| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
How do scientists construct phylogenetic trees? Presently, the most accepted method for constructing phylogenetic trees is a method called cladistics . This method sorts organisms into clades , groups of organisms that are most closely related to each other and the ancestor from which they descended. For example, in [link] , all of the organisms in the shaded region evolved from a single ancestor that had amniotic eggs. Consequently, all of these organisms also have amniotic eggs and make a single clade, also called a monophyletic group . Clades must include the ancestral species and all of the descendants from a branch point.
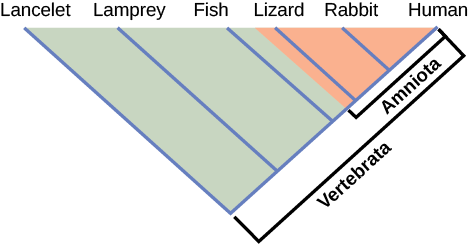
Which animals in this figure belong to a clade that includes animals with hair? Which evolved first: hair or the amniotic egg?
Clades can vary in size depending on which branch point is being referenced. The important factor is that all of the organisms in the clade or monophyletic group stem from a single point on the tree. This can be remembered because monophyletic breaks down into “mono,” meaning one, and “phyletic,” meaning evolutionary relationship.
Cladistics rests on three assumptions. The first is that living things are related by descent from a common ancestor, which is a general assumption of evolution. The second is that speciation occurs by splits of one species into two, never more than two at a time, and essentially at one point in time. This is somewhat controversial, but is acceptable to most biologists as a simplification. The third assumption is that traits change enough over time to be considered to be in a different state .It is also assumed that one can identify the actual direction of change for a state. In other words, we assume that an amniotic egg is a later character state than non-amniotic eggs. This is called the polarity of the character change. We know this by reference to a group outside the clade: for example, insects have non-amniotic eggs; therefore, this is the older or ancestral character state. Cladistics compares ingroups and outgroups. An ingroup (lizard, rabbit and human in our example) is the group of taxa being analyzed. An outgroup (lancelet, lamprey and fish in our example) is a species or group of species that diverged before the lineage containing the group(s) of interest. By comparing ingroup members to each other and to the outgroup members, we can determine which characteristics are evolutionary modifications determining the branch points of the ingroup’s phylogeny.
If a characteristic is found in all of the members of a group, it is a shared ancestral character because there has been no change in the trait during the descent of each of the members of the clade. Although these traits appear interesting because they unify the clade, in cladistics they are considered not helpful when we are trying to determine the relationships of the members of the clade because every member is the same. In contrast, consider the amniotic egg characteristic of [link] . Only some of the organisms have this trait, and to those that do, it is called a shared derived character because this trait changed at some point during descent. This character does tell us about the relationships among the members of the clade; it tells us that lizards, rabbits, and humans group more closely together than any of these organisms do with fish, lampreys, and lancelets.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?