| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As was the case for gaseous substances, the kinetic molecular theory may be used to explain the behavior of solids and liquids. In the following description, the term particle will be used to refer to an atom, molecule, or ion. Note that we will use the popular phrase “intermolecular attraction” to refer to attractive forces between the particles of a substance, regardless of whether these particles are molecules, atoms, or ions.
Consider these two aspects of the molecular-level environments in solid, liquid, and gaseous matter:
The differences in the properties of a solid, liquid, or gas reflect the strengths of the attractive forces between the atoms, molecules, or ions that make up each phase. The phase in which a substance exists depends on the relative extents of its intermolecular forces (IMFs) and the kinetic energies (KE) of its molecules. IMFs are the various forces of attraction that may exist between the atoms and molecules of a substance due to electrostatic phenomena, as will be detailed in this module. These forces serve to hold particles close together, whereas the particles’ KE provides the energy required to overcome the attractive forces and thus increase the distance between particles. [link] illustrates how changes in physical state may be induced by changing the temperature, hence, the average KE, of a given substance.
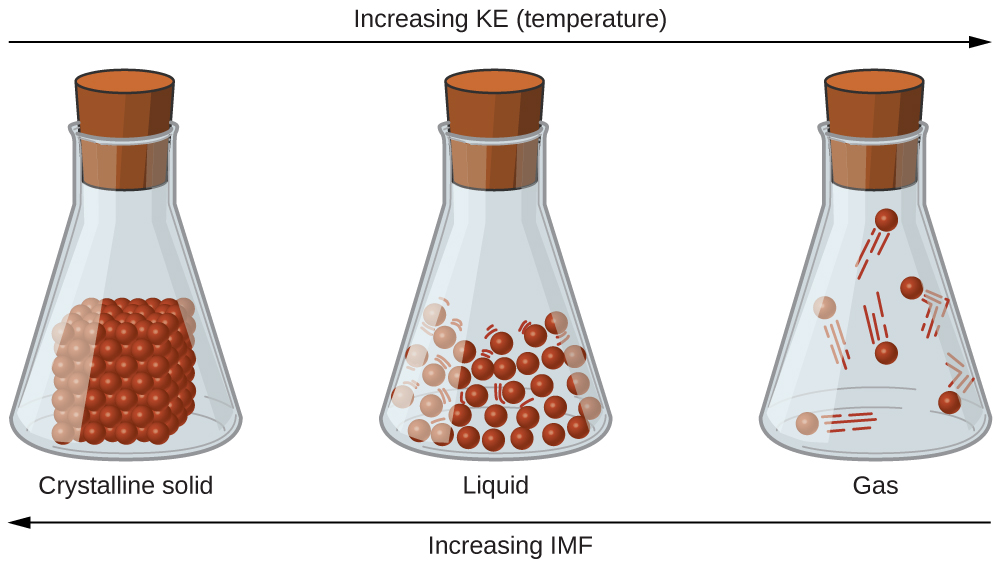
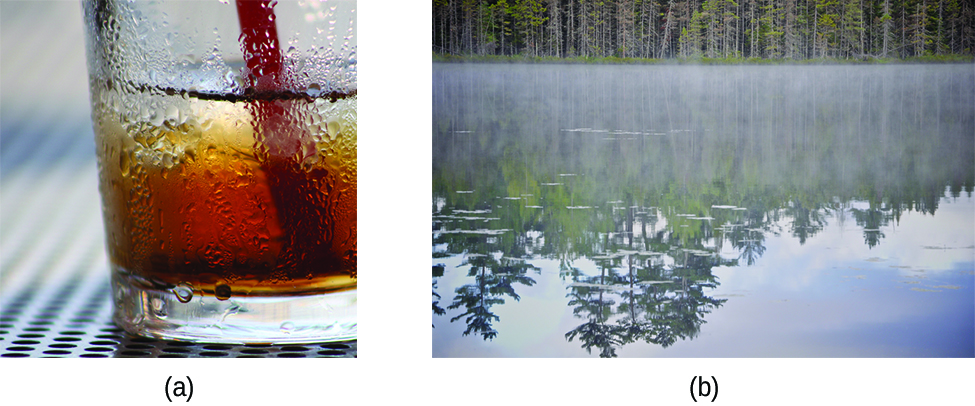
As an example of the processes depicted in this figure, consider a sample of water. When gaseous water is cooled sufficiently, the attractions between H 2 O molecules will be capable of holding them together when they come into contact with each other; the gas condenses, forming liquid H 2 O. For example, liquid water forms on the outside of a cold glass as the water vapor in the air is cooled by the cold glass, as seen in [link] .


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?