| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. For example, think about someone opening a bottle of perfume in a room filled with people. The perfume is at its highest concentration in the bottle and is at its lowest at the edges of the room. The perfume vapor will diffuse, or spread away, from the bottle, and gradually, more and more people will smell the perfume as it spreads. Materials move within the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion ( [link] ). Diffusion expends no energy. Rather the different concentrations of materials in different areas are a form of potential energy, and diffusion is the dissipation of that potential energy as materials move down their concentration gradients, from high to low.
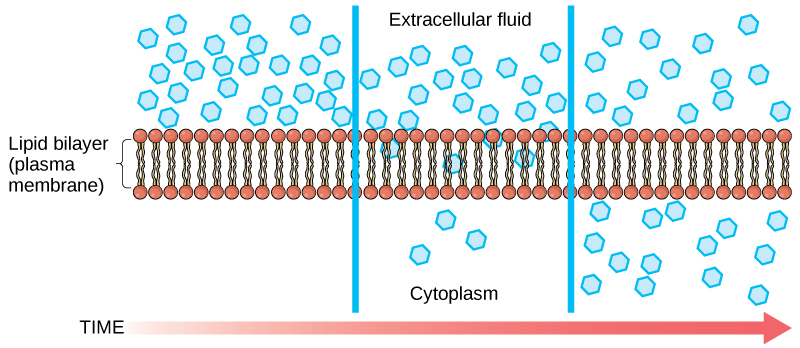
Each separate substance in a medium, such as the extracellular fluid, has its own concentration gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other materials. Additionally, each substance will diffuse according to that gradient.
Several factors affect the rate of diffusion.
For an animation of the diffusion process in action, view this short video on cell membrane transport.
In facilitated transport , also called facilitated diffusion, material moves across the plasma membrane with the assistance of transmembrane proteins down a concentration gradient (from high to low concentration) without the expenditure of cellular energy. However, the substances that undergo facilitated transport would otherwise not diffuse easily or quickly across the plasma membrane. The solution to moving polar substances and other substances across the plasma membrane rests in the proteins that span its surface. The material being transported is first attached to protein or glycoprotein receptors on the exterior surface of the plasma membrane. This allows the material that is needed by the cell to be removed from the extracellular fluid. The substances are then passed to specific integral proteins that facilitate their passage, because they form channels or pores that allow certain substances to pass through the membrane. The integral proteins involved in facilitated transport are collectively referred to as transport proteins, and they function as either channels for the material or carriers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?