| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the time F.W. de Klerk succeeded P.W. Botha as president in 1989, SA had been plunged into a situation of worsening crisis because of international sanctions. The government realised that they could not govern without a state of emergency and that they had no choice but to negotiate with the black majority. On 2 February 1990, the bans on the ANC, PAC, SACP and 33 other organisations were lifted. Nine days later, on 11 February, Nelson Mandela was released from jail after 27 years. (SWA, the present Namibia, became independent in the same year.) The Group Areas Act was repealed in 1991.
A NEW CONSTITUTION
The last of the apartheid laws were abolished during 1991 and 1992 and the government started negotiations with the ANC for the first time, after 78 years. This led to the Groote Schuur Agreement. CODESA (Convention for a Democratic South Africa) began. This comprised a series of meetings, during which the various political parties and organisations negotiated in order to establish a temporary, fair and democratic constitution. The date for an election in 1994 was agreed to at the end of 1993.
(a) Discuss the following three sources in class. Relate the event from the perspective of the different leaders. Also use your own sources.
SOURCE A

SOURCE B
Negotiations between Mandela and De Klerk

SOURCE C
Nelson Mandela and F.W. de Klerk receive the Nobel Prize for Peace.

From: Benjamin, A. 1990. The Alternative Mandela Album. Johannesburg: Argus.
(a) The sources provided reflect the points of view during the 90’s. When you play the role of historian, you should select and present (communicate) information from different sources. Answer the questions on the provided sources in your groups.
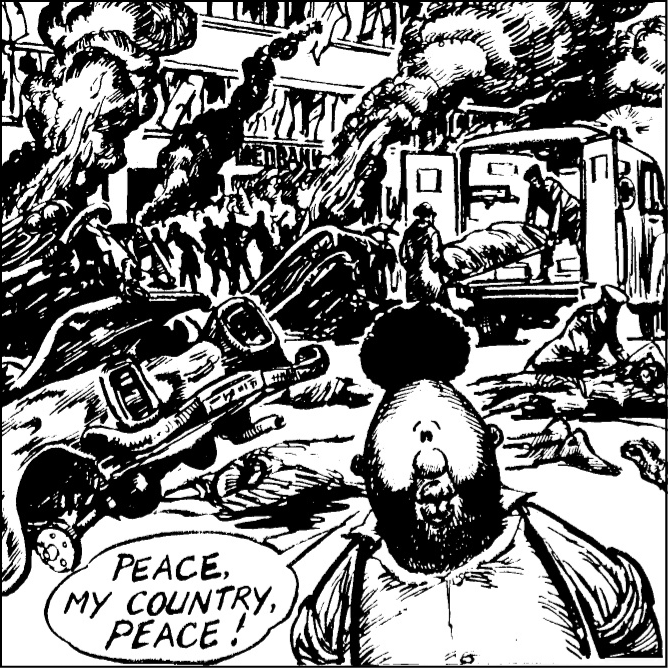

The Sowetan , 12 July 1990
Die Burger , 10 May 1990
PEACE . . . HUMAN RIGHTS . . . AT LAST!
The ANC won the first election and Nelson Mandela became the first black president of the "new SA."
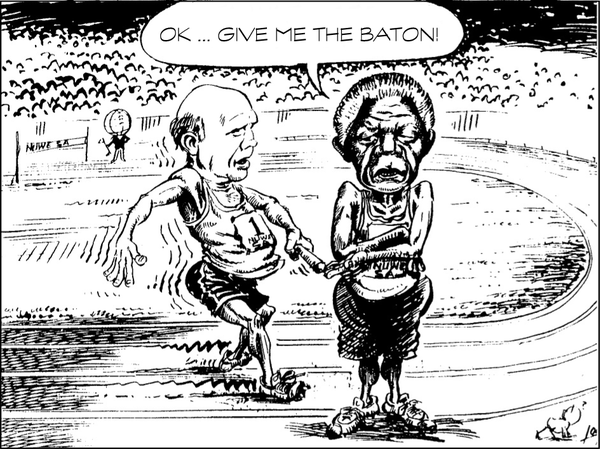

(c) Describe the thoughts of the two leaders.
The largest number of heads of state and important leaders ever to attend an inauguration ceremony, gathered for president Nelson Mandela's inauguration. SA was welcomed into the world community with open arms once more. Here are some examples of what this meant:
| LO 2 |
| HISTORICAL KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING The learner will be able to demonstrate historical knowledge and understanding. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 2.1 chronology and time: |
|
| 2.2 cause and effect: |
|
| 2.3 change and continuity: |
|
| LO 3 |
| HISTORICAL INTERPRETATION The learner will be able to interpret aspects of history. |
| We know this when the learner: |
| 3.1 interprets sources: |
|
| 3.2 reconstructs the past: |
|
| 3.3 representation of the past: |
|

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'History grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?