| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
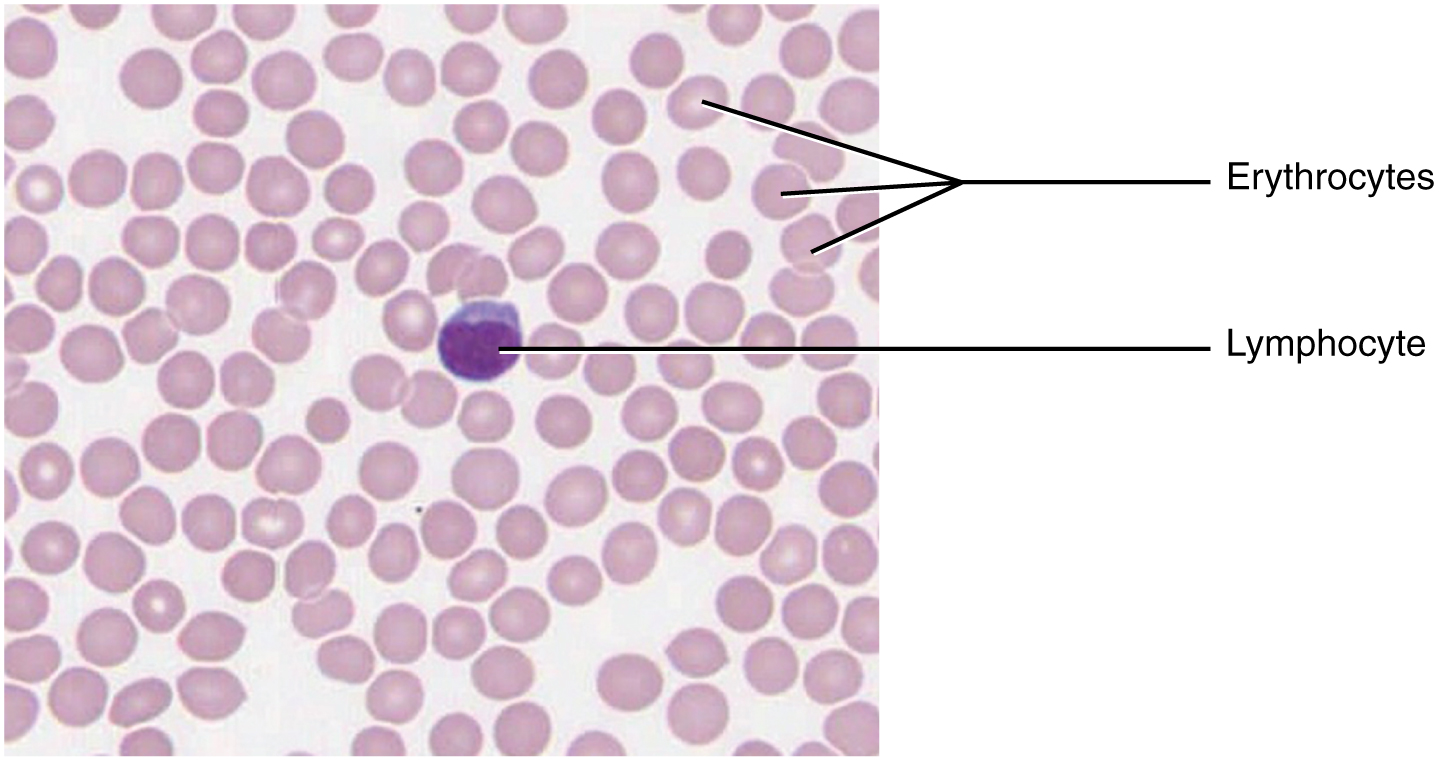
Lymph contains a liquid matrix and white blood cells. Lymphatic capillaries are extremely permeable, allowing larger molecules and excess fluid from interstitial spaces to enter the lymphatic vessels. Lymph drains into blood vessels, delivering molecules to the blood that could not otherwise directly enter the bloodstream. In this way, specialized lymphatic capillaries transport absorbed fats away from the intestine and deliver these molecules to the blood.
Connective tissue is a heterogeneous tissue with many cell shapes and tissue architecture. Structurally, all connective tissues contain cells that are embedded in an extracellular matrix stabilized by proteins. The chemical nature and physical layout of the extracellular matrix and proteins vary enormously among tissues, reflecting the variety of functions that connective tissue fulfills in the body. Connective tissues separate and cushion organs, protecting them from shifting or traumatic injury. Connect tissues provide support and assist movement, store and transport energy molecules, protect against infections, and contribute to temperature homeostasis.
Many different cells contribute to the formation of connective tissues. Fibroblasts are the most abundant and secrete many protein fibers, adipocytes specialize in fat storage, stem cells from the bone marrow give rise to all the blood cells, chondrocytes form cartilage, and osteocytes form bone. The extracellular matrix contains fluid, proteins, polysaccharide derivatives, and, in the case of bone, mineral crystals. Protein fibers fall into three major groups: collagen fibers that are thick, strong, flexible, and resist stretch; reticular fibers that are thin and form a supportive mesh; and elastin fibers that are thin and elastic.
The major types of connective tissue are connective tissue proper, supportive tissue, and fluid tissue. Loose connective tissue proper includes adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves. The matrix is the most abundant feature for loose tissue although adipose tissue does not have much extracellular matrix. Dense connective tissue proper is richer in fibers and may be regular, with fibers oriented in parallel as in ligaments and tendons, or irregular, with fibers oriented in several directions. Organ capsules (collagenous type) and walls of arteries (elastic type) contain dense irregular connective tissue. Cartilage and bone are supportive tissue. Cartilage contains chondrocytes and is somewhat flexible. Hyaline cartilage is smooth and clear, covers joints, and is found in the growing portion of bones. Fibrocartilage is tough because of extra collagen fibers and forms, among other things, the intervertebral discs. Elastic cartilage can stretch and recoil to its original shape because of its high content of elastic fibers. The matrix contains very few blood vessels. Bones are made of a rigid, mineralized matrix containing calcium salts, crystals, and osteocytes lodged in lacunae. Bone tissue is highly vascularized. Cancellous bone is spongy and less solid than compact bone. Fluid tissue, for example blood and lymph, is characterized by a liquid matrix and no supporting fibers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Histology' conversation and receive update notifications?