| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Remark 3.4 The converse to Theorem 3.3 is false: there exist non-Legendrian isotopic Legendrian knots whose Lagrangian projections are related by a finite sequence of the moves and .
Definition 4.1 The rotation number of an oriented Legendrian knot is
where is the number of down cusps in the front projection and is the number of up cusps.
Definition 4.2 The Thurston-Bennequin invariant , , is the linking number between and , where is a slight push-off of in the -direction.
That is, is one-half the signed count of the intersections between and , where we assign to intersections as in the following diagram:
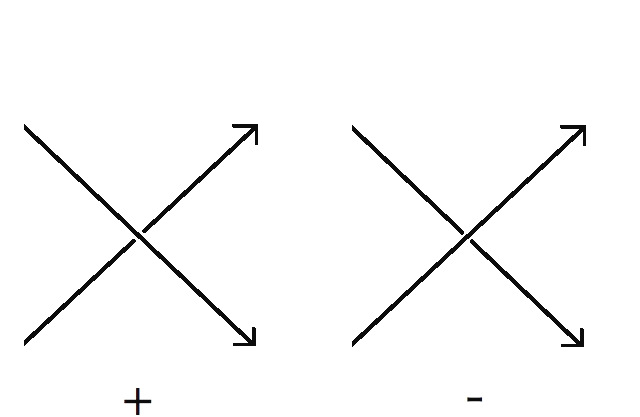
Theorem 4.3 Two oriented Legendrian torus knots are Legendrian isotopic if and only if their Thurston-Bennequin invariants, rotation numbers, and (topological) knot types agree.
Remark 4.4 Theorem 4.3 is not true for all knots. Y. Chekanov and Y. Eliashberg independently gave examples of non-Legendrian isotopic Legendrian knots with the same Thurston-Bennequin invariant, rotation number, and topological knot type.
Definition 5.1 A stick knot is the image of a PL-embedding of in . That is, a knot composed of line segments attached to each other at their endpoints. We call the segments edges and the joined endpoints vertices , and we require that exactly two edges meet at each vertex. The stick number of a knot is the minimum number of sticks necessary to make in .
Definition 5.2 A Legendrian stick knot is a stick knot that is Legendrian everywhere except at its vertices. The Legendrian stick number of a Legendrian knot , denoted , is the minimum number of sticks necessary to make a stick knot that is Legendrian isotopic to away from its vertices. The front stick number of , , is the minimum number of sticks in a front diagram of .
Remark 5.3 It is not hard to see that . For, if a stick lies in then it is parametrized by a line segment
for such that . In particular, either , in which case the stick runs perpendicular to the -plane, or , and the stick lies in a plane parallel to the -plane.
Example 5.4
This Connexions module describes work conducted as part of Rice University's VIGRE program, supported by National Science Foundation grant DMS-0739420. We would like to thank Dr. Josh Sabloff for suggesting this problem on Legendrian sticks, Dr. Shelly Harvey for assisting in the organization of our PFUG, and the undergraduate members C. Buenger, A. Jamshidi, S. Kruzick, A. Mehta, and M. Scherf.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'The art of the pfug' conversation and receive update notifications?