| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We were introduced to hyperbolic functions in Introduction to Functions and Graphs , along with some of their basic properties. In this section, we look at differentiation and integration formulas for the hyperbolic functions and their inverses.
Recall that the hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine are defined as
The other hyperbolic functions are then defined in terms of and The graphs of the hyperbolic functions are shown in the following figure.
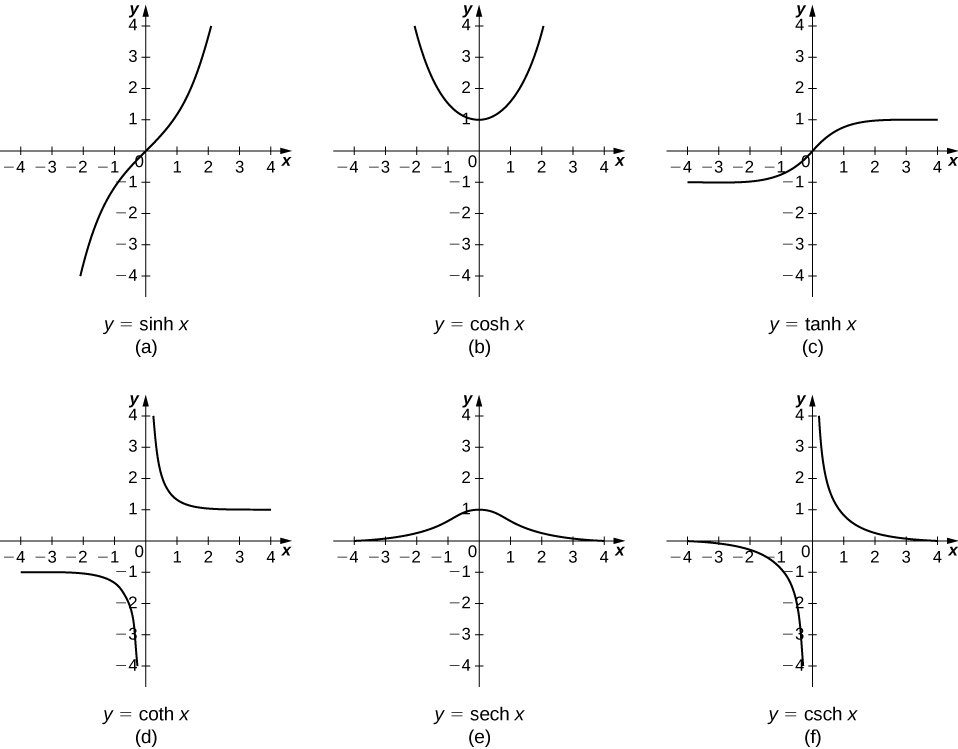
It is easy to develop differentiation formulas for the hyperbolic functions. For example, looking at we have
Similarly, We summarize the differentiation formulas for the hyperbolic functions in the following table.
Let’s take a moment to compare the derivatives of the hyperbolic functions with the derivatives of the standard trigonometric functions. There are a lot of similarities, but differences as well. For example, the derivatives of the sine functions match: and The derivatives of the cosine functions, however, differ in sign: but As we continue our examination of the hyperbolic functions, we must be mindful of their similarities and differences to the standard trigonometric functions.
These differentiation formulas for the hyperbolic functions lead directly to the following integral formulas.
Evaluate the following derivatives:
Using the formulas in [link] and the chain rule, we get
Evaluate the following integrals:
We can use u -substitution in both cases.
Looking at the graphs of the hyperbolic functions, we see that with appropriate range restrictions, they all have inverses. Most of the necessary range restrictions can be discerned by close examination of the graphs. The domains and ranges of the inverse hyperbolic functions are summarized in the following table.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?