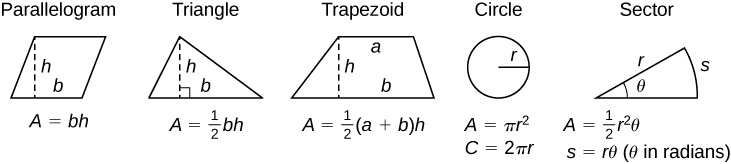
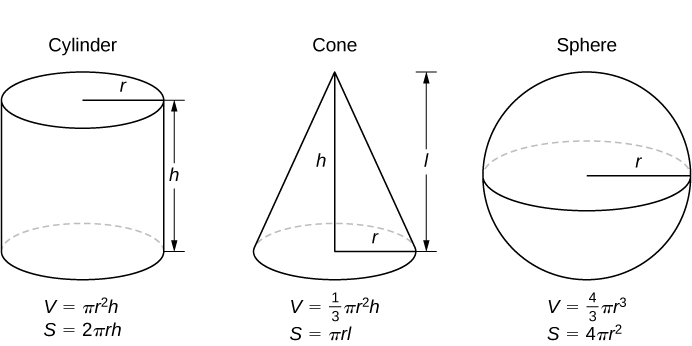
A
=
area
,
V
=
Volume
,
and
S
=
lateral surface area
Laws of exponents
x
m
x
n
=
x
m
+
n
x
m
x
n
=
x
m
−
n
(
x
m
)
n
=
x
m
n
x
−
n
=
1
x
n
(
x
y
)
n
=
x
n
y
n
(
x
y
)
n
=
x
n
y
n
x
1
/
n
=
x
n
x
y
n
=
x
n
y
n
x
y
n
=
x
n
y
n
x
m
/
n
=
x
m
n
=
(
x
n
)
m
Special factorizations
x
2
−
y
2
=
(
x
+
y
)
(
x
−
y
)
x
3
+
y
3
=
(
x
+
y
)
(
x
2
−
x
y
+
y
2
)
x
3
−
y
3
=
(
x
−
y
)
(
x
2
+
x
y
+
y
2
)
If
a
x
2
+
b
x
+
c
=
0
, then
x
=
−
b
±
b
2
−
4
c
a
2
a
.
Binomial theorem
(
a
+
b
)
n
=
a
n
+
(
n
1
)
a
n
−
1
b
+
(
n
2
)
a
n
−
2
b
2
+
⋯
+
(
n
n
−
1
)
a
b
n
−
1
+
b
n
,
where
(
n
k
)
=
n
(
n
−
1
)
(
n
−
2
)
⋯
(
n
−
k
+
1
)
k
(
k
−
1
)
(
k
−
2
)
⋯
3
⋅
2
⋅
1
=
n
!
k
!
(
n
−
k
)
!
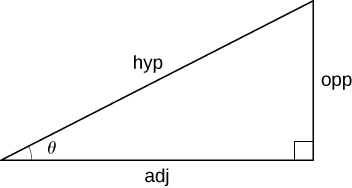
Right-angle trigonometry
sin
θ
=
opp
hyp
csc
θ
=
hyp
opp
cos
θ
=
adj
hyp
sec
θ
=
hyp
adj
tan
θ
=
opp
adj
cot
θ
=
adj
opp
Trigonometric functions of important angles
θ
Radians
sin
θ
cos
θ
tan
θ
0
°
0
0
1
0
30
°
π
/
6
1
/
2
3
/
2
3
/
3
45
°
π
/
4
2
/
2
2
/
2
1
60
°
π
/
3
3
/
2
1
/
2
3
90
°
π
/
2
1
0
—
Fundamental identities
sin
2
θ
+
cos
2
θ
=
1
sin
(
−
θ
)
=
−
sin
θ
1
+
tan
2
θ
=
sec
2
θ
cos
(
−
θ
)
=
cos
θ
1
+
cot
2
θ
=
csc
2
θ
tan
(
−
θ
)
=
−
tan
θ
sin
(
π
2
−
θ
)
=
cos
θ
sin
(
θ
+
2
π
)
=
sin
θ
cos
(
π
2
−
θ
)
=
sin
θ
cos
(
θ
+
2
π
)
=
cos
θ
tan
(
π
2
−
θ
)
=
cot
θ
tan
(
θ
+
π
)
=
tan
θ
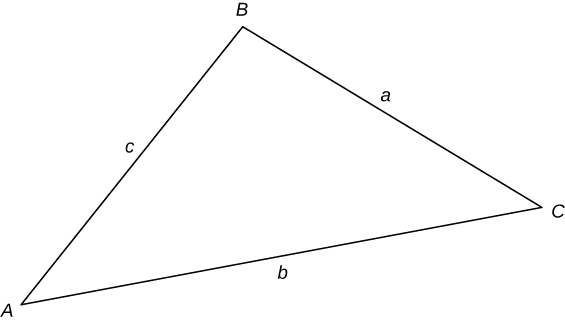
Law of sines
sin
A
a
=
sin
B
b
=
sin
C
c
Law of cosines
a
2
=
b
2
+
c
2
−
2
b
c
cos
A
b
2
=
a
2
+
c
2
−
2
a
c
cos
B
c
2
=
a
2
+
b
2
−
2
a
b
cos
C
sin
(
x
+
y
)
=
sin
x
cos
y
+
cos
x
sin
y
sin
(
x
−
y
)
=
sin
x
cos
y
−
cos
x
sin
y
cos
(
x
+
y
)
=
cos
x
cos
y
−
sin
x
sin
y
cos
(
x
−
y
)
=
cos
x
cos
y
+
sin
x
sin
y
tan
(
x
+
y
)
=
tan
x
+
tan
y
1
−
tan
x
tan
y
tan
(
x
−
y
)
=
tan
x
−
tan
y
1
+
tan
x
tan
y
sin
2
x
=
2
sin
x
cos
x
cos
2
x
=
cos
2
x
−
sin
2
x
=
2
cos
2
x
−
1
=
1
−
2
sin
2
x
tan
2
x
=
2
tan
x
1
−
tan
2
x
sin
2
x
=
1
−
cos
2
x
2
cos
2
x
=
1
+
cos
2
x
2