| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A living cell’s primary tasks of obtaining, transforming, and using energy to do work may seem simple. However, the second law of thermodynamics explains why these tasks are harder than they appear. None of the energy transfers we’ve discussed, along with all energy transfers and transformations in the universe, is completely efficient. In every energy transfer, some amount of energy is lost in a form that is unusable. In most cases, this form is heat energy. Thermodynamically, heat energy is defined as the energy transferred from one system to another that is not doing work. For example, when an airplane flies through the air, some of the energy of the flying plane is lost as heat energy due to friction with the surrounding air. This friction actually heats the air by temporarily increasing the speed of air molecules. Likewise, some energy is lost as heat energy during cellular metabolic reactions. This is good for warm-blooded creatures like us, because heat energy helps to maintain our body temperature. Strictly speaking, no energy transfer is completely efficient, because some energy is lost in an unusable form.
An important concept in physical systems is that of order and disorder (also known as randomness). The more energy that is lost by a system to its surroundings, the less ordered and more random the system is. Scientists refer to the measure of randomness or disorder within a system as entropy . High entropy means high disorder and low energy ( [link] ). To better understand entropy, think of a student’s bedroom. If no energy or work were put into it, the room would quickly become messy. It would exist in a very disordered state, one of high entropy. Energy must be put into the system, in the form of the student doing work and putting everything away, in order to bring the room back to a state of cleanliness and order. This state is one of low entropy. Similarly, a car or house must be constantly maintained with work in order to keep it in an ordered state. Left alone, the entropy of the house or car gradually increases through rust and degradation. Molecules and chemical reactions have varying amounts of entropy as well. For example, as chemical reactions reach a state of equilibrium, entropy increases, and as molecules at a high concentration in one place diffuse and spread out, entropy also increases.
All physical systems can be thought of in this way: Living things are highly ordered, requiring constant energy input to be maintained in a state of low entropy. As living systems take in energy-storing molecules and transform them through chemical reactions, they lose some amount of usable energy in the process, because no reaction is completely efficient. They also produce waste and by-products that aren’t useful energy sources. This process increases the entropy of the system’s surroundings. Since all energy transfers result in the loss of some usable energy, the second law of thermodynamics states that every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe. Even though living things are highly ordered and maintain a state of low entropy, the entropy of the universe in total is constantly increasing due to the loss of usable energy with each energy transfer that occurs. Essentially, living things are in a continuous uphill battle against this constant increase in universal entropy.
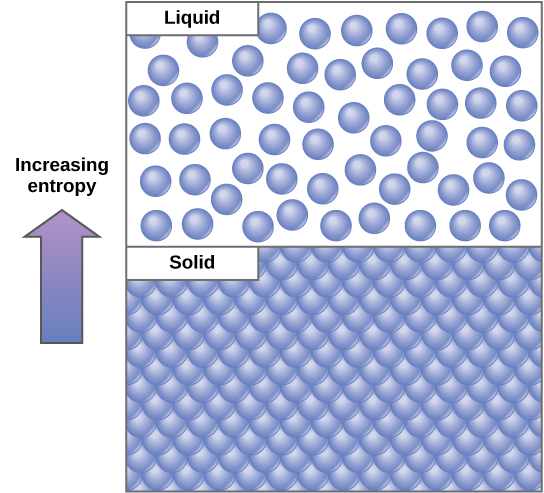
In studying energy, scientists use the term “system” to refer to the matter and its environment involved in energy transfers. Everything outside of the system is called the surroundings. Single cells are biological systems. Systems can be thought of as having a certain amount of order. It takes energy to make a system more ordered. The more ordered a system is, the lower its entropy. Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. As a system becomes more disordered, the lower its energy and the higher its entropy become.
A series of laws, called the laws of thermodynamics, describe the properties and processes of energy transfer. The first law states that the total amount of energy in the universe is constant. This means that energy can’t be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed. The second law of thermodynamics states that every energy transfer involves some loss of energy in an unusable form, such as heat energy, resulting in a more disordered system. In other words, no energy transfer is completely efficient and tends toward disorder.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?