| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Population growth is regulated in a variety of ways. These are grouped into density-dependent factors, in which the density of the population affects growth rate and mortality, and density-independent factors, which cause mortality in a population regardless of population density. Wildlife biologists, in particular, want to understand both types because this helps them manage populations and prevent extinction or overpopulation.
Most density-dependent factors are biological in nature and include predation, inter- and intraspecific competition, and parasites. Usually, the denser a population is, the greater its mortality rate. For example, during intra- and interspecific competition, the reproductive rates of the species will usually be lower, reducing their populations’ rate of growth. In addition, low prey density increases the mortality of its predator because it has more difficulty locating its food source. Also, when the population is denser, diseases spread more rapidly among the members of the population, which affect the mortality rate.
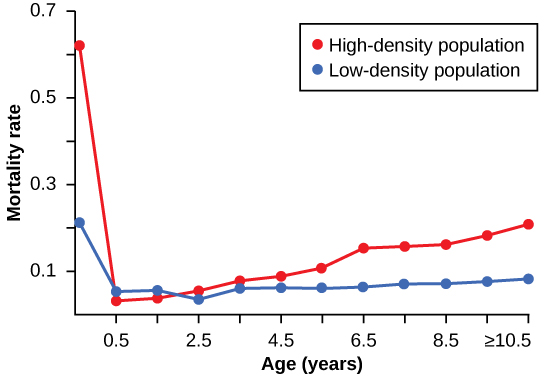
Density dependent regulation was studied in a natural experiment with wild donkey populations on two sites in Australia. David Choquenot, “Density-Dependent Growth, Body Condition, and Demography in Feral Donkeys: Testing the Food Hypothesis,” Ecology 72, no. 3 (June 1991):805–813. On one site the population was reduced by a population control program; the population on the other site received no interference. The high-density plot was twice as dense as the low-density plot. From 1986 to 1987 the high-density plot saw no change in donkey density, while the low-density plot saw an increase in donkey density. The difference in the growth rates of the two populations was caused by mortality, not by a difference in birth rates. The researchers found that numbers of offspring birthed by each mother was unaffected by density. Growth rates in the two populations were different mostly because of juvenile mortality caused by the mother’s malnutrition due to scarce high-quality food in the dense population. [link] shows the difference in age-specific mortalities in the two populations.
Many factors that are typically physical in nature cause mortality of a population regardless of its density. These factors include weather, natural disasters, and pollution. An individual deer will be killed in a forest fire regardless of how many deer happen to be in that area. Its chances of survival are the same whether the population density is high or low. The same holds true for cold winter weather.
In real-life situations, population regulation is very complicated and density-dependent and independent factors can interact. A dense population that suffers mortality from a density-independent cause will be able to recover differently than a sparse population. For example, a population of deer affected by a harsh winter will recover faster if there are more deer remaining to reproduce.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?