| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Eukaryotic cells, in contrast, have intracellular organelles and are much more complex. Recall that in eukaryotic cells, the DNA is contained inside the cell’s nucleus and it is transcribed into mRNA there. The newly synthesized mRNA is then transported out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where ribosomes translate the mRNA into protein. The processes of transcription and translation are physically separated by the nuclear membrane; transcription occurs only within the nucleus, and translation only occurs outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. The regulation of gene expression can occur at all stages of the process ( [link] ). Regulation may occur when the DNA is uncoiled and loosened from nucleosomes to bind transcription factors ( epigenetic level), when the RNA is transcribed (transcriptional level), when RNA is processed and exported to the cytoplasm after it is transcribed ( post-transcriptional level), when the RNA is translated into protein (translational level), or after the protein has been made ( post-translational level).
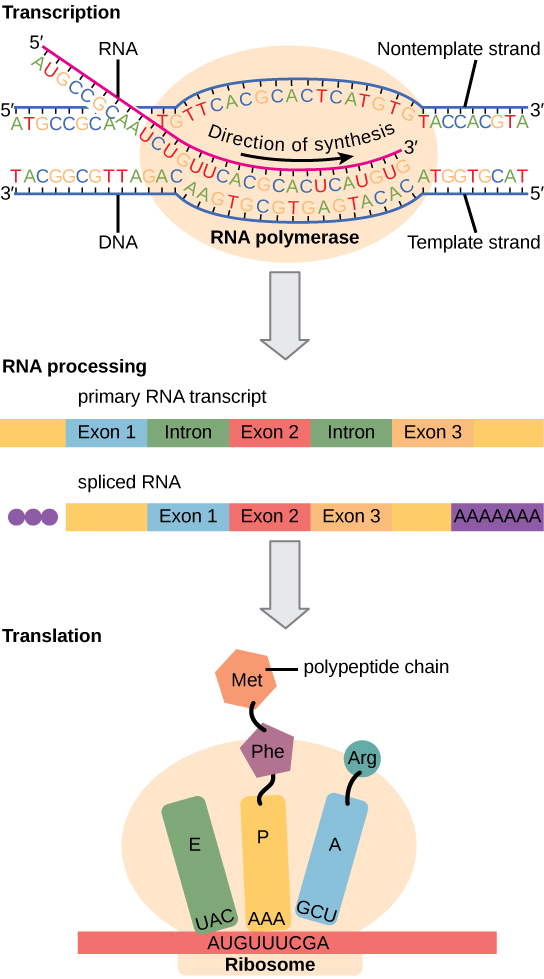
The differences in the regulation of gene expression between prokaryotes and eukaryotes are summarized in [link] .
| Differences in the Regulation of Gene Expression of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Organisms | |
|---|---|
| Prokaryotic organisms | Eukaryotic organisms |
| Lack nucleus | Contain nucleus |
| RNA transcription and protein translation occur almost simultaneously |
|
| Gene expression is regulated primarily at the transcriptional level | Gene expression is regulated at many levels (epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational) |
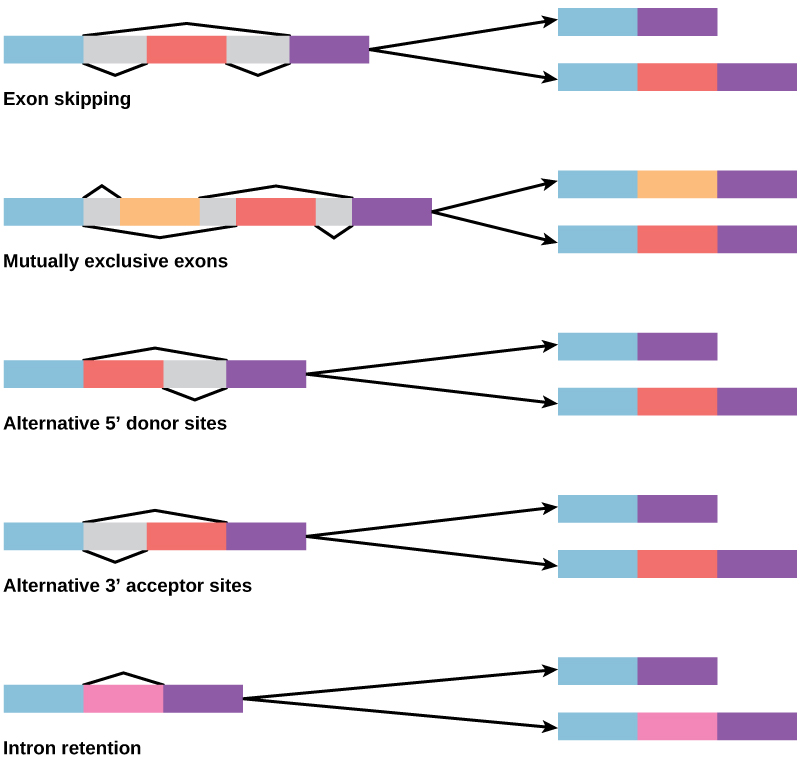
How could alternative splicing evolve? Introns have a beginning and ending recognition sequence, and it is easy to imagine the failure of the splicing mechanism to identify the end of an intron and find the end of the next intron, thus removing two introns and the intervening exon. In fact, there are mechanisms in place to prevent such exon skipping, but mutations are likely to lead to their failure. Such “mistakes” would more than likely produce a nonfunctional protein. Indeed, the cause of many genetic diseases is alternative splicing rather than mutations in a sequence. However, alternative splicing would create a protein variant without the loss of the original protein, opening up possibilities for adaptation of the new variant to new functions. Gene duplication has played an important role in the evolution of new functions in a similar way—by providing genes that may evolve without eliminating the original functional protein.
While all somatic cells within an organism contain the same DNA, not all cells within that organism express the same proteins. Prokaryotic organisms express the entire DNA they encode in every cell, but not necessarily all at the same time. Proteins are expressed only when they are needed. Eukaryotic organisms express a subset of the DNA that is encoded in any given cell. In each cell type, the type and amount of protein is regulated by controlling gene expression. To express a protein, the DNA is first transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins. In prokaryotic cells, these processes occur almost simultaneously. In eukaryotic cells, transcription occurs in the nucleus and is separate from the translation that occurs in the cytoplasm. Gene expression in prokaryotes is regulated only at the transcriptional level, whereas in eukaryotic cells, gene expression is regulated at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?