| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The liquid component of blood is called plasma, and it is separated by spinning or centrifuging the blood at high rotations (3000 rpm or higher). The blood cells and platelets are separated by centrifugal forces to the bottom of a specimen tube. The upper liquid layer, the plasma, consists of 90 percent water along with various substances required for maintaining the body’s pH, osmotic load, and for protecting the body. The plasma also contains the coagulation factors and antibodies.
The plasma component of blood without the coagulation factors is called the serum . Serum is similar to interstitial fluid in which the correct composition of key ions acting as electrolytes is essential for normal functioning of muscles and nerves. Other components in the serum include proteins that assist with maintaining pH and osmotic balance while giving viscosity to the blood. The serum also contains antibodies, specialized proteins that are important for defense against viruses and bacteria. Lipids, including cholesterol, are also transported in the serum, along with various other substances including nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste, plus external substances, such as, drugs, viruses, and bacteria.
Human serum albumin is the most abundant protein in human blood plasma and is synthesized in the liver. Albumin, which constitutes about half of the blood serum protein, transports hormones and fatty acids, buffers pH, and maintains osmotic pressures. Immunoglobin is a protein antibody produced in the mucosal lining and plays an important role in antibody mediated immunity.
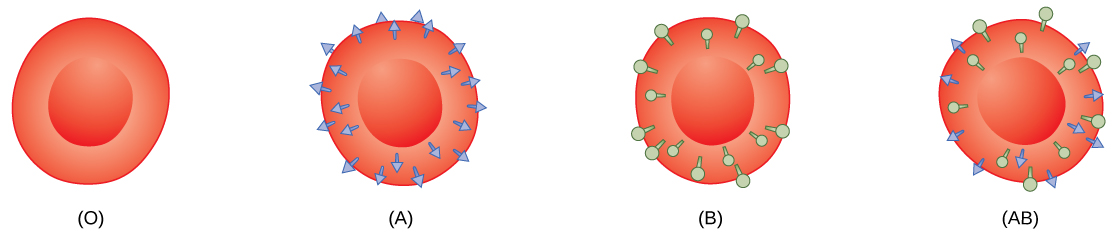
The Rh blood group was first discovered in Rhesus monkeys. Most people have the Rh antigen (Rh+) and do not have anti-Rh antibodies in their blood. The few people who do not have the Rh antigen and are Rh– can develop anti-Rh antibodies if exposed to Rh+ blood. This can happen after a blood transfusion or after an Rh– woman has an Rh+ baby. The first exposure does not usually cause a reaction; however, at the second exposure, enough antibodies have built up in the blood to produce a reaction that causes agglutination and breakdown of red blood cells. An injection can prevent this reaction.
Play a blood typing game on the Nobel Prize website to solidify your understanding of blood types.
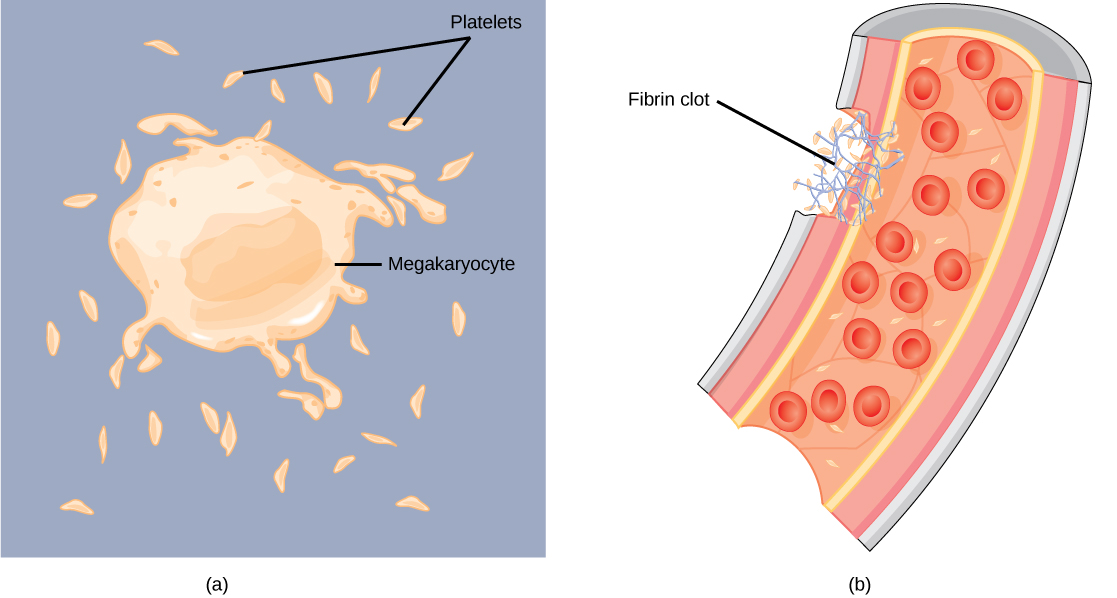
Specific components of the blood include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and the plasma, which contains coagulation factors and serum. Blood is important for regulation of the body’s pH, temperature, osmotic pressure, the circulation of nutrients and removal of waste, the distribution of hormones from endocrine glands, and the elimination of excess heat; it also contains components for blood clotting. Red blood cells are specialized cells that contain hemoglobin and circulate through the body delivering oxygen to cells. White blood cells are involved in the immune response to identify and target invading bacteria, viruses, and other foreign organisms; they also recycle waste components, such as old red blood cells. Platelets and blood clotting factors cause the change of the soluble protein fibrinogen to the insoluble protein fibrin at a wound site forming a plug. Plasma consists of 90 percent water along with various substances, such as coagulation factors and antibodies. The serum is the plasma component of the blood without the coagulation factors.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?