| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To make two daughter cells, the contents of the nucleus and the cytoplasm must be divided. The mitotic phase is a multistep process during which the duplicated chromosomes are aligned, separated, and moved to opposite poles of the cell, and then the cell is divided into two new identical daughter cells. The first portion of the mitotic phase, mitosis , is composed of five stages, which accomplish nuclear division. The second portion of the mitotic phase, called cytokinesis , is the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells.
Mitosis is divided into a series of phases—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—that result in the division of the cell nucleus ( [link] ).

During prophase , the “first phase,” several events must occur to provide access to the chromosomes in the nucleus. The nuclear envelope starts to break into small vesicles, and the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum fragment and disperse to the periphery of the cell. The nucleolus disappears. The centrosomes begin to move to opposite poles of the cell. The microtubules that form the basis of the mitotic spindle extend between the centrosomes, pushing them farther apart as the microtubule fibers lengthen. The sister chromatids begin to coil more tightly and become visible under a light microscope.
During prometaphase , many processes that were begun in prophase continue to advance and culminate in the formation of a connection between the chromosomes and cytoskeleton. The remnants of the nuclear envelope disappear. The mitotic spindle continues to develop as more microtubules assemble and stretch across the length of the former nuclear area. Chromosomes become more condensed and visually discrete. Each sister chromatid attaches to spindle microtubules at the centromere via a protein complex called the kinetochore .
During metaphase , all of the chromosomes are aligned in a plane called the metaphase plate , or the equatorial plane, midway between the two poles of the cell. The sister chromatids are still tightly attached to each other. At this time, the chromosomes are maximally condensed.
During anaphase , the sister chromatids at the equatorial plane are split apart at the centromere. Each chromatid, now called a chromosome, is pulled rapidly toward the centrosome to which its microtubule was attached. The cell becomes visibly elongated as the non-kinetochore microtubules slide against each other at the metaphase plate where they overlap.
During telophase , all of the events that set up the duplicated chromosomes for mitosis during the first three phases are reversed. The chromosomes reach the opposite poles and begin to decondense (unravel). The mitotic spindles are broken down into monomers that will be used to assemble cytoskeleton components for each daughter cell. Nuclear envelopes form around chromosomes.
Cytokinesis is the second part of the mitotic phase during which cell division is completed by the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells. Although the stages of mitosis are similar for most eukaryotes, the process of cytokinesis is quite different for eukaryotes that have cell walls, such as plant cells.
In cells such as animal cells that lack cell walls, cytokinesis begins following the onset of anaphase. A contractile ring composed of actin filaments forms just inside the plasma membrane at the former metaphase plate. The actin filaments pull the equator of the cell inward, forming a fissure. This fissure, or “crack,” is called the cleavage furrow . The furrow deepens as the actin ring contracts, and eventually the membrane and cell are cleaved in two ( [link] ).
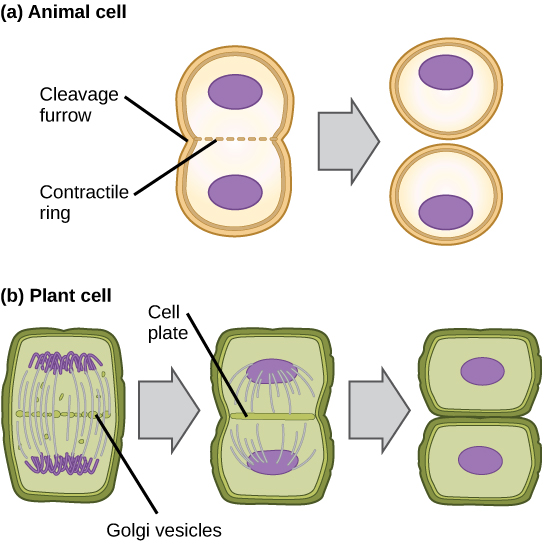
The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Interphase is divided into G 1 , S, and G 2 phases. Mitosis consists of five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis is usually accompanied by cytokinesis, during which the cytoplasmic components of the daughter cells are separated either by an actin ring (animal cells) or by cell plate formation (plant cells).
[link] Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis?
[link] D. The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. The kinetochore breaks apart and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?