| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
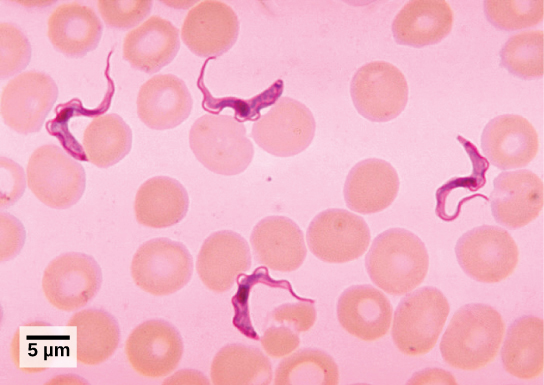
T . brucei , the parasite that is responsible for African sleeping sickness, confounds the human immune system by changing its thick layer of surface glycoproteins with each infectious cycle ( [link] ). The glycoproteins are identified by the immune system as foreign matter, and a specific antibody defense is mounted against the parasite. However, T . brucei has thousands of possible antigens, and with each subsequent generation, the protist switches to a glycoprotein coating with a different molecular structure. In this way, T . brucei is capable of replicating continuously without the immune system ever succeeding in clearing the parasite. Without treatment, African sleeping sickness leads invariably to death because of damage it does to the nervous system. During epidemic periods, mortality from the disease can be high. Greater surveillance and control measures have led to a reduction in reported cases; some of the lowest numbers reported in 50 years (fewer than 10,000 cases in all of sub-Saharan Africa) have happened since 2009.
In Latin America, another species in the genus, T . cruzi , is responsible for Chagas disease. T . cruzi infections are mainly caused by a blood-sucking bug. The parasite inhabits heart and digestive system tissues in the chronic phase of infection, leading to malnutrition and heart failure caused by abnormal heart rhythms. An estimated 10 million people are infected with Chagas disease, which caused 10,000 deaths in 2008.
This movie discusses the pathogenesis of Trypanosoma brucei , the causative agent of African sleeping sickness.
Protist parasites of terrestrial plants include agents that destroy food crops. The oomycete Plasmopara viticola parasitizes grape plants, causing a disease called downy mildew ( [link] a ). Grape plants infected with P . viticola appear stunted and have discolored withered leaves. The spread of downy mildew caused the near collapse of the French wine industry in the nineteenth century.
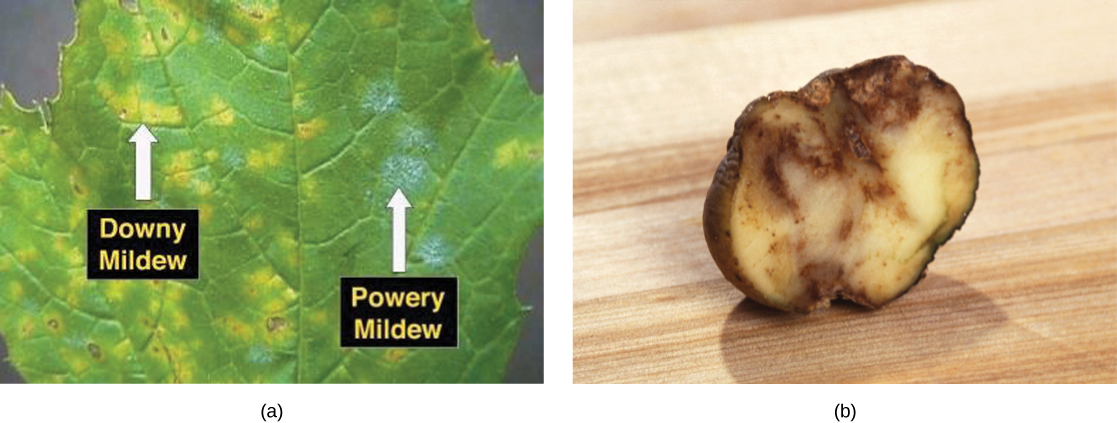

Phytophthora infestans is an oomycete responsible for potato late blight, which causes potato stalks and stems to decay into black slime ( [link] b ). Widespread potato blight caused by P . infestans precipitated the well-known Irish potato famine in the nineteenth century that claimed the lives of approximately 1 million people and led to the emigration from Ireland of at least 1 million more. Late blight continues to plague potato crops in certain parts of the United States and Russia, wiping out as much as 70 percent of crops when no pesticides are applied.
Protists play critically important ecological roles as producers particularly in the world’s oceans. They are equally important on the other end of food webs as decomposers.
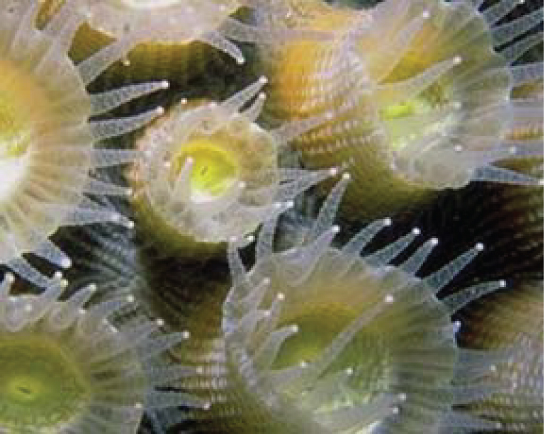
Protists are essential sources of nutrition for many other organisms. In some cases, as in plankton, protists are consumed directly. Alternatively, photosynthetic protists serve as producers of nutrition for other organisms by carbon fixation. For instance, photosynthetic dinoflagellates called zooxanthellae pass on most of their energy to the coral polyps that house them ( [link] ). In this mutually beneficial relationship, the polyps provide a protective environment and nutrients for the zooxanthellae. The polyps secrete the calcium carbonate that builds coral reefs. Without dinoflagellate symbionts, corals lose algal pigments in a process called coral bleaching, and they eventually die. This explains why reef-building corals do not reside in waters deeper than 20 meters: Not enough light reaches those depths for dinoflagellates to photosynthesize.

Protists themselves and their products of photosynthesis are essential—directly or indirectly—to the survival of organisms ranging from bacteria to mammals. As primary producers, protists feed a large proportion of the world’s aquatic species. (On land, terrestrial plants serve as primary producers.) In fact, approximately one-quarter of the world’s photosynthesis is conducted by protists, particularly dinoflagellates, diatoms, and multicellular algae.
Protists do not create food sources only for sea-dwelling organisms. For instance, certain anaerobic species exist in the digestive tracts of termites and wood-eating cockroaches, where they contribute to digesting cellulose ingested by these insects as they bore through wood. The actual enzyme used to digest the cellulose is actually produced by bacteria living within the protist cells. The termite provides the food source to the protist and its bacteria, and the protist and bacteria provide nutrients to the termite by breaking down the cellulose.
Many fungus-like protists are saprobes , organisms that feed on dead organisms or the waste matter produced by organisms (saprophyte is an equivalent term), and are specialized to absorb nutrients from nonliving organic matter. For instance, many types of oomycetes grow on dead animals or algae. Saprobic protists have the essential function of returning inorganic nutrients to the soil and water. This process allows for new plant growth, which in turn generates sustenance for other organisms along the food chain. Indeed, without saprobic species, such as protists, fungi, and bacteria, life would cease to exist as all organic carbon became “tied up” in dead organisms.
Protists are extremely diverse in terms of biological and ecological characteristics due in large part to the fact that they are an artificial assemblage of phylogenetically unrelated groups. Protists display highly varied cell structures, several types of reproductive strategies, virtually every possible type of nutrition, and varied habitats. Most single-celled protists are motile, but these organisms use diverse structures for transportation.
The process of classifying protists into meaningful groups is ongoing, but genetic data in the past 20 years have clarified many relationships that were previously unclear or mistaken. The majority view at present is to order all eukaryotes into six supergroups. The goal of this classification scheme is to create clusters of species that all are derived from a common ancestor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?