| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
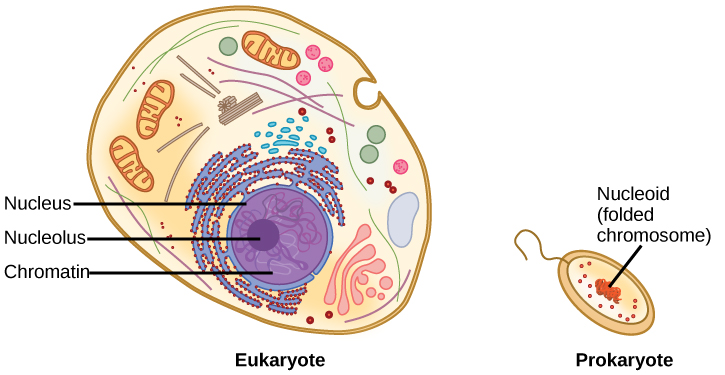
In eukaryotic cells, DNA and RNA synthesis occur in a separate compartment from protein synthesis. In prokaryotic cells, both processes occur together. What advantages might there be to separating the processes? What advantages might there be to having them occur together?
The size of the genome in one of the most well-studied prokaryotes, E.coli, is 4.6 million base pairs (approximately 1.1 mm, if cut and stretched out). So how does this fit inside a small bacterial cell? The DNA is twisted by what is known as supercoiling. Supercoiling means that DNA is either under-wound (less than one turn of the helix per 10 base pairs) or over-wound (more than 1 turn per 10 base pairs) from its normal relaxed state. Some proteins are known to be involved in the supercoiling; other proteins and enzymes such as DNA gyrase help in maintaining the supercoiled structure.
Eukaryotes, whose chromosomes each consist of a linear DNA molecule, employ a different type of packing strategy to fit their DNA inside the nucleus ( [link] ). At the most basic level, DNA is wrapped around proteins known as histones to form structures called nucleosomes. The histones are evolutionarily conserved proteins that are rich in basic amino acids and form an octamer. The DNA (which is negatively charged because of the phosphate groups) is wrapped tightly around the histone core. This nucleosome is linked to the next one with the help of a linker DNA. This is also known as the “beads on a string” structure. This is further compacted into a 30 nm fiber, which is the diameter of the structure. At the metaphase stage, the chromosomes are at their most compact, are approximately 700 nm in width, and are found in association with scaffold proteins.
In interphase, eukaryotic chromosomes have two distinct regions that can be distinguished by staining. The tightly packaged region is known as heterochromatin, and the less dense region is known as euchromatin. Heterochromatin usually contains genes that are not expressed, and is found in the regions of the centromere and telomeres. The euchromatin usually contains genes that are transcribed, with DNA packaged around nucleosomes but not further compacted.
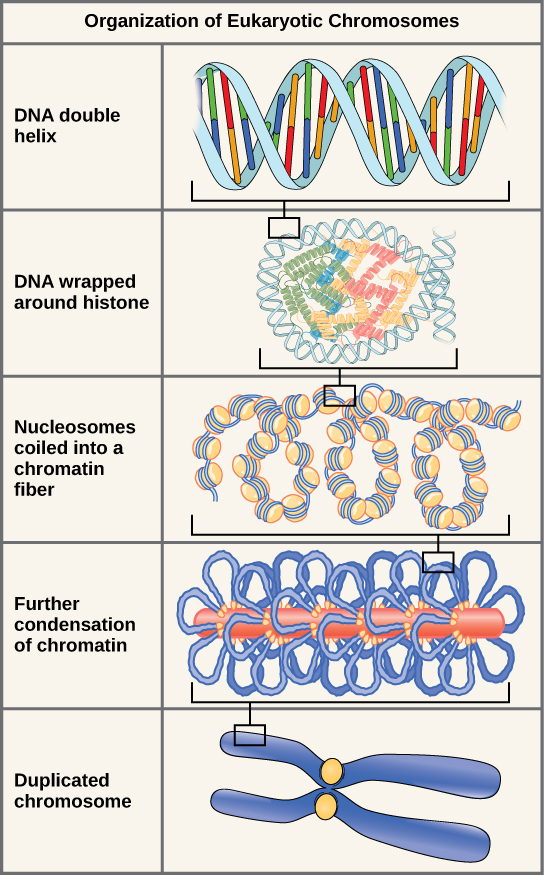
The currently accepted model of the double-helix structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and Crick. Some of the salient features are that the two strands that make up the double helix are complementary and anti-parallel in nature. Deoxyribose sugars and phosphates form the backbone of the structure, and the nitrogenous bases are stacked inside. The diameter of the double helix, 2 nm, is uniform throughout. A purine always pairs with a pyrimidine; A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. One turn of the helix has ten base pairs. During cell division, each daughter cell receives a copy of the DNA by a process known as DNA replication. Prokaryotes are much simpler than eukaryotes in many of their features. Most prokaryotes contain a single, circular chromosome. In general, eukaryotic chromosomes contain a linear DNA molecule packaged into nucleosomes, and have two distinct regions that can be distinguished by staining, reflecting different states of packaging and compaction.
[link] In eukaryotic cells, DNA and RNA synthesis occur in a separate compartment from protein synthesis. In prokaryotic cells, both processes occur together. What advantages might there be to separating the processes? What advantages might there be to having them occur together?
[link] Compartmentalization enables a eukaryotic cell to divide processes into discrete steps so it can build more complex protein and RNA products. But there is an advantage to having a single compartment as well: RNA and protein synthesis occurs much more quickly in a prokaryotic cell.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?