| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
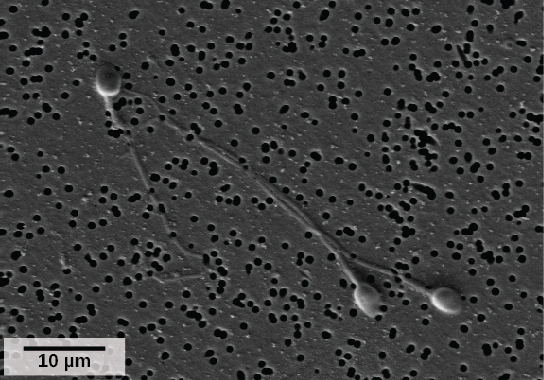
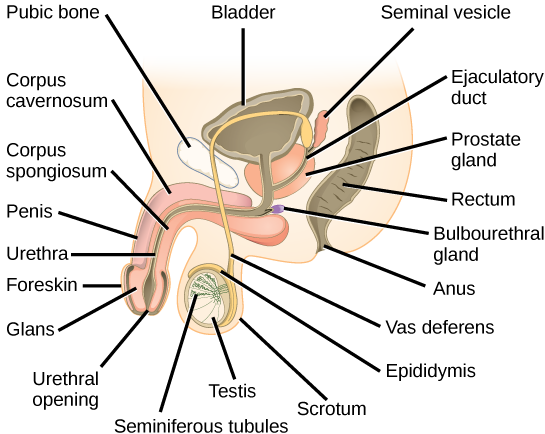
Sperm form in the walls of seminiferous tubules that are coiled inside the testes ( [link] ; [link] ). The walls of the seminiferous tubules are made up of the developing sperm cells, with the least developed sperm at the periphery of the tubule and the fully developed sperm next to the lumen. The sperm cells are associated with Sertoli cells that nourish and promote the development of the sperm. Other cells present between the walls of the tubules are the interstitial cells of Leydig , which produce testosterone once the male reaches adolescence.
When the sperm have developed flagella they leave the seminiferous tubules and enter the epididymis ( [link] ; [link] ). This structure lies along the top and posterior of the testes and is the site of sperm maturation. The sperm leave the epididymis and enter the vas deferens, which carries the sperm behind the bladder, and forms the ejaculatory duct with the duct from the seminal vesicles. During a vasectomy, a section of the vas deferens is removed, preventing sperm (but not the secretions of the accessory glands) from being passed out of the body during ejaculation and preventing fertilization.
The bulk of the semen comes from the accessory glands associated with the male reproductive system. These are the seminal vesicles , the prostate gland , and the bulbourethral gland ( [link] ; [link] ). The secretions from the accessory glands provide important compounds for the sperm including nutrients, electrolytes, and pH buffering. There are also coagulation factors that affect sperm delivery and motility.
Which of the following statements about the male reproductive system is false?
| Male Reproductive Anatomy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Organ | Location | Function |
| Scrotum | External | Supports testes and regulates their temperature |
| Penis | External | Delivers urine, copulating organ |
| Testes | Internal | Produce sperm and male hormones |
| Seminal Vesicles | Internal | Contribute to semen production |
| Prostate Gland | Internal | Contributes to semen production |
| Bulbourethtral Glands | Internal | Neutralize urine in urethra |
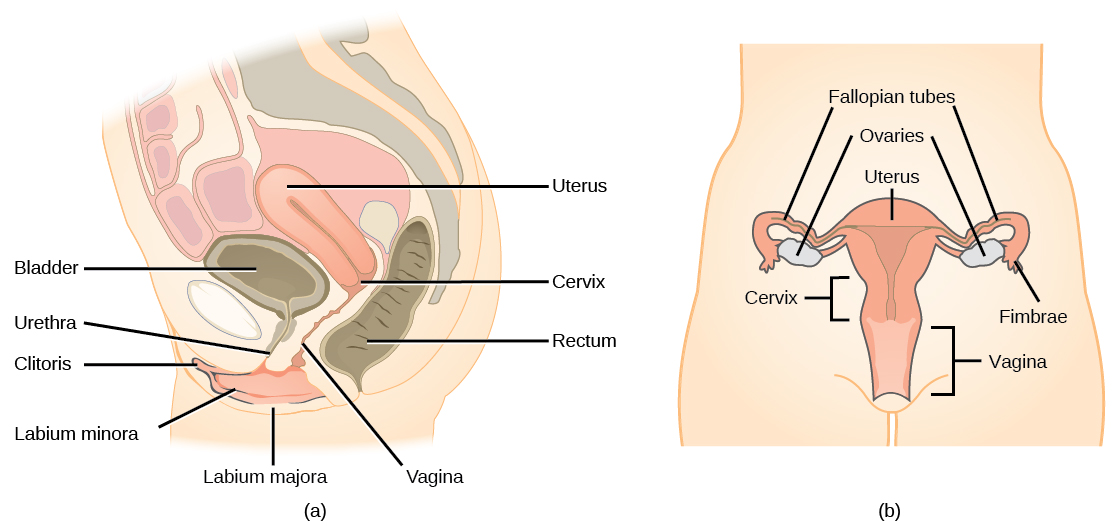
A number of female reproductive structures are exterior to the body. These include the breasts and the vulva, which consists of the mons pubis, clitoris , labia majora , labia minora , and the vestibular glands ( [link] ; [link] ).
The breasts consist of mammary glands and fat. Each gland consists of 15 to 25 lobes that have ducts that empty at the nipple and that supply the nursing child with nutrient- and antibody-rich milk to aid development and protect the child.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?