| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Note that when solving a related-rates problem, it is crucial not to substitute known values too soon. For example, if the value for a changing quantity is substituted into an equation before both sides of the equation are differentiated, then that quantity will behave as a constant and its derivative will not appear in the new equation found in step 4. We examine this potential error in the following example.
Let’s now implement the strategy just described to solve several related-rates problems. The first example involves a plane flying overhead. The relationship we are studying is between the speed of the plane and the rate at which the distance between the plane and a person on the ground is changing.
An airplane is flying overhead at a constant elevation of A man is viewing the plane from a position from the base of a radio tower. The airplane is flying horizontally away from the man. If the plane is flying at the rate of at what rate is the distance between the man and the plane increasing when the plane passes over the radio tower?
Step 1. Draw a picture, introducing variables to represent the different quantities involved.
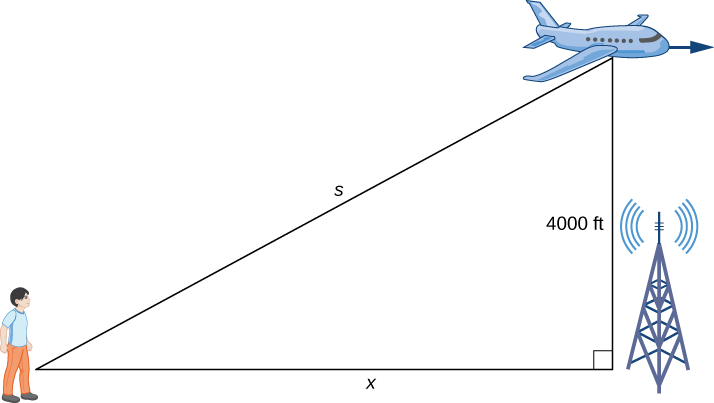
As shown, denotes the distance between the man and the position on the ground directly below the airplane. The variable denotes the distance between the man and the plane. Note that both and are functions of time. We do not introduce a variable for the height of the plane because it remains at a constant elevation of Since an object’s height above the ground is measured as the shortest distance between the object and the ground, the line segment of length 4000 ft is perpendicular to the line segment of length feet, creating a right triangle.
Step 2. Since denotes the horizontal distance between the man and the point on the ground below the plane, represents the speed of the plane. We are told the speed of the plane is 600 ft/sec. Therefore, ft/sec. Since we are asked to find the rate of change in the distance between the man and the plane when the plane is directly above the radio tower, we need to find when
Step 3. From the figure, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to write an equation relating and
Step 4. Differentiating this equation with respect to time and using the fact that the derivative of a constant is zero, we arrive at the equation
Step 5. Find the rate at which the distance between the man and the plane is increasing when the plane is directly over the radio tower. That is, find when Since the speed of the plane is we know that We are not given an explicit value for however, since we are trying to find when we can use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the distance when and the height is Solving the equation
for we have at the time of interest. Using these values, we conclude that is a solution of the equation
Therefore,
Note : When solving related-rates problems, it is important not to substitute values for the variables too soon. For example, in step 3, we related the variable quantities and by the equation
Since the plane remains at a constant height, it is not necessary to introduce a variable for the height, and we are allowed to use the constant 4000 to denote that quantity. However, the other two quantities are changing. If we mistakenly substituted into the equation before differentiating, our equation would have been
After differentiating, our equation would become
As a result, we would incorrectly conclude that

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?