| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The replacing of the electron enables chlorophyll to respond to another photon. The oxygen molecules produced as byproducts find their way to the surrounding environment. The hydrogen ions play critical roles in the remainder of the light-dependent reactions.
Keep in mind that the purpose of the light-dependent reactions is to convert solar energy into chemical carriers that will be used in the Calvin cycle. In eukaryotes and some prokaryotes, two photosystems exist. The first is called photosystem II, which was named for the order of its discovery rather than for the order of the function.
After the photon hits, photosystem II transfers the free electron to the first in a series of proteins inside the thylakoid membrane called the electron transport chain. As the electron passes along these proteins, energy from the electron fuels membrane pumps that actively move hydrogen ions against their concentration gradient from the stroma into the thylakoid space. This is quite analogous to the process that occurs in the mitochondrion in which an electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial stroma across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, creating an electrochemical gradient. After the energy is used, the electron is accepted by a pigment molecule in the next photosystem, which is called photosystem I ( [link] ).
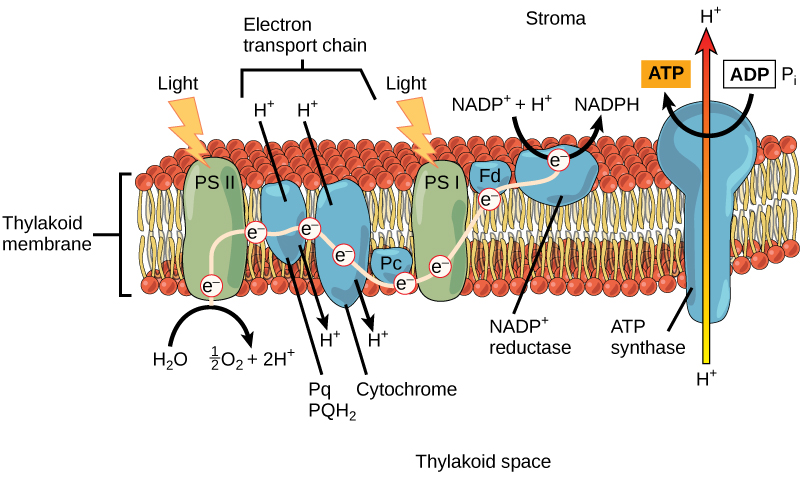
In the light-dependent reactions, energy absorbed by sunlight is stored by two types of energy-carrier molecules: ATP and NADPH. The energy that these molecules carry is stored in a bond that holds a single atom to the molecule. For ATP, it is a phosphate atom, and for NADPH, it is a hydrogen atom. Recall that NADH was a similar molecule that carried energy in the mitochondrion from the citric acid cycle to the electron transport chain. When these molecules release energy into the Calvin cycle, they each lose atoms to become the lower-energy molecules ADP and NADP + .
The buildup of hydrogen ions in the thylakoid space forms an electrochemical gradient because of the difference in the concentration of protons (H + ) and the difference in the charge across the membrane that they create. This potential energy is harvested and stored as chemical energy in ATP through chemiosmosis, the movement of hydrogen ions down their electrochemical gradient through the transmembrane enzyme ATP synthase, just as in the mitochondrion.
The hydrogen ions are allowed to pass through the thylakoid membrane through an embedded protein complex called ATP synthase. This same protein generated ATP from ADP in the mitochondrion. The energy generated by the hydrogen ion stream allows ATP synthase to attach a third phosphate to ADP, which forms a molecule of ATP in a process called photophosphorylation. The flow of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase is called chemiosmosis, because the ions move from an area of high to low concentration through a semi-permeable structure.
The remaining function of the light-dependent reaction is to generate the other energy-carrier molecule, NADPH. As the electron from the electron transport chain arrives at photosystem I, it is re-energized with another photon captured by chlorophyll. The energy from this electron drives the formation of NADPH from NADP + and a hydrogen ion (H + ). Now that the solar energy is stored in energy carriers, it can be used to make a sugar molecule.
In the first part of photosynthesis, the light-dependent reaction, pigment molecules absorb energy from sunlight. The most common and abundant pigment is chlorophyll a . A photon strikes photosystem II to initiate photosynthesis. Energy travels through the electron transport chain, which pumps hydrogen ions into the thylakoid space. This forms an electrochemical gradient. The ions flow through ATP synthase from the thylakoid space into the stroma in a process called chemiosmosis to form molecules of ATP, which are used for the formation of sugar molecules in the second stage of photosynthesis. Photosystem I absorbs a second photon, which results in the formation of an NADPH molecule, another energy carrier for the Calvin cycle reactions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?