| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The harmonic series is particularly important for brass instruments. A pianist or xylophone player only gets one note from each key. A string player who wants a different note from a string holds the string tightly in a different place. This basically makes a vibrating string of a new length, with a new fundamental.
But a brass player, without changing the length of the instrument, gets different notes by actually playing the harmonics of the instrument. Woodwinds also do this, although not as much. Most woodwinds can get two different octaves with essentially the same fingering; the lower octave is the fundamental of the column of air inside the instrument at that fingering. The upper octave is the first harmonic.
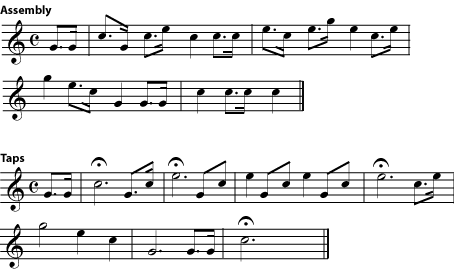
It is the brass instruments that excel in getting different notes from the same length of tubing. The sound of a brass instruments starts with vibrations of the player's lips. By vibrating the lips at different speeds, the player can cause a harmonic of the air column to sound instead of the fundamental. Thus a bugle player can play any note in the harmonic series of the instrument that falls within the player's range. Compare these well-known bugle calls to the harmonic series above .
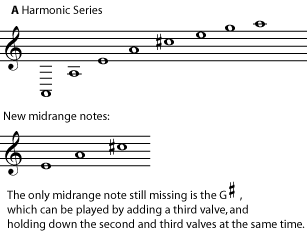
For centuries, all brass instruments were valveless. A brass instrument could play only the notes of one harmonic series. (An important exception was the trombone and its relatives, which can easily change their length and harmonic series using a slide.) The upper octaves of the series, where the notes are close enough together to play an interesting melody, were often difficult to play, and some of the harmonics sound quite out of tune to ears that expect equal temperament. The solution to these problems, once brass valves were perfected, was to add a few valves to the instrument; three is usually enough. Each valve opens an extra length of tube, making the instrument a little longer, and making available a whole new harmonic series. Usually one valve gives the harmonic series one half step lower than the valveless intrument; another, one whole step lower; and the third, one and a half steps lower. The valves can be used in combination, too, making even more harmonic series available. So a valved brass instrument can find, in the comfortable middle of its range (its middle register ), a valve combination that will give a reasonably in-tune version for every note of the chromatic scale . (For more on the history of valved brass, see History of the French Horn . For more on how and why harmonics are produced in wind instruments, please see Standing Waves and Wind Instruments )

Write the harmonic series for the instrument above when both the first and second valves are open. (You can use this PDF file if you need staff paper.) What new notes are added in the instrument's middle range? Are any notes still missing?
Opening both first and second valves gives the harmonic series one-and-a-half steps lower than "no valves".
String players also use harmonics, although not as much as brass players. Harmonics on strings have a very different timbre from ordinary string sounds. They give a quieter, thinner, more bell-like tone, and are usually used as a kind of ear-catching special-effect.
Normally a string player holds a string down very tightly. This shortens the length of the vibrating part of the string, in effect making a (temporarily) shorter vibrating string, which has its own full set of harmonics.
To "play a harmonic", the string is touched very, very lightly instead. The length of the string does not change. Instead, the light touch interferes with all of the vibrations that don't have a node at that spot.
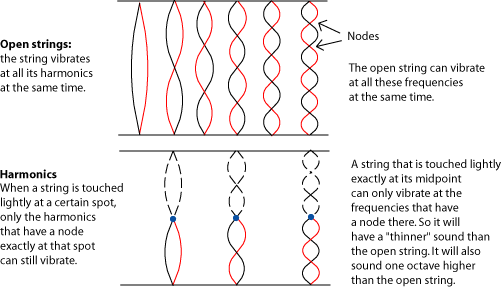
The thinner, quieter sound of "playing harmonics" is caused by the fact that much of the harmonic series is missing from the sound, which will of course affect the timbre . Lightly touching the string in most places will result in no sound at all. This technique only works well at places on the string where a main harmonic (one of the longer, louder lower-numbered harmonics) has a node. Some string players can get more harmonics by both holding the string down in one spot and touching it lightly in another spot, but this is an advanced technique.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Understanding basic music theory' conversation and receive update notifications?