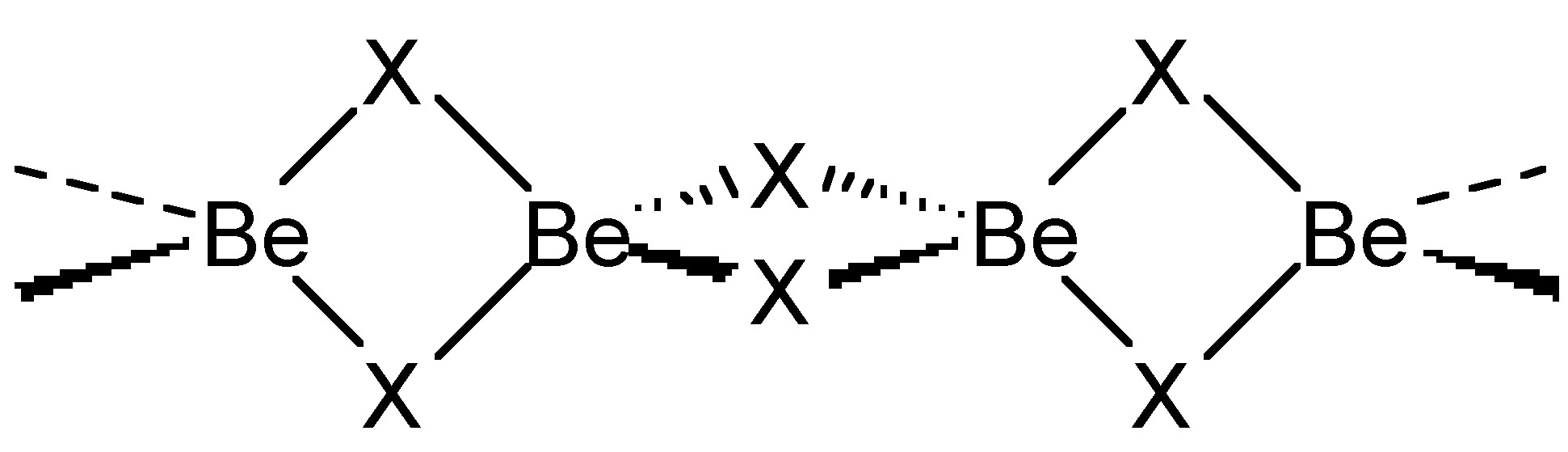
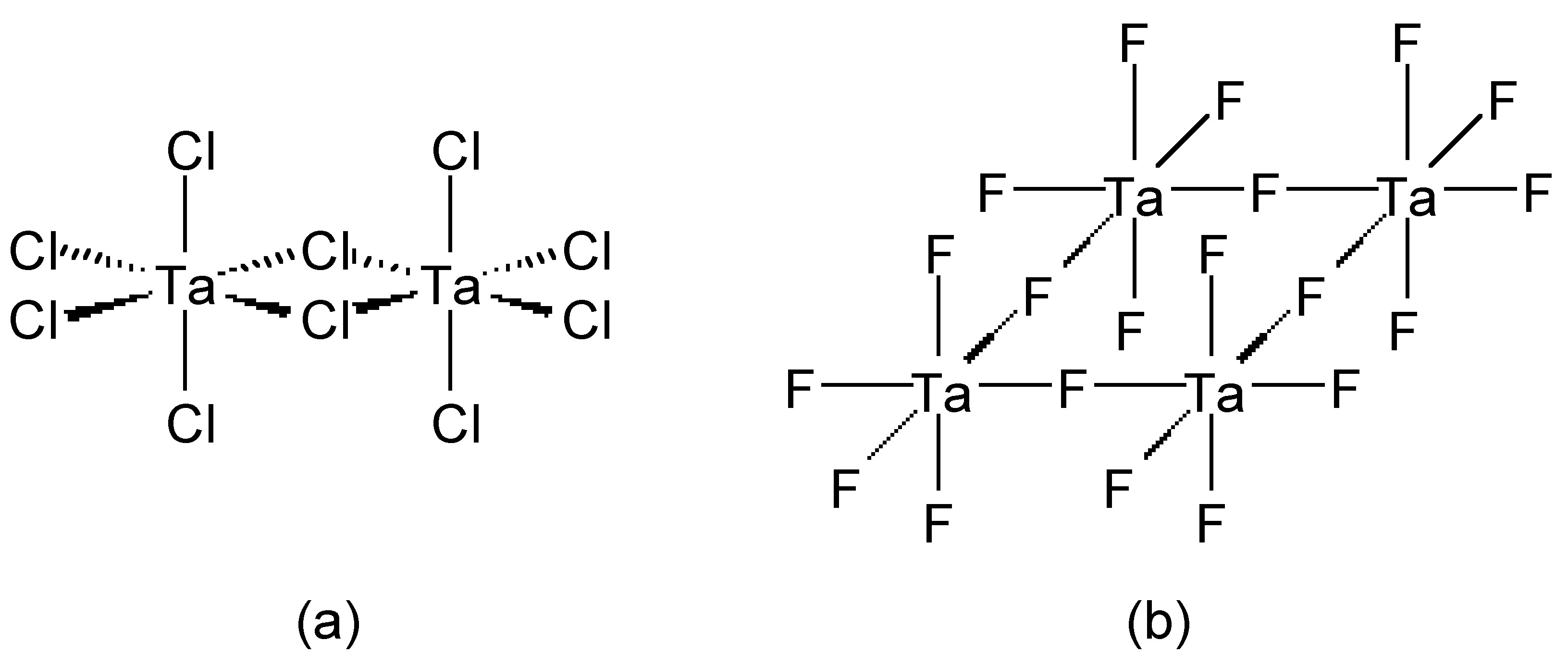
The bridging halide bonds can be described by both Lewis and molecular orbital (MO) theory. In a simple picture, the lone pair of a terminal halide can be thought to act as a Lewis base donor ligand to the second Lewis acidic metal center. Indeed some bridging halides are asymmetric consistent with this view; however, the symmetrical ones can be described by a resonance form. From a molecular orbital point of view, the bridging halide is represented by a combination of two metal centered orbitals with two halogen orbitals.
Hydrogen chloride (HCl) is prepared by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ) with either NaCl or concentrated HCl solution.
Hydrogen chloride is a polar molecule with a dipole of 1.08 D. However, the lower polarity as compared to that of hydrogen fluoride (1.91 D) is consistent with the physical and chemical properties. Hydrogen chloride is a gas at room temperature (Mp = -114.25 °C, Bp = -85.09 °C), and its low boiling point is consistent with weak hydrogen bonding in the liquid state. While self-ionization, [link] , is very small, liquid HCl dissolves some inorganic compounds to give conducting solutions, [link] .
Hydrogen chloride is soluble (and reacts) in water, [link] . The pK a of the reaction (-7.0) is larger than observed for fluorine (3.2) and as such HCl is a stronger acid than HF.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?