| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A variation of pinocytosis is called potocytosis . This process uses a coating protein, called caveolin , on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane, which performs a similar function to clathrin. The cavities in the plasma membrane that form the vacuoles have membrane receptors and lipid rafts in addition to caveolin. The vacuoles or vesicles formed in caveolae (singular caveola) are smaller than those in pinocytosis. Potocytosis is used to bring small molecules into the cell and to transport these molecules through the cell for their release on the other side of the cell, a process called transcytosis.
A targeted variation of endocytosis employs receptor proteins in the plasma membrane that have a specific binding affinity for certain substances ( [link] ).
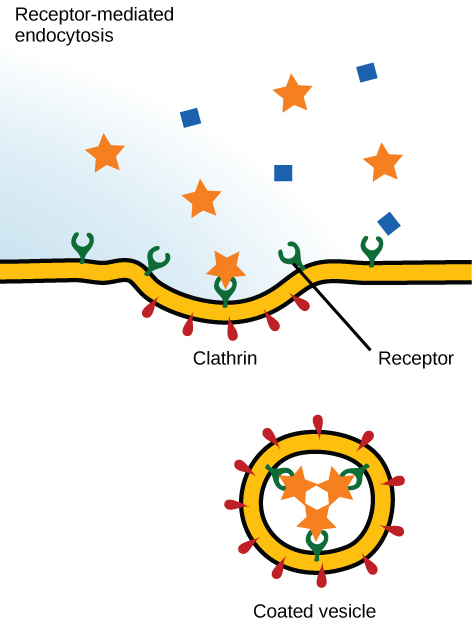
In receptor-mediated endocytosis , as in phagocytosis, clathrin is attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane. If uptake of a compound is dependent on receptor-mediated endocytosis and the process is ineffective, the material will not be removed from the tissue fluids or blood. Instead, it will stay in those fluids and increase in concentration. Some human diseases are caused by the failure of receptor-mediated endocytosis. For example, the form of cholesterol termed low-density lipoprotein or LDL (also referred to as “bad” cholesterol) is removed from the blood by receptor-mediated endocytosis. In the human genetic disease familial hypercholesterolemia, the LDL receptors are defective or missing entirely. People with this condition have life-threatening levels of cholesterol in their blood, because their cells cannot clear LDL particles from their blood.
Although receptor-mediated endocytosis is designed to bring specific substances that are normally found in the extracellular fluid into the cell, other substances may gain entry into the cell at the same site. Flu viruses, diphtheria, and cholera toxin all have sites that cross-react with normal receptor-binding sites and gain entry into cells.
See receptor-mediated endocytosis in action, and click on different parts for a focused animation.
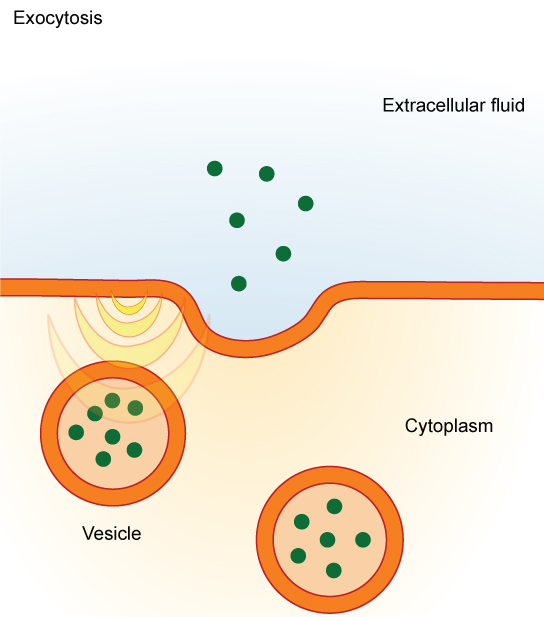
The reverse process of moving material into a cell is the process of exocytosis. Exocytosis is the opposite of the processes discussed above in that its purpose is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid. Waste material is enveloped in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane. This fusion opens the membranous envelope on the exterior of the cell, and the waste material is expelled into the extracellular space ( [link] ). Other examples of cells releasing molecules via exocytosis include the secretion of proteins of the extracellular matrix and secretion of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by synaptic vesicles.
| Methods of Transport, Energy Requirements, and Types of Material Transported | ||
|---|---|---|
| Transport Method | Active/Passive | Material Transported |
| Diffusion | Passive | Small-molecular weight material |
| Osmosis | Passive | Water |
| Facilitated transport/diffusion | Passive | Sodium, potassium, calcium, glucose |
| Primary active transport | Active | Sodium, potassium, calcium |
| Secondary active transport | Active | Amino acids, lactose |
| Phagocytosis | Active | Large macromolecules, whole cells, or cellular structures |
| Pinocytosis and potocytosis | Active | Small molecules (liquids/water) |
| Receptor-mediated endocytosis | Active | Large quantities of macromolecules |
Active transport methods require the direct use of ATP to fuel the transport. Large particles, such as macromolecules, parts of cells, or whole cells, can be engulfed by other cells in a process called phagocytosis. In phagocytosis, a portion of the membrane invaginates and flows around the particle, eventually pinching off and leaving the particle entirely enclosed by an envelope of plasma membrane. Vesicle contents are broken down by the cell, with the particles either used as food or dispatched. Pinocytosis is a similar process on a smaller scale. The plasma membrane invaginates and pinches off, producing a small envelope of fluid from outside the cell. Pinocytosis imports substances that the cell needs from the extracellular fluid. The cell expels waste in a similar but reverse manner: it pushes a membranous vacuole to the plasma membrane, allowing the vacuole to fuse with the membrane and incorporate itself into the membrane structure, releasing its contents to the exterior.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?