| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The continuity of life from one cell to another has its foundation in the reproduction of cells by way of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events in the life of a cell from the division of a single parent cell to produce two new daughter cells, to the subsequent division of those daughter cells. The mechanisms involved in the cell cycle are highly conserved across eukaryotes. Organisms as diverse as protists, plants, and animals employ similar steps.
Before discussing the steps a cell undertakes to replicate, a deeper understanding of the structure and function of a cell’s genetic information is necessary. A cell’s complete complement of DNA is called its genome . In prokaryotes, the genome is composed of a single, double-stranded DNA molecule in the form of a loop or circle. The region in the cell containing this genetic material is called a nucleoid. Some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that are not essential for normal growth.
In eukaryotes, the genome comprises several double-stranded, linear DNA molecules ( [link] ) bound with proteins to form complexes called chromosomes. Each species of eukaryote has a characteristic number of chromosomes in the nuclei of its cells. Human body cells (somatic cells) have 46 chromosomes. A somatic cell contains two matched sets of chromosomes, a configuration known as diploid . The letter n is used to represent a single set of chromosomes; therefore a diploid organism is designated 2 n . Human cells that contain one set of 23 chromosomes are called gametes , or sex cells; these eggs and sperm are designated n , or haploid .
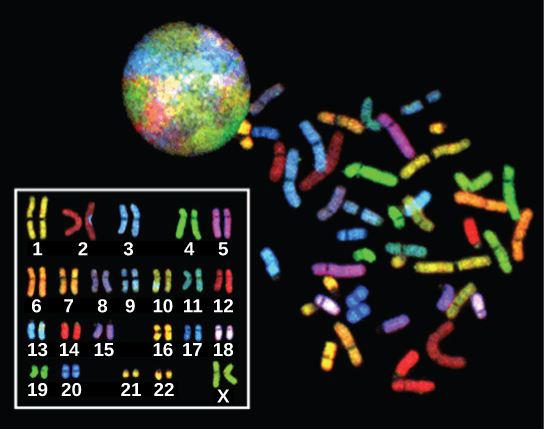
The matched pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism are called homologous chromosomes . Homologous chromosomes are the same length and have specific nucleotide segments called genes in exactly the same location, or locus . Genes, the functional units of chromosomes, determine specific characteristics by coding for specific proteins. Traits are the different forms of a characteristic. For example, the shape of earlobes is a characteristic with traits of free or attached.
Each copy of the homologous pair of chromosomes originates from a different parent; therefore, the copies of each of the genes themselves may not be identical. The variation of individuals within a species is caused by the specific combination of the genes inherited from both parents. For example, there are three possible gene sequences on the human chromosome that codes for blood type: sequence A, sequence B, and sequence O. Because all diploid human cells have two copies of the chromosome that determines blood type, the blood type (the trait) is determined by which two versions of the marker gene are inherited. It is possible to have two copies of the same gene sequence, one on each homologous chromosome (for example, AA, BB, or OO), or two different sequences, such as AB.
Minor variations in traits such as those for blood type, eye color, and height contribute to the natural variation found within a species. The sex chromosomes, X and Y, are the single exception to the rule of homologous chromosomes; other than a small amount of homology that is necessary to reliably produce gametes, the genes found on the X and Y chromosomes are not the same.
Prokaryotes have a single loop chromosome, whereas eukaryotes have multiple, linear chromosomes surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes consisting of two sets of 22 homologous chromosomes and a pair of nonhomologous sex chromosomes. This is the 2 n, or diploid, state. Human gametes have 23 chromosomes or one complete set of chromosomes. This is the n, or haploid, state. Genes are segments of DNA that code for a specific protein or RNA molecule. An organism’s traits are determined in large part by the genes inherited from each parent, but also by the environment that they experience. Genes are expressed as characteristics of the organism and each characteristic may have different variants called traits that are caused by differences in the DNA sequence for a gene.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?