| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
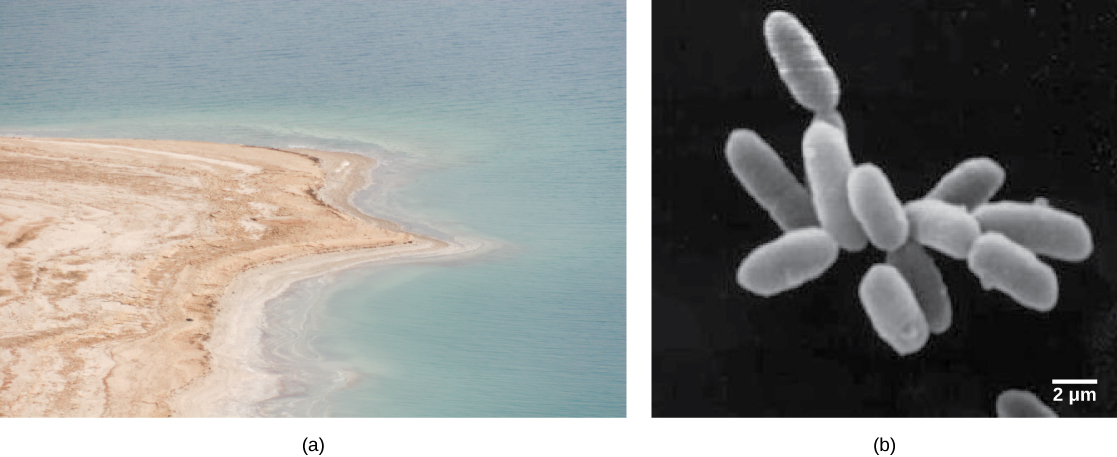
What sort of prokaryotes do we find in the Dead Sea? The extremely salt-tolerant bacterial mats include Halobacterium , Haloferax volcanii (which is found in other locations, not only the Dead Sea), Halorubrum sodomense , and Halobaculum gomorrense , and the archaea Haloarcula marismortui , among others.
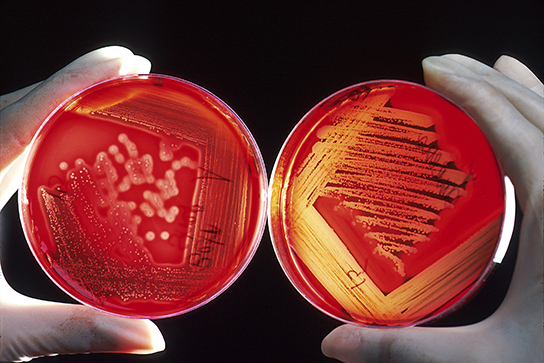
Microbiologists typically grow prokaryotes in the laboratory using an appropriate culture medium containing all the nutrients needed by the target organism. The medium can be liquid, broth, or solid. After an incubation time at the right temperature, there should be evidence of microbial growth ( [link] ). The process of culturing bacteria is complex and is one of the greatest discoveries of modern science. German physician Robert Koch is credited with discovering the techniques for pure culture, including staining and using growth media. His assistant Julius Petri invented the Petri dish whose use persists in today’s laboratories. Koch worked primarily with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium that causes tuberculosis and developed postulates to identify disease-causing organisms that continue to be widely used in the medical community. Koch’s postulates include that an organism can be identified as the cause of disease when it is present in all infected samples and absent in all healthy samples, and it is able to reproduce the infection after being cultured multiple times. Today, cultures remain a primary diagnostic tool in medicine and other areas of molecular biology.
Some prokaryotes, however, cannot grow in a laboratory setting. In fact, over 99 percent of bacteria and archaea are unculturable. For the most part, this is due to a lack of knowledge as to what to feed these organisms and how to grow them; they have special requirements for growth that remain unknown to scientists, such as needing specific micronutrients, pH, temperature, pressure, co-factors, or co-metabolites. Some bacteria cannot be cultured because they are obligate intracellular parasites and cannot be grown outside a host cell.
In other cases, culturable organisms become unculturable under stressful conditions, even though the same organism could be cultured previously. Those organisms that cannot be cultured but are not dead are in a viable-but-non-culturable (VBNC) state. The VBNC state occurs when prokaryotes respond to environmental stressors by entering a dormant state that allows their survival. The criteria for entering into the VBNC state are not completely understood. In a process called resuscitation , the prokaryote can go back to “normal” life when environmental conditions improve.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?