| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Geheuekaart:
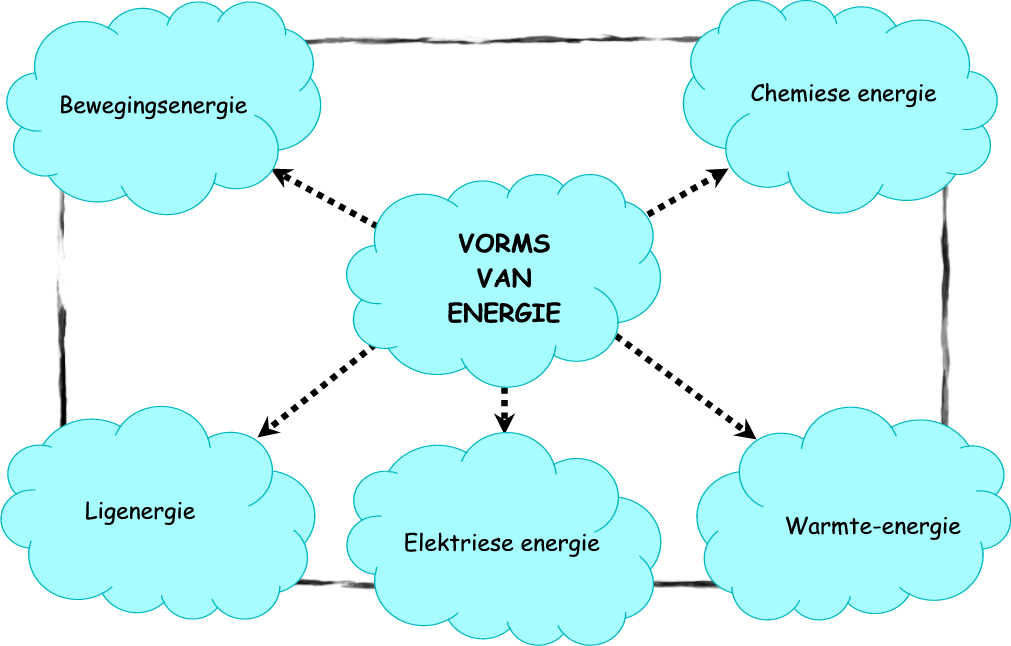
Bewegingsenergie: wind en water
Chemiese energie: voedsel
Warmte-energie: son
Elektriese energie: selle, batterye, dinamo’s, kragstasies
Ligenergie: son
Benewens chemiese energie is daar baie ander vorms van energie. Warmte-energie en ligenergie word hoofsaaklik van die son verkry. Bewegingsenergie word bv. verkry wanneer bewegende water ‘n waterwiel laat draai of wanneer bewegende lug (wind) ‘n windpomp laat werk.
Klankenergie word veroorsaak deur vibrerende voorwerpe, bv. die snare van ‘n kitaar.
Elektriese energie is die vorm van energie wat die meeste in die alledaagse lewe gebruik word. Elektriese energie word met behulp van dinamo’s opgewek. Elektriese energie is baie gerieflik, omdat dit met drade oor lang afstande vervoer kan word. Elektriese energie kan ook uit selle (bv. flitsselle) of batterye verkry word.
Gebruik die inleidingsparagraaf en voltooi die geheuekaart deur 'n bron van elke vorm van energie neer te skryf (probeer onthou wat jy in Graad 5 geleer het).
Leeruitkomste 2: Die leerder ken, interpreteer en pas wetenskaplike, tegnologiese en omgewingskennis toe.
Assesseringstandaard 2.1: Dit is duidelik wanneer die leerder betekenisvolle inligting onthou.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natuurwetenskappe graad 6' conversation and receive update notifications?