| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
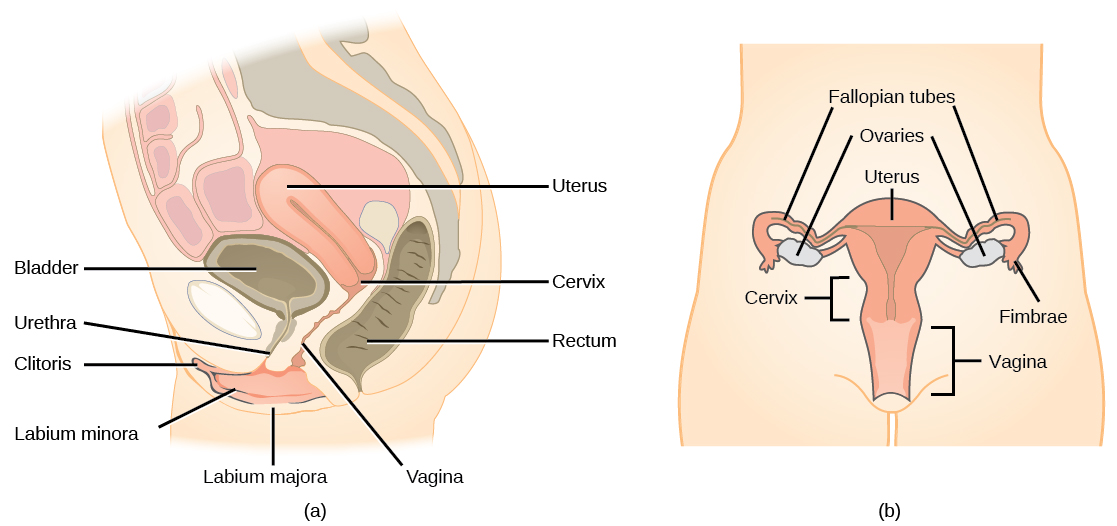
A number of female reproductive structures are exterior to the body. These include the breasts and the vulva, which consists of the mons pubis, clitoris , and labia . ( [link] ; [link] ).
The breasts consist of mammary glands and fat. Each gland consists of 15 to 25 lobes that have ducts that empty at the nipple and that supply the nursing child with nutrient- and antibody-rich milk to aid development and protect the child.
Internal female reproductive structures include ovaries, oviducts, the uterus, and the vagina ( [link] ; [link] ). The pair of ovaries is held in place in the abdominal cavity by a system of ligaments. The outermost layer of the ovary is made up of follicles that surround, nourish, and protect a single egg. During the menstrual period, a batch of follicles develops and prepares their eggs for release. At ovulation, one follicle ruptures and one egg is released. Following ovulation, the follicular tissue that surrounded the ovulated egg stays within the ovary and grows to form a solid mass called the corpus luteum . The corpus luteum secretes additional estrogen and the hormone progesterone that helps maintain the uterine lining during pregnancy. The ovaries also produce hormones, such as estrogen.
The oviducts , or fallopian tubes, extend from the uterus in the lower abdominal cavity to the ovaries, but they are not in contact with the ovaries. The lateral ends of the oviducts flare out into a trumpet-like structure and have a fringe of finger-like projections called fimbrae. When an egg is released at ovulation, the fimbrae help the nonmotile egg enter into the tube. The walls of the oviducts have a ciliated epithelium over smooth muscle. The cilia beat, and the smooth muscle contracts, moving the egg toward the uterus. Fertilization usually takes place within the oviduct and the developing embryo is moved toward the uterus. It usually takes the egg or embryo a week to travel through the oviduct.
Sterilization in women is called a tubal ligation; it is analogous to a vasectomy in males in that the oviducts are severed and sealed, preventing sperm from reaching the egg.
The uterus is a structure about the size of a woman’s fist. The uterus has a thick muscular wall and is lined with an endometrium rich in blood vessels and mucus glands that develop and thicken during the female cycle. Thickening of the endometrium prepares the uterus to receive the fertilized egg or zygote, which will then implant itself in the endometrium. The uterus supports the developing embryo and fetus during gestation. Contractions of the smooth muscle in the uterus aid in forcing the baby through the vagina during labor. If fertilization does not occur, a portion of the lining of the uterus sloughs off during each menstrual period. The endometrium builds up again in preparation for implantation. Part of the uterus, called the cervix, protrudes into the top of the vagina.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?