| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In galvanic cells, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. The opposite is true for electrolytic cells. In electrolytic cells , electrical energy causes nonspontaneous reactions to occur in a process known as electrolysis . The charging electric car pictured in [link] at the beginning of this chapter shows one such process. Electrical energy is converted into the chemical energy in the battery as it is charged. Once charged, the battery can be used to power the automobile.
The same principles are involved in electrolytic cells as in galvanic cells. We will look at three electrolytic cells and the quantitative aspects of electrolysis.
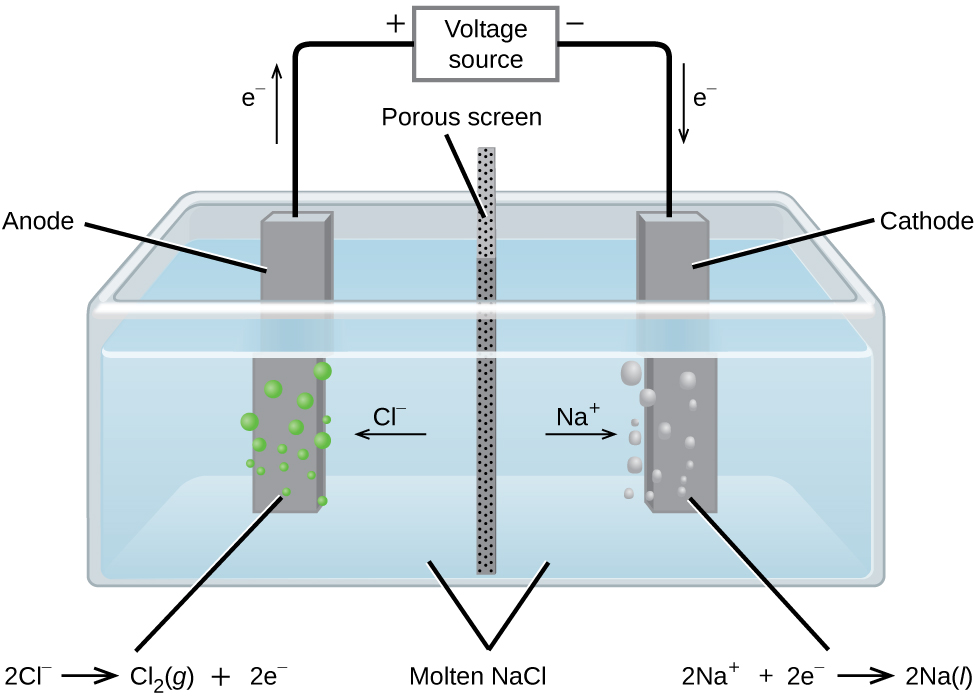
In molten sodium chloride, the ions are free to migrate to the electrodes of an electrolytic cell. A simplified diagram of the cell commercially used to produce sodium metal and chlorine gas is shown in [link] . Sodium is a strong reducing agent and chlorine is used to purify water, and is used in antiseptics and in paper production. The reactions are
The power supply (battery) must supply a minimum of 4 V, but, in practice, the applied voltages are typically higher because of inefficiencies in the process itself.
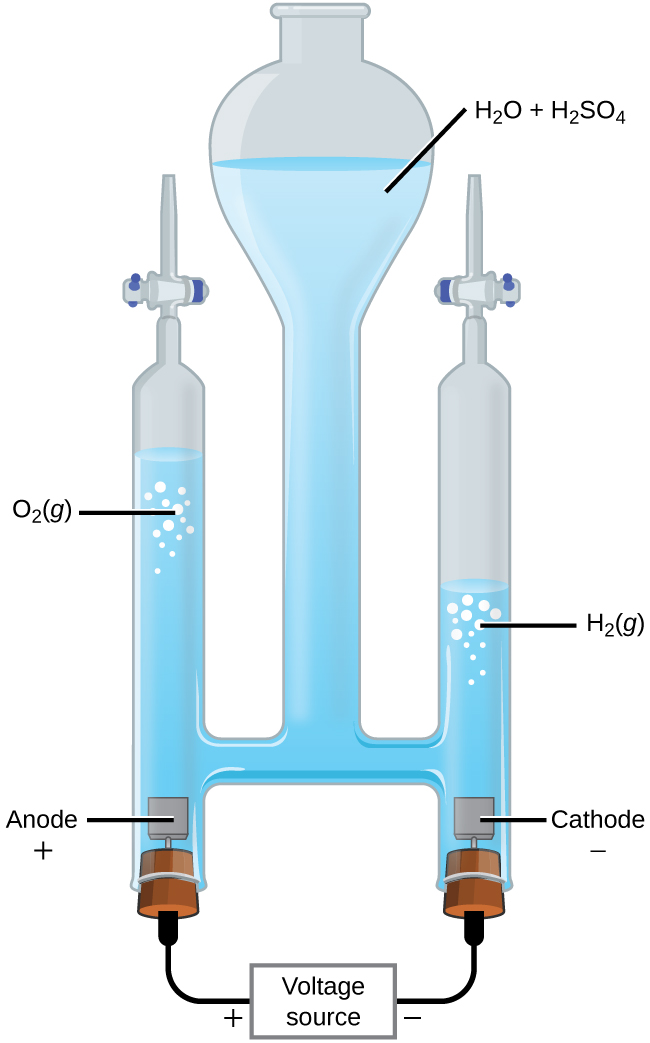
It is possible to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gas by electrolysis. Acids are typically added to increase the concentration of hydrogen ion in solution ( [link] ). The reactions are
Note that the sulfuric acid is not consumed and that the volume of hydrogen gas produced is twice the volume of oxygen gas produced. The minimum applied voltage is 1.229 V.
The electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride is the more common example of electrolysis because more than one species can be oxidized and reduced. Considering the anode first, the possible reactions are
These values suggest that water should be oxidized at the anode because a smaller potential would be needed—using reaction (ii) for the oxidation would give a less-negative cell potential. When the experiment is run, it turns out chlorine, not oxygen, is produced at the anode. The unexpected process is so common in electrochemistry that it has been given the name overpotential. The overpotential is the difference between the theoretical cell voltage and the actual voltage that is necessary to cause electrolysis. It turns out that the overpotential for oxygen is rather high and effectively makes the reduction potential more positive. As a result, under normal conditions, chlorine gas is what actually forms at the anode.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?