| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
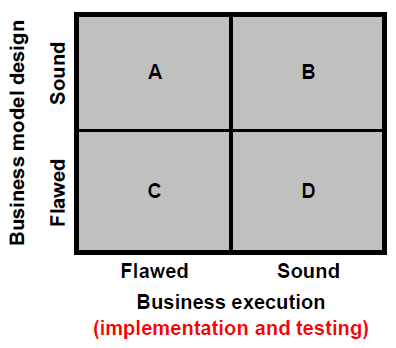
Having established what a business model is, it is important to separate it from the design of a model actually implementing it, i.e. testing it and putting it into practice. The design is best defined as the strategy. If a business model design is not well outlined; the implementation and testing will also fail. Taking a very simple framework from Alexander Osterwalder (Business Model Design Blogpost, June, 2006) shown in [link] , business model design is separated from business model execution, preceded, of course, by business execution implementation and testing. Companies in quadrant “B” with sound business model designs and effective execution are successful companies, and they must focus on staying in that quadrant. Companies in quadrant “C” need to re-examine their business vision and strategy, while companies in quadrant “D” do not have a good design but are effective on its implementation; this latter usually happens with the appearance of disruptive technologies that “shake up” established industries and business models much the way iTunes and the iPod did. It is very common for companies to have a sound business model design but fail to implement and test it properly (quadrant “A”).
If we seek to have a successful test result from a business model it is mandatory to have a clear vision as well as a sound business model design. The rest is a matter of testing and implementations, or “execution” as it is often called. Still, successful execution is sometimes the most difficult task of all.
The focus of the balance of this section will be to review the main issues companies must consider in order to successfully implement and test a business model.
A model must have the following pre-requisites in order to implement and test it:
Usually companies have a tendency to be very optimistic about outcomes when a business model is tested. Companies must be balanced between being aggressive and demanding about the model benefits and be realistic when evaluating outcomes of the test. The main benefits to show when a business model is tested must be outlined around the next three aspects.
Economical: They must reflect tangible economical benefits, such as: cost reductions or sales increases.
Process: They must improve connections between the company’s value chain activities such as production, maintenance, procurement, finance, human resources, etc. so they are better coordinated and decision making processes are more effective and timely.
Practice: They must improve the work flow of how things are done in the company. These improvements can be translated into creating better historical data for a company e.g. real time inventory transactions from a plant warehouse, or complete and accurate recording of a maintenance job performed on a specific item of plant equipment. This creates a more accurate data set, later used as important information to make decisions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Business fundamentals' conversation and receive update notifications?