| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Some atoms are more stable when they gain or lose an electron (or possibly two) and form ions. This fills their outermost electron shell and makes them energetically more stable. Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a net charge.
This movement of electrons from one element to another is referred to as electron transfer . As [link] illustrates, sodium (Na) only has one electron in its outer electron shell. It takes less energy for sodium to donate that one electron than it does to accept seven more electrons to fill the outer shell. If sodium loses an electron, it now has 11 protons, 11 neutrons, and only 10 electrons, leaving it with an overall charge of +1. It is now referred to as a sodium ion. Chlorine (Cl) in its lowest energy state (called the ground state) has seven electrons in its outer shell. Again, it is more energy-efficient for chlorine to gain one electron than to lose seven. Therefore, it tends to gain an electron to create an ion with 17 protons, 17 neutrons, and 18 electrons, giving it a net negative (–1) charge. It is now referred to as a chloride ion. In this example, sodium will donate its one electron to empty its shell, and chlorine will accept that electron to fill its shell. Both ions now satisfy the octet rule and have complete outermost shells. Because the number of electrons is no longer equal to the number of protons, each is now an ion and has a +1 (sodium ion) or –1 (chloride ion) charge. Note that these transactions can normally only take place simultaneously: in order for a sodium atom to lose an electron, it must be in the presence of a suitable recipient like a chlorine atom.
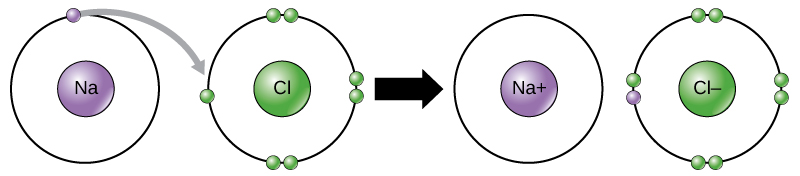
Ionic bonds are formed between ions with opposite charges. For instance, positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions bond together to make crystals of sodium chloride, or table salt, creating a crystalline molecule with zero net charge.
Certain salts are referred to in physiology as electrolytes (including sodium, potassium, and calcium), ions necessary for nerve impulse conduction, muscle contractions and water balance. Many sports drinks and dietary supplements provide these ions to replace those lost from the body via sweating during exercise.
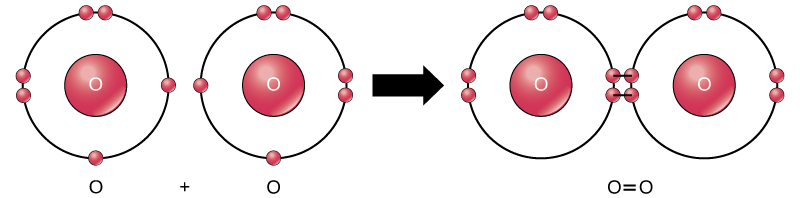
Another way the octet rule can be satisfied is by the sharing of electrons between atoms to form covalent bonds . These bonds are stronger and much more common than ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms. Covalent bonds are commonly found in carbon-based organic molecules, such as our DNA and proteins. Covalent bonds are also found in inorganic molecules like H 2 O, CO 2 , and O 2 . One, two, or three pairs of electrons may be shared, making single, double, and triple bonds, respectively. The more covalent bonds between two atoms, the stronger their connection. Thus, triple bonds are the strongest.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?