| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[link] shows how the levels move toward specificity with other organisms. Notice how the dog shares a domain with the widest diversity of organisms, including plants and butterflies. At each sublevel, the organisms become more similar because they are more closely related. Historically, scientists classified organisms using characteristics, but as DNA technology developed, more precise phylogenies have been determined.
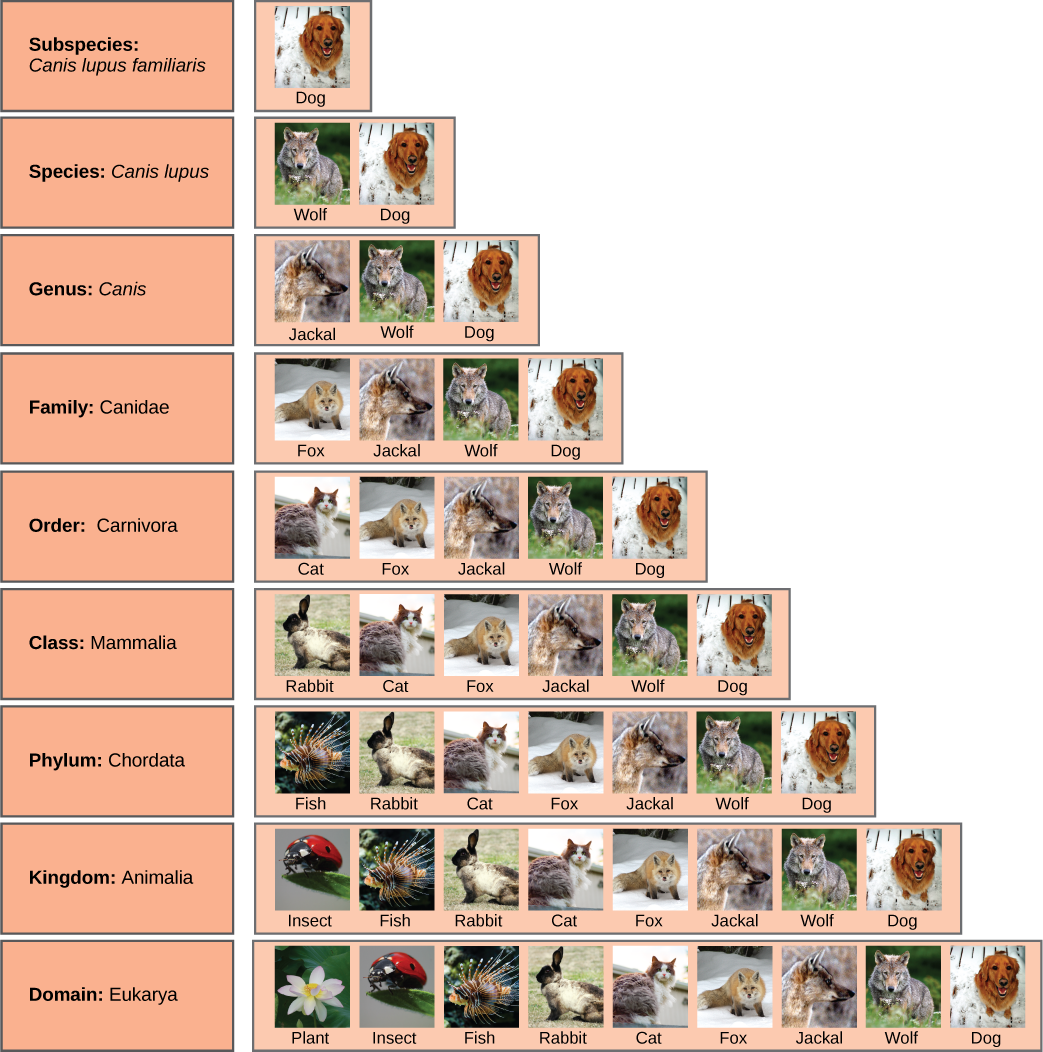
At what levels are cats and dogs considered to be part of the same group?
Visit this website to classify three organisms—bear, orchid, and sea cucumber—from kingdom to species. To launch the game, under Classifying Life, click the picture of the bear or the Launch Interactive button.
Recent genetic analysis and other advancements have found that some earlier phylogenetic classifications do not align with the evolutionary past; therefore, changes and updates must be made as new discoveries occur. Recall that phylogenetic trees are hypotheses and are modified as data becomes available. In addition, classification historically has focused on grouping organisms mainly by shared characteristics and does not necessarily illustrate how the various groups relate to each other from an evolutionary perspective. For example, despite the fact that a hippopotamus resembles a pig more than a whale, the hippopotamus may be the closest living relative of the whale.
Scientists continually gain new information that helps understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Each group of organisms went through its own evolutionary journey, called its phylogeny. Each organism shares relatedness with others, and based on morphologic and genetic evidence, scientists attempt to map the evolutionary pathways of all life on Earth. Historically, organisms were organized into a taxonomic classification system. However, today many scientists build phylogenetic trees to illustrate evolutionary relationships.
To build phylogenetic trees, scientists must collect accurate information that allows them to make evolutionary connections between organisms. Using morphologic and molecular data, scientists work to identify homologous characteristics and genes. Similarities between organisms can stem either from shared evolutionary history (homologies) or from separate evolutionary paths (analogies). Newer technologies can be used to help distinguish homologies from analogies. After homologous information is identified, scientists use cladistics to organize these events as a means to determine an evolutionary timeline. Scientists apply the concept of maximum parsimony, which states that the order of events probably occurred in the most obvious and simple way with the least amount of steps. For evolutionary events, this would be the path with the least number of major divergences that correlate with the evidence.
[link] Which animals in this figure belong to a clade that includes animals with hair? Which evolved first, hair or the amniotic egg?
[link] Rabbits and humans belong in the clade that includes animals with hair. The amniotic egg evolved before hair because the Amniota clade is larger than the clade that encompasses animals with hair.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?