| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The system can be divided into two types of defense systems: the innate immune system, which is nonspecific toward a particular kind of pathogen, and the adaptive immune system, which is specific ( [link] ). Innate immunity is not caused by an infection or vaccination and depends initially on physical and chemical barriers that work on all pathogens, sometimes called the first line of defense. The second line of defense of the innate system includes chemical signals that produce inflammation and fever responses as well as mobilizing protective cells and other chemical defenses. The adaptive immune system mounts a highly specific response to substances and organisms that do not belong in the body. The adaptive system takes longer to respond and has a memory system that allows it to respond with greater intensity should the body reencounter a pathogen even years later.
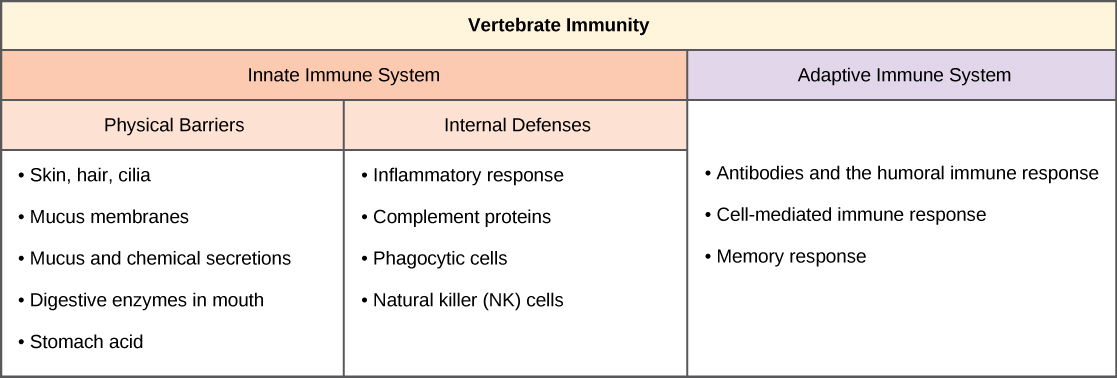
The body has significant physical barriers to potential pathogens. The skin contains the protein keratin, which resists physical entry into cells. Other body surfaces, particularly those associated with body openings, are protected by the mucous membranes. The sticky mucus provides a physical trap for pathogens, preventing their movement deeper into the body. The openings of the body, such as the nose and ears, are protected by hairs that catch pathogens, and the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract have cilia that constantly move pathogens trapped in the mucus coat up to the mouth.
The skin and mucous membranes also create a chemical environment that is hostile to many microorganisms. The surface of the skin is acidic, which prevents bacterial growth. Saliva, mucus, and the tears of the eye contain an enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls. The stomach secretions create a highly acidic environment, which kills many pathogens entering the digestive system.
Finally, the surface of the body and the lower digestive system have a community of microorganisms such as bacteria, archaea, and fungi that coexist without harming the body. There is evidence that these organisms are highly beneficial to their host, combating disease-causing organisms and outcompeting them for nutritional resources provided by the host body. Despite these defenses, pathogens may enter the body through skin abrasions or punctures, or by collecting on mucosal surfaces in large numbers that overcome the protections of mucus or cilia.
When pathogens enter the body, the innate immune system responds with a variety of internal defenses. These include the inflammatory response, phagocytosis, natural killer cells, and the complement system. White blood cells in the blood and lymph recognize pathogens as foreign to the body. A white blood cell is larger than a red blood cell, is nucleated, and is typically able to move using amoeboid locomotion. Because they can move on their own, white blood cells can leave the blood to go to infected tissues. For example, a monocyte is a type of white blood cell that circulates in the blood and lymph and develops into a macrophage after it moves into infected tissue. A macrophage is a large cell that engulfs foreign particles and pathogens. Mast cells are produced in the same way as white blood cells, but unlike circulating white blood cells, mast cells take up residence in connective tissues and especially mucosal tissues. They are responsible for releasing chemicals in response to physical injury. They also play a role in the allergic response, which will be discussed later in the chapter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?