| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
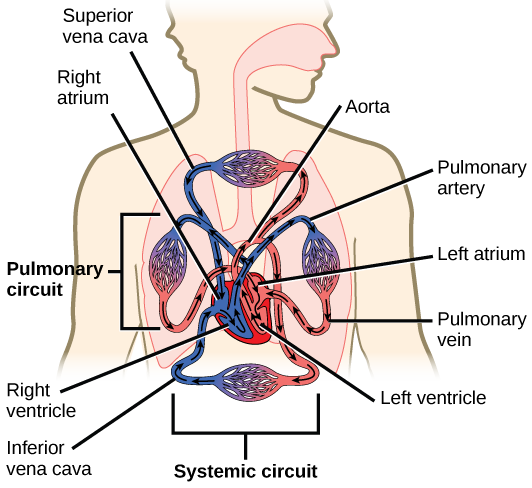
The heart is asymmetrical, with the left side being larger than the right side, correlating with the different sizes of the pulmonary and systemic circuits ( [link] ). In humans, the heart is about the size of a clenched fist; it is divided into four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. There is one atrium and one ventricle on the right side and one atrium and one ventricle on the left side. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation through the major veins: the superior vena cava , which drains blood from the head and from the veins that come from the arms, as well as the inferior vena cava , which drains blood from the veins that come from the lower organs and the legs. This deoxygenated blood then passes to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve , which prevents the backflow of blood. After it is filled, the right ventricle contracts, pumping the blood to the lungs for reoxygenation. The left atrium receives the oxygen-rich blood from the lungs. This blood passes through the bicuspid valve to the left ventricle where the blood is pumped into the aorta . The aorta is the major artery of the body, taking oxygenated blood to the organs and muscles of the body. This pattern of pumping is referred to as double circulation and is found in all mammals. ( [link] ).
Which of the following statements about the circulatory system is false?
The main purpose of the heart is to pump blood through the body; it does so in a repeating sequence called the cardiac cycle. The cardiac cycle is the flow of blood through the heart coordinated by electrochemical signals that cause the heart muscle to contract and relax. In each cardiac cycle, a sequence of contractions pushes out the blood, pumping it through the body; this is followed by a relaxation phase, where the heart fills with blood. These two phases are called the systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation), respectively ( [link] ). The signal for contraction begins at a location on the outside of the right atrium. The electrochemical signal moves from there across the atria causing them to contract. The contraction of the atria forces blood through the valves into the ventricles. Closing of these valves caused by the contraction of the ventricles produces a “lub” sound. The signal has, by this time, passed down the walls of the heart, through a point between the right atrium and right ventricle. The signal then causes the ventricles to contract. The ventricles contract together forcing blood into the aorta and the pulmonary arteries. Closing of the valves to these arteries caused by blood being drawn back toward the heart during ventricular relaxation produces a monosyllabic “dub” sound.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?