| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Whether the organism is a bacterium, plant, or animal, all living things access energy by breaking down carbohydrate molecules. But if plants make carbohydrate molecules, why would they need to break them down, especially when it has been shown that the gas organisms release as a “waste product” (CO 2 ) acts as a substrate for the formation of more food in photosynthesis? Remember, living things need energy to perform life functions. In addition, an organism can either make its own food or eat another organism—either way, the food still needs to be broken down. Finally, in the process of breaking down food, called cellular respiration, heterotrophs release needed energy and produce “waste” in the form of CO 2 gas.
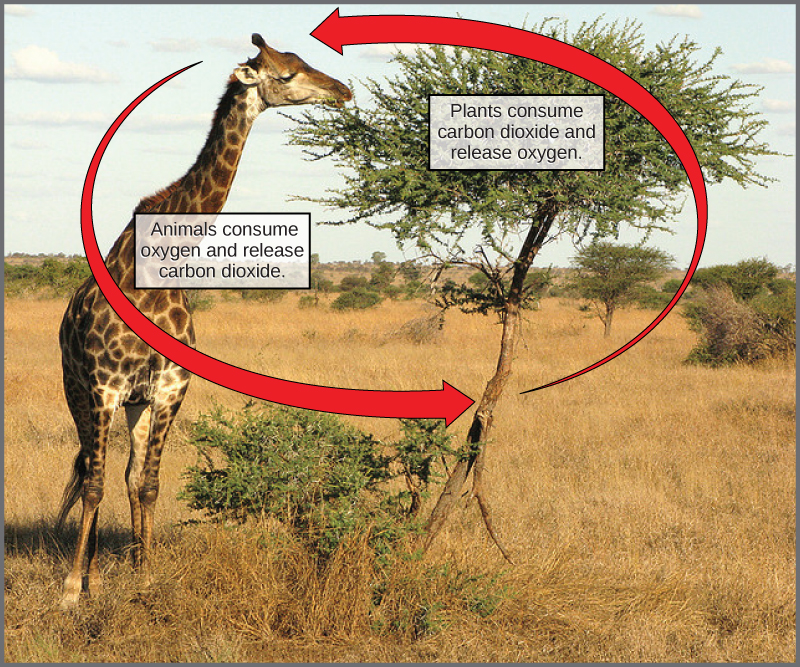
In nature, there is no such thing as waste. Every single atom of matter and energy is conserved, recycling over and over infinitely. Substances change form or move from one type of molecule to another, but their constituent atoms never disappear ( [link] ).
CO 2 is no more a form of waste than oxygen is wasteful to photosynthesis. Both are byproducts of reactions that move on to other reactions. Photosynthesis absorbs light energy to build carbohydrates in chloroplasts, and aerobic cellular respiration releases energy by using oxygen to metabolize carbohydrates in the cytoplasm and mitochondria. Both processes use electron transport chains to capture the energy necessary to drive other reactions. These two powerhouse processes, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, function in biological, cyclical harmony to allow organisms to access life-sustaining energy that originates millions of miles away in a burning star humans call the sun.
Using the energy carriers formed in the first steps of photosynthesis, the light-independent reactions, or the Calvin cycle, take in CO 2 from the environment. An enzyme, RuBisCO, catalyzes a reaction with CO 2 and another molecule, RuBP. After three cycles, a three-carbon molecule of G3P leaves the cycle to become part of a carbohydrate molecule. The remaining G3P molecules stay in the cycle to be regenerated into RuBP, which is then ready to react with more CO 2 . Photosynthesis forms an energy cycle with the process of cellular respiration. Plants need both photosynthesis and respiration for their ability to function in both the light and dark, and to be able to interconvert essential metabolites. Therefore, plants contain both chloroplasts and mitochondria.
[link] Which of the following statements is true?
[link] D

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?