| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
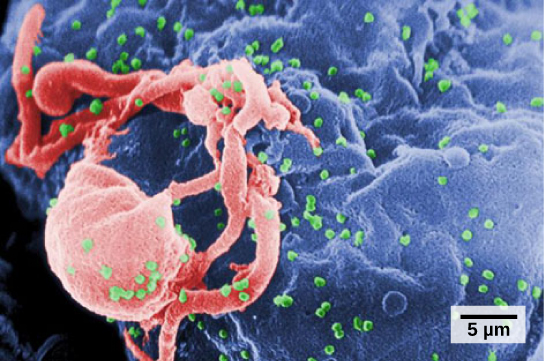
A functioning immune system is essential for survival, but even the sophisticated cellular and molecular defenses of the mammalian immune response can be defeated by pathogens at virtually every step. In the competition between immune protection and pathogen evasion, pathogens have the advantage of more rapid evolution because of their shorter generation time, large population sizes and often higher mutation rates. Thus pathogens have evolved a diverse array of immune escape mechanisms. For instance, Streptococcus pneumoniae (the bacterium that causes pneumonia and meningitis) surrounds itself with a capsule that inhibits phagocytes from engulfing it and displaying antigens to the adaptive immune system. Staphylococcus aureus (the bacterium that can cause skin infections, abscesses, and meningitis) synthesizes a toxin called leukocidin that kills phagocytes after they engulf the bacterium. Other pathogens can also hinder the adaptive immune system. HIV infects T H cells using their CD4 surface molecules, gradually depleting the number of T H cells in the body ( [link] ); this inhibits the adaptive immune system’s capacity to generate sufficient responses to infection or tumors. As a result, HIV-infected individuals often suffer from infections that would not cause illness in people with healthy immune systems but which can cause devastating illness to immune-compromised individuals.
Inappropriate responses of immune cells and molecules themselves can also disrupt the proper functioning of the entire system, leading to host-cell damage that can become fatal.
Immunodeficiency is a failure, insufficiency, or delay in the response of the immune system, which may be acquired or inherited. Immunodeficiency can allow pathogens or tumor cells to gain a foothold and replicate or proliferate to high enough levels so that the immune system becomes overwhelmed. Immunodeficiency can be acquired as a result of infection with certain pathogens that attack the cells of the immune system itself (such as HIV), chemical exposure (including certain medical treatments such as chemotherapy), malnutrition, or extreme stress. For instance, radiation exposure can destroy populations of lymphocytes and elevate an individual’s susceptibility to infections and cancer. Rarely, primary immunodeficiencies that are present from birth may also occur. For example, severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) is a condition in which children are born without functioning B or T cells.
A maladaptive immune response toward harmless foreign substances or self-antigens that occur after tissue sensitization is termed a hypersensitivity . Types of hypersensitivities include immediate, delayed, and autoimmune. A large proportion of the human population is affected by one or more types of hypersensitivity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?