| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
C expressions are arranged in the following groups based on the operators they contain and how you use them:
Expressions are used as
A subprogram (also known as a procedure or subroutine) is nothing more than a collection of instructions forming a program unit written independently of the main program yet associated with it through a transfer/return process. Control is passed to the subprogram at the time its services are required, and then control is returned to the main program after the subprogram has finished.
The syntax used to represent the request of subprogram varies among the different language. The techniques used to describe a subprogram also varies from language to language. Many systems allow such program units to be written in languages other than that of the main program.
In most procedural programming languages, a subprogram is implemented as though it were completely separate entity with its own data and algorithm so that an item of data in either the main program or the subprogram is not automatically accessible from within the other. With this arrangement, any transfer of data between the two program parts must be specified by the programmer. This is usually done by listing the items called parameters to be transferred in the same syntactic structure used to request the subprogram’s execution.
The names used for the parameters within the subprogram can be thought of as merely standing in for the actual data values that are supplied when the subprogram is requested. As a result, you often hear them called formal parameters, whereas the data values supplied from the main program are refereed to actual parameters.
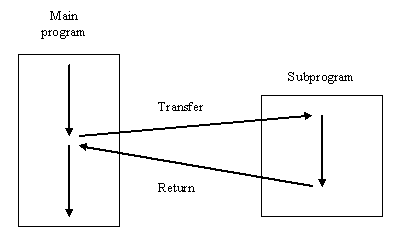
C only accept one kind of subprogram, function. A function is a sub program in which input values are transferred through a parameter list. However, information is returned from a function to the main program in the form of the “value of the function”. That is the value returned by a function is associated with the name of the function in a manner similar to the association between a value and a variable name. The difference is that the value associated with a function name is computed (according to the function’s definition) each time it is required, whereas when a variable ‘s value is required, it is merely retrieve from memory.
C also provide a rich collection of built-in functions.There are more than twenty functions declared in<math.h>. Here are some of the more frequently used.
| Name | Description | Math Symbols | Example |
| sqrt(x) | square root | sqrt(16.0) is 4.0 | |
| pow(x,y) | compute a value taken to an exponent, xy | pow(2,3) is 8 | |
| exp(x) | exponential function, computes ex | exp(1.0) is 2.718282 | |
| log(x) | natural logarithm | ln x | log(2.718282) is 1.0 |
| log10(x) | base-10 logarithm | log x | log10(100) is 2 |
| sin(x) | sine | sin x | sin(0.0) is 0.0 |
| cos(x) | cosine | cos x | cos(0.0) is 1.0 |
| tan(x) | tangent | tg x | tan(0.0) is 0.0 |
| ceil(x) | smallest integer not less than parameter | ceil(2.5) is 3; ceil(-2.5) is –2 | |
| floor(x) | largest integer not greater than parameter | floor(2.5) is 2; floor(-2.5) is –3 |
Library
The library is not part of the C language proper, but an environment that support C will provide the function declarations and type and macro definitions of this library.The functions, types and macro of the library are declared in headers.
C header files have extensions .h. Header files should not contain any source code. They are used purely to store function prototypes, common #define constants, and any other information you wish to export from the C file that the header file belongs to.
A header can be accessed by
#include<header>
Here are some headers of Turbo C library
stdio.h Provides functions for performing input and output.
stdlib.h Defines several general operation functions and macros.
conio.h Declares several useful library functions for performing "console input and output" from a program.
math.h Defines several mathematic functions.
string.h Provides many functions useful for manipulating strings (character arrays).
io.h Defines the file handle and low-level input and output functions
graphics.h Includes graphics functions
A statement specifies one or more action to be perform during the execution of a program.
C requires a semicolon at the end of every statement.
Comments are marked by symbol “/*” and “*/”. C also use // to mark the start of a comment and the end of a line to indicate the end of a comment.
1. The Hello program written using the first commenting style of C
/* A simple program to demonstrateC style comments
The following line is essentialin the C version of the hello HUT program
*/#include<stdio.h>main()
{printf /* just print */ ("Hello HUT\n");
}The Hello program written using the second commenting style of C
// A simple program to demonstrate// C style comments
//// The following line is essential
// in the C version of the hello HUT program#include<stdio.h>main()
{printf("Hello HUT\n"); //print the string and then go to a new line
} By the first way, a program may have a multi-line comments and comments in the middle of a line of code.However, you shouldn’t mix the two style in the same program.
A C program basically has the following form:


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to computer science' conversation and receive update notifications?