| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
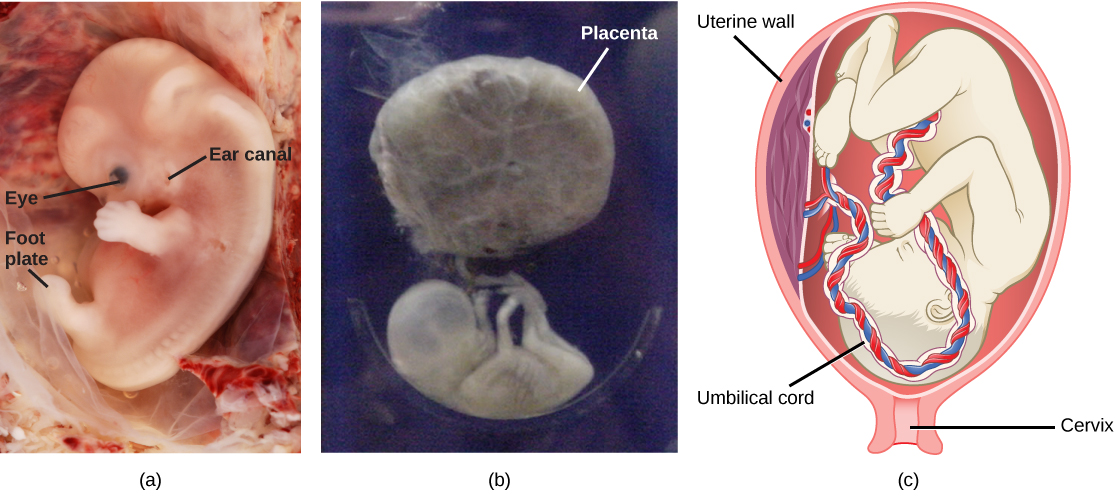
During the second trimester, the fetus grows to about 30 cm (about 12 inches) ( [link] b ). It becomes active and the mother usually feels the first movements. All organs and structures continue to develop. The placenta has taken over the functions of nutrition and waste elimination and the production of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum, which has degenerated. The placenta will continue functioning up through the delivery of the baby. During the third trimester, the fetus grows to 3 to 4 kg (6.5–8.5 lbs.) and about 50 cm (19–20 inches) long ( [link] c ). This is the period of the most rapid growth during the pregnancy as all organ systems continue to grow and develop.
Visit this website to see the stages of human fetal development.
Labor is the muscular contractions to expel the fetus and placenta from the uterus. Toward the end of the third trimester, estrogen causes receptors on the uterine wall to develop and bind the hormone oxytocin. At this time, the baby reorients, facing forward and down with the back or crown of the head engaging the cervix (uterine opening). This causes the cervix to stretch and nerve impulses are sent to the hypothalamus, which signals the release of oxytocin from the posterior pituitary. Oxytocin causes smooth muscle in the uterine wall to contract. At the same time, the placenta releases prostaglandins into the uterus, increasing the contractions. A positive feedback relay occurs between the uterus, hypothalamus, and the posterior pituitary to assure an adequate supply of oxytocin. As more smooth muscle cells are recruited, the contractions increase in intensity and force.
There are three stages to labor. During stage one, the cervix thins and dilates. This is necessary for the baby and placenta to be expelled during birth. The cervix will eventually dilate to about 10 cm. During stage two, the baby is expelled from the uterus. The uterus contracts and the mother pushes as she compresses her abdominal muscles to aid the delivery. The last stage is the passage of the placenta after the baby has been born and the organ has completely disengaged from the uterine wall. If labor should stop before stage two is reached, synthetic oxytocin, known as Pitocin, can be administered to restart and maintain labor.
The reproductive structures that evolved in land animals allow males and females to mate, fertilize internally, and support the growth and development of offspring. Gametogenesis, the production of sperm (spermatogenesis) and eggs (oogenesis), takes place through the process of meiosis.
The male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by hormones released from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary and hormones from reproductive tissues and organs. The hypothalamus monitors the need for FSH and LH production and release from the anterior pituitary. FSH and LH affect reproductive structures to cause the formation of sperm and the preparation of eggs for release and possible fertilization. In the male, FSH and LH stimulate Sertoli cells and interstitial cells of Leydig in the testes to facilitate sperm production. The Leydig cells produce testosterone, which also is responsible for the secondary sexual characteristics of males. In females, FSH and LH cause estrogen and progesterone to be produced. They regulate the female reproductive cycle, which is divided into the ovarian cycle and the menstrual cycle.
Human pregnancy begins with fertilization of an egg and proceeds through the three trimesters of gestation. The first trimester lays down the basic structures of the body, including the limb buds, heart, eyes, and the liver. The second trimester continues the development of all of the organs and systems. The third trimester exhibits the greatest growth of the fetus and culminates in labor and delivery. The labor process has three stages (contractions, delivery of the fetus, and expulsion of the placenta), each propelled by hormones.
[link] Which of the following statements about the male reproductive system is false?
[link] D
[link] Which of the following statements about hormone regulation of the female reproductive cycle is false?
[link] C

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?