| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Similarly, the frequency of the sinusoid for the fifth plot was 1.75 cycles per second. The peak for this sinusoid should have appeared 0.75 cycles persecond above the folding frequency, but appeared instead 0.75 cycles per second below the folding frequency. In other words, the spectrum folded around thefolding frequency so that this peak appeared below the folding frequency.
I am going to show you two more views of the spectra of these sinusoids to help you better understand the folding phenomena.
Let's go back and examine another view of the case that has no sampling problems. This view is shown in Figure 9 .
| Figure 9. Spectral analyses of five sinusoids with no sampling problems. |
|---|
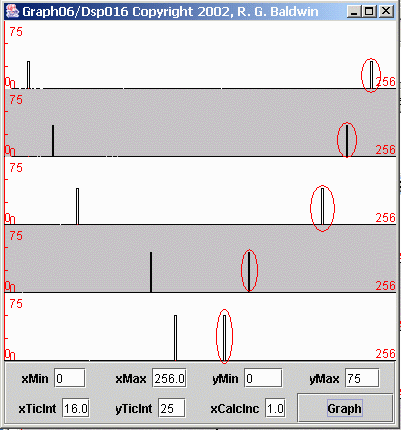 |
This is the case where all five sinusoids are sampled at a sampling frequency of four samples per second, resulting in a folding frequency of two cycles persecond. If you compare Figure 9 with Figure 7 , you will see that the left half of Figure 9 is very similar to Figure 7 .
In Figure 7 , the spectral data was computed and displayed from zero frequency on the left to the folding frequency (two cycles per second) on the right. In Figure 9 , the spectral data was computed and displayed from zero frequency on the left to the sampling frequency (four cycles per second) on the right.
Thus, the total frequency range for Figure 9 is twice the frequency range for Figure 7 .
In Figure 9 , the folding frequency is exactly in the center of each plot. In other words, the center of the plots in Figure 9 corresponds to the right edge of the plots in Figure 7 . Everything to the left of center in Figure 9 corresponds to the plots in Figure 7 . The material to the right of center in Figure 9 was not shown in Figure 7 .
Hopefully the display in Figure 9 will explain why the frequency that is half the sampling frequency is called the folding frequency. The computed spectrumfolds around that frequency. Everything to the right of the folding frequency is a mirror image of everything to the left of the folding frequency.
All the peaks to the left of center in Figure 9 are valid spectral peaks associated with the corresponding sinusoids. However, all the peaks to the rightof center, which I marked with red ovals, are artifacts of the sampling process. Those peaks do not exist in the true spectrum of the original raw data. Theywere created by the sampling process.
Normally we don't worry about this mirror image above the folding frequency when doing spectral analyses. We know it is there and we simply ignore it.
In fact, for reasons of economy, when doing spectral analyses using discrete Fourier transforms, we usually don't even compute the spectrum at frequenciesabove the folding frequency. Since it is always a mirror image of the spectrum below the folding frequency, we know what it looks like without even computingit.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Digital signal processing - dsp' conversation and receive update notifications?