| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The chemistry of carbon is extensive; however, most of this chemistry is not relevant to this chapter. The other aspects of the chemistry of carbon will appear in the chapter covering organic chemistry. In this chapter, we will focus on the carbonate ion and related substances. The metals of groups 1 and 2, as well as zinc, cadmium, mercury, and lead(II), form ionic carbonates —compounds that contain the carbonate anions, The metals of group 1, magnesium, calcium, strontium, and barium also form hydrogen carbonates —compounds that contain the hydrogen carbonate anion, also known as the bicarbonate anion .
With the exception of magnesium carbonate, it is possible to prepare carbonates of the metals of groups 1 and 2 by the reaction of carbon dioxide with the respective oxide or hydroxide. Examples of such reactions include:
The carbonates of the alkaline earth metals of group 12 and lead(II) are not soluble. These carbonates precipitate upon mixing a solution of soluble alkali metal carbonate with a solution of soluble salts of these metals. Examples of net ionic equations for the reactions are:
Pearls and the shells of most mollusks are calcium carbonate. Tin(II) or one of the trivalent or tetravalent ions such as Al 3+ or Sn 4+ behave differently in this reaction as carbon dioxide and the corresponding oxide form instead of the carbonate.
Alkali metal hydrogen carbonates such as NaHCO 3 and CsHCO 3 form by saturating a solution of the hydroxides with carbon dioxide. The net ionic reaction involves hydroxide ion and carbon dioxide:
It is possible to isolate the solids by evaporation of the water from the solution.
Although they are insoluble in pure water, alkaline earth carbonates dissolve readily in water containing carbon dioxide because hydrogen carbonate salts form. For example, caves and sinkholes form in limestone when CaCO 3 dissolves in water containing dissolved carbon dioxide:
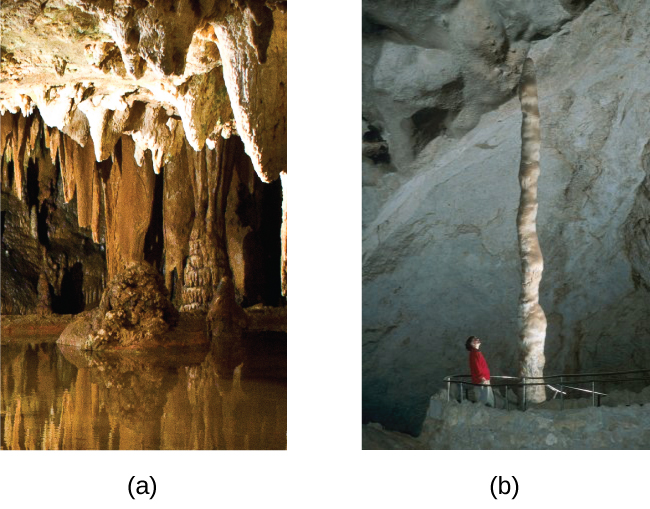
Hydrogen carbonates of the alkaline earth metals remain stable only in solution; evaporation of the solution produces the carbonate. Stalactites and stalagmites, like those shown in [link] , form in caves when drops of water containing dissolved calcium hydrogen carbonate evaporate to leave a deposit of calcium carbonate.
The two carbonates used commercially in the largest quantities are sodium carbonate and calcium carbonate. In the United States, sodium carbonate is extracted from the mineral trona, Na 3 (CO 3 )(HCO 3 )(H 2 O) 2 . Following recrystallization to remove clay and other impurities, heating the recrystallized trona produces Na 2 CO 3 :
Carbonates are moderately strong bases. Aqueous solutions are basic because the carbonate ion accepts hydrogen ion from water in this reversible reaction:
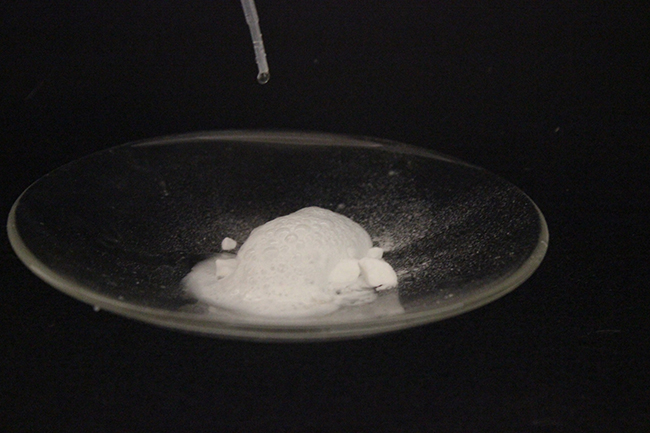
Carbonates react with acids to form salts of the metal, gaseous carbon dioxide, and water. The reaction of calcium carbonate, the active ingredient of the antacid Tums, with hydrochloric acid (stomach acid), as shown in [link] , illustrates the reaction:

Other applications of carbonates include glass making—where carbonate ions serve as a source of oxide ions—and synthesis of oxides.
Hydrogen carbonates are amphoteric because they act as both weak acids and weak bases. Hydrogen carbonate ions act as acids and react with solutions of soluble hydroxides to form a carbonate and water:
With acids, hydrogen carbonates form a salt, carbon dioxide, and water. Baking soda (bicarbonate of soda or sodium bicarbonate) is sodium hydrogen carbonate. Baking powder contains baking soda and a solid acid such as potassium hydrogen tartrate (cream of tartar), KHC 4 H 4 O 6 . As long as the powder is dry, no reaction occurs; immediately after the addition of water, the acid reacts with the hydrogen carbonate ions to form carbon dioxide:
Dough will trap the carbon dioxide, causing it to expand during baking, producing the characteristic texture of baked goods.
The usual method for the preparation of the carbonates of the alkali and alkaline earth metals is by reaction of an oxide or hydroxide with carbon dioxide. Other carbonates form by precipitation. Metal carbonates or hydrogen carbonates such as limestone (CaCO 3 ), the antacid Tums (CaCO 3 ), and baking soda (NaHCO 3 ) are common examples. Carbonates and hydrogen carbonates decompose in the presence of acids and most decompose on heating.
Carbon forms the ion, yet silicon does not form an analogous ion. Why?
Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(a) hardening of plaster containing slaked lime
(b) removal of sulfur dioxide from the flue gas of power plants
(c) the reaction of baking powder that produces carbon dioxide gas and causes bread to rise
(a)
(b)
(c)
Heating a sample of Na 2 CO 3 ⋅ x H 2 O weighing 4.640 g until the removal of the water of hydration leaves 1.720 g of anhydrous Na 2 CO 3 . What is the formula of the hydrated compound?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?