| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
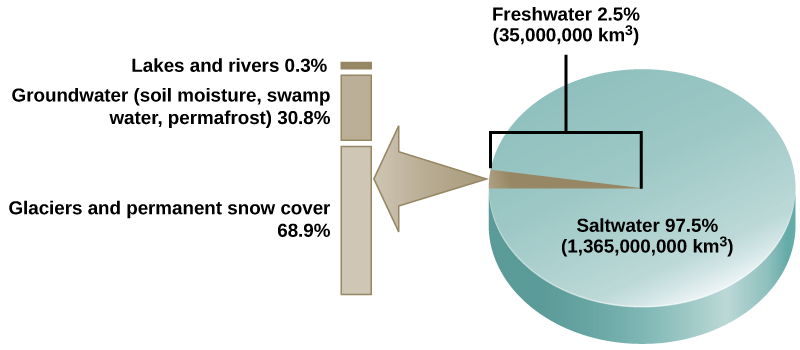
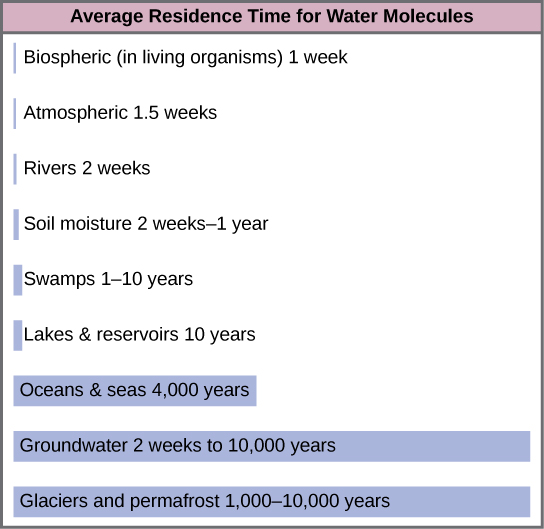
Water cycling is extremely important to ecosystem dynamics. Water has a major influence on climate and, thus, on the environments of ecosystems, some located on distant parts of the Earth. Most of the water on Earth is stored for long periods in the oceans, underground, and as ice. [link] illustrates the average time that an individual water molecule may spend in the Earth’s major water reservoirs. Residence time is a measure of the average time an individual water molecule stays in a particular reservoir. A large amount of the Earth’s water is locked in place in these reservoirs as ice, beneath the ground, and in the ocean, and, thus, is unavailable for short-term cycling (only surface water can evaporate).
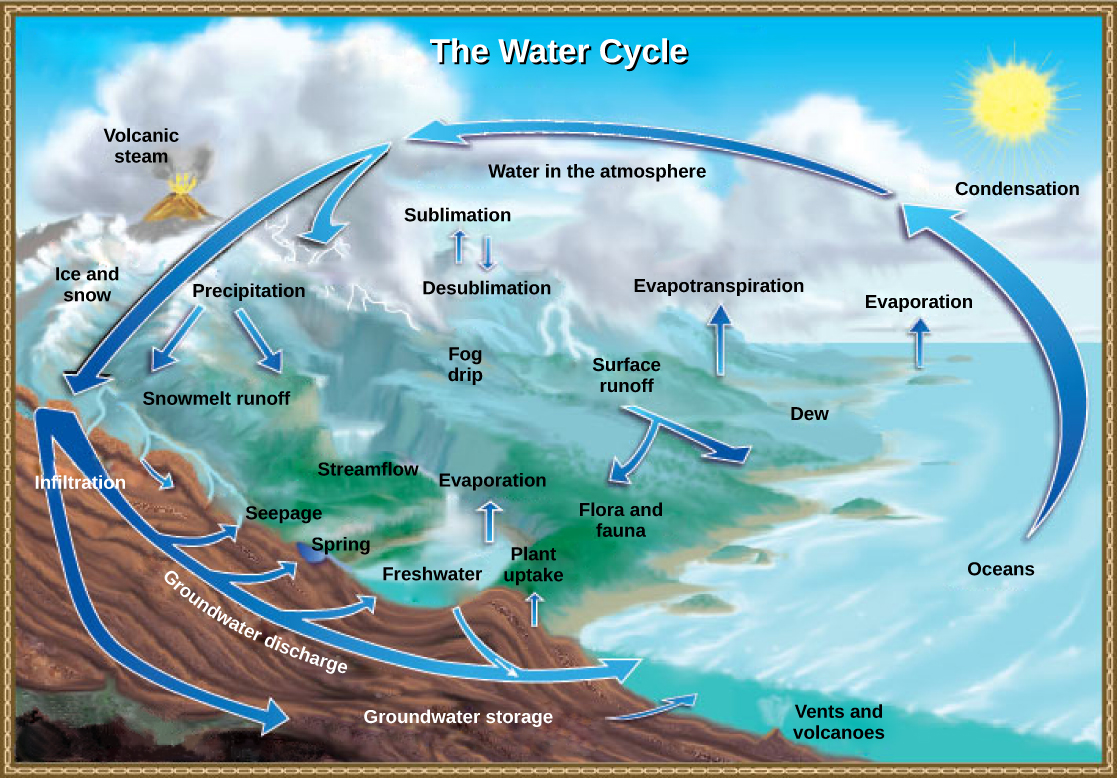
There are various processes that occur during the cycling of water, shown in [link] . These processes include the following:
The water cycle is driven by the sun’s energy as it warms the oceans and other surface waters. This leads to the evaporation (water to water vapor) of liquid surface water and the sublimation (ice to water vapor) of frozen water, which deposits large amounts of water vapor into the atmosphere. Over time, this water vapor condenses into clouds as liquid or frozen droplets and is eventually followed by precipitation (rain or snow), which returns water to the Earth’s surface. Rain eventually permeates into the ground, where it may evaporate again if it is near the surface, flow beneath the surface, or be stored for long periods. More easily observed is surface runoff: the flow of fresh water either from rain or melting ice. Runoff can then make its way through streams and lakes to the oceans or flow directly to the oceans themselves.
Head to this website to learn more about the world’s fresh water supply.
Rain and surface runoff are major ways in which minerals, including carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur, are cycled from land to water. The environmental effects of runoff will be discussed later as these cycles are described.
Carbon is the second most abundant element in living organisms. Carbon is present in all organic molecules, and its role in the structure of macromolecules is of primary importance to living organisms. Carbon compounds contain especially high energy, particularly those derived from fossilized organisms, mainly plants, which humans use as fuel. Since the 1800s, the number of countries using massive amounts of fossil fuels has increased. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, global demand for the Earth’s limited fossil fuel supplies has risen; therefore, the amount of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere has increased. This increase in carbon dioxide has been associated with climate change and other disturbances of the Earth’s ecosystems and is a major environmental concern worldwide. Thus, the “carbon footprint” is based on how much carbon dioxide is produced and how much fossil fuel countries consume.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?